中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1569-1579.doi: 10.12307/2026.609
• 组织构建相关数据分析 Date analysis of organization construction • 上一篇 下一篇
DYRK2:基于东亚和欧洲人群揭示类风湿关节炎合并骨质疏松症的治疗新靶点
吴治林1,2,何 秦1,王枰稀1,石 现1,袁 松1,张 骏2,王 浩1
- 1四川省达州市中心医院骨科,四川省达州市 635000;2重庆医科大学骨科实验室,重庆市 400014
DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations
Wu Zhilin1, 2, He Qin1, Wang Pingxi1, Shi Xian1, Yuan Song1, Zhang Jun2, Wang Hao1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Dazhou Central Hospital, Dazhou 635000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Orthopedic Laboratory, Chongqing Medical University, Chongqing 400014, China
摘要:
文题释义:
孟德尔随机化:是基于等位基因在配子形成时遵循随机分配原则,可用单核苷酸多态性作为研究中间表型的工具变量来推断暴露因素与疾病状态的因果关联。
骨质疏松症:是一种慢性代谢性骨骼疾病,特征是骨量减少、骨组织微结构退化、骨张力和强度降低,以及脆性骨折风险增加。
类风湿关节炎:是一种伴有关节组织增生和滑膜炎症的全身性自身免疫性疾病,典型的症状和体征包括关节疼痛、僵硬和肿胀。
背景:研究表明,类风湿关节炎与骨质疏松症呈正相关趋势,但因果关系和相关机制仍未得到证实。随着计算机科学和生命科学的交叉融合,基于全基因组关联研究数据和转录组测序数据进行孟德尔随机化和生信分析,可以评估两疾病间的因果关系、探索相关机制以及挖掘治疗靶点,这将利于类风湿关节炎合并骨质疏松症的精准治疗。
