中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (22): 5792-5803.doi: 10.12307/2026.180
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
miRNA靶向治疗骨质疏松症的应用策略
吴灵杰1,郑开元2