目的:采用双样本孟德尔随机化分析类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症间的因果关系,同时基于汇总数据的孟德尔随机化分析和生信分析挖掘潜在共病靶点和靶向药物,旨在为类风湿关节炎合并骨质疏松症的机制探索和精准治疗提供理论依据。
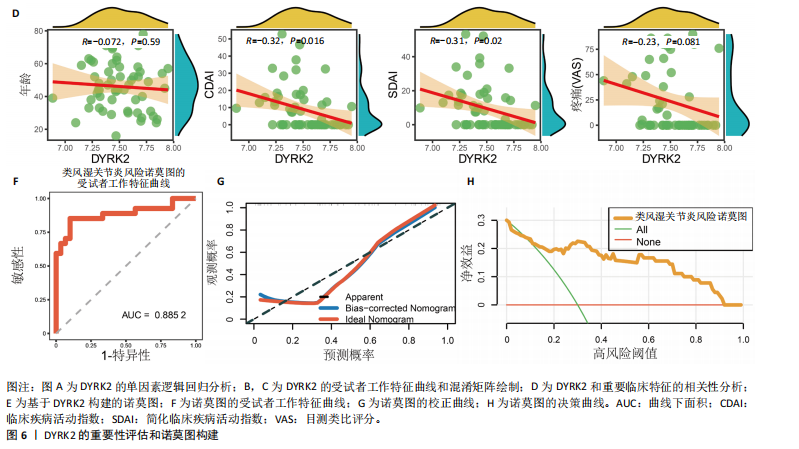
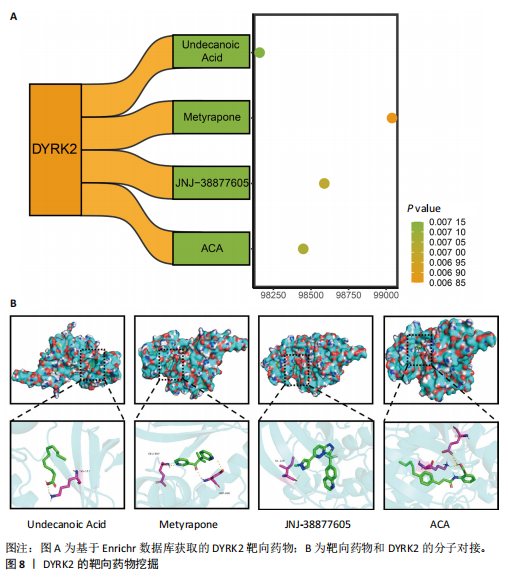
方法:①从基于亚洲人群和欧洲人群的GWAS Catalog、IEU Open GWAS、FinnGen以及eQTLGen 数据库下载类风湿关节炎、骨质疏松症和顺式表达数量性状位点的全基因组关联研究数据,用于双样本孟德尔随机化和基于汇总数据的孟德尔随机化分析。②从GEO数据库下载类风湿关节炎的转录组测序数据(GSE93272和GSE15573),用于生物信息学分析。③以逆方差加权法作为主要分析方法,进行类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症之间的正向和反向双样本孟德尔随机化分析,并用MR Egger法、简单模式法、加权中位数法和加权模式法对结果加以佐证。④基于汇总数据的孟德尔随机化分析鉴定与类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症相关的基因,并基于交叉分析挖掘出类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症共病靶点。同时,基于生信分析和细胞实验验证共病靶点的生物学功能。⑤此外,基于DYRK2构建类风湿关节炎风险预测诺莫图,通过受试者特征曲线、矫正曲线和决策曲线验证预测性能。最后,基于Enrichr数据库挖掘靶点潜在药物并进行分子对接。
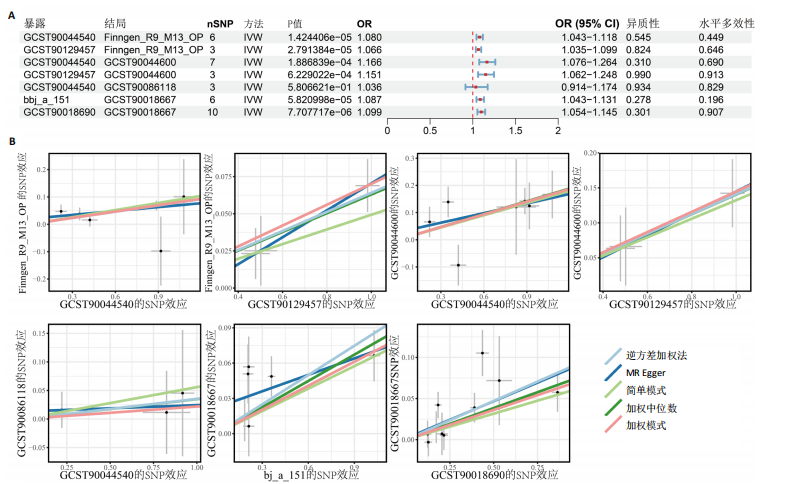
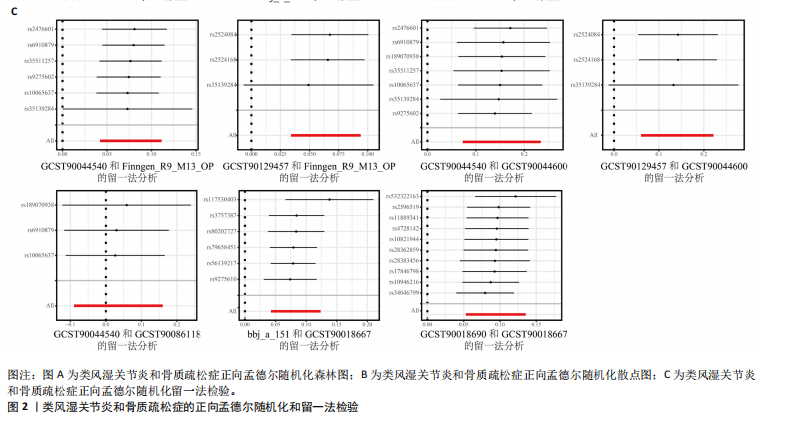
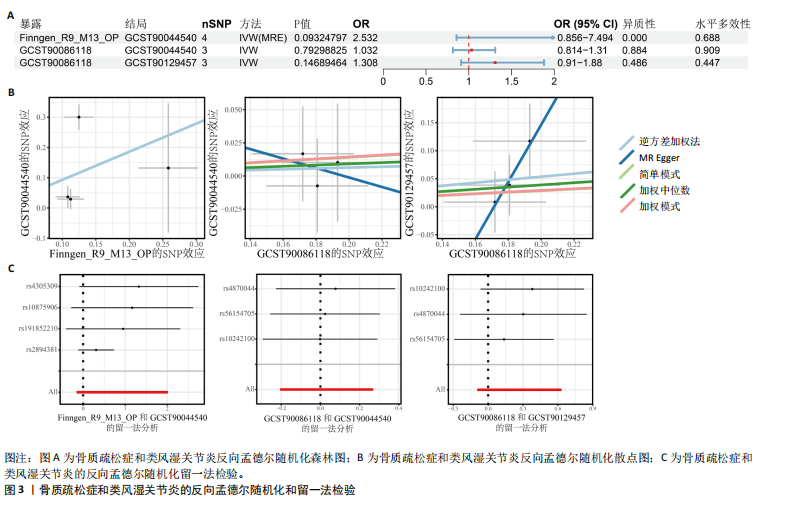
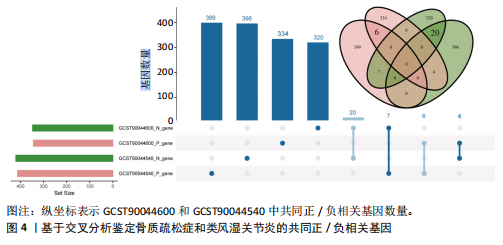
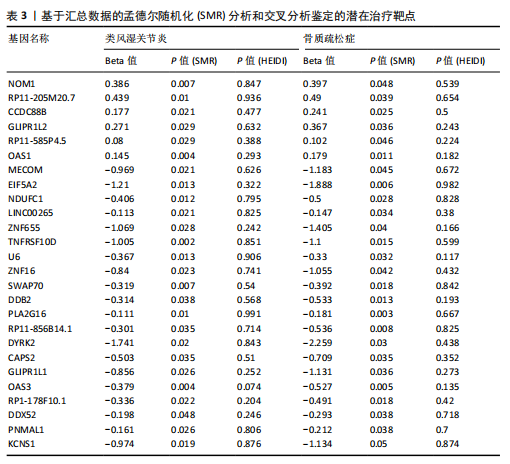
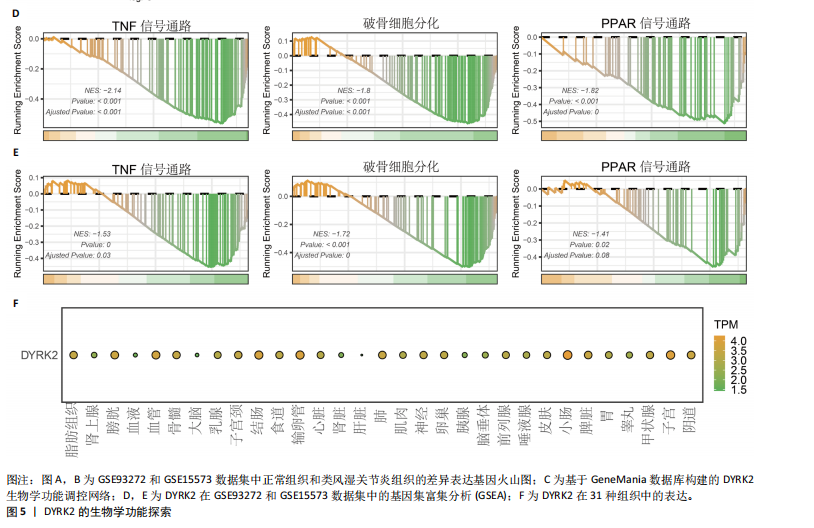
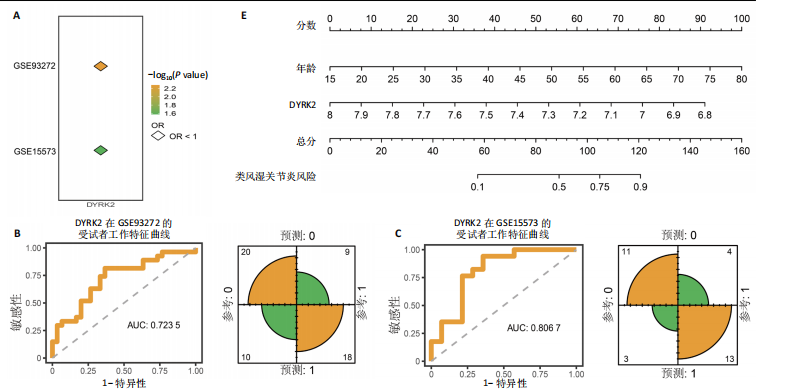
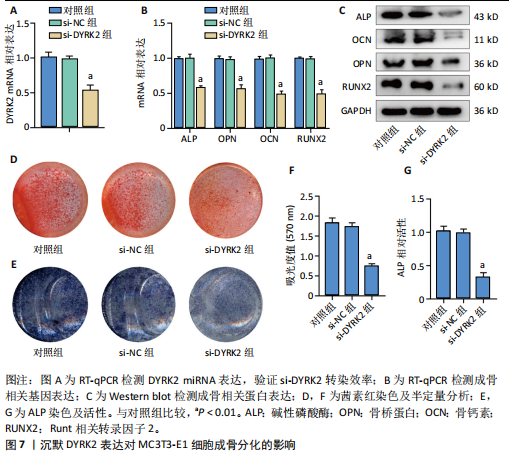
结果与结论:①正向孟德尔随机化分析结果显示,除外GCST90044540和GCST90086118无统计学意义,其他所有结果均表明类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症间存在显著因果关系,并且呈正相关。②反向孟德尔随机化分析结果提示,骨质疏松症和类风湿关节炎间未见显著因果关系。③基于汇总数据的孟德尔随机化分析共鉴定出412和344个与类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症正相关的基因,421和347个负相关基因。基于交叉分析得到26个共病基因。其中,DYRK2是潜在治疗靶点,后续生信分析和细胞实验证实DYRK2在类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症的进展过程中发挥重要作用。④此外,构建的诺莫图具有出色的预测性能。最后,挖掘出4个DYRK2的潜在靶向药物(Undecanoic Acid、Metyrapone、JNJ-38877605和ACA),分子对接也证明具有可靠的靶向能力。⑤总之,基于亚洲人群和欧洲人群的全基因组关联研究数据证明了类风湿关节炎和骨质疏松症在遗传学层面存在着因果关系,DYRK2是潜在治疗靶点,有4种小分子是潜在靶向药物。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7173-7961(吴治林)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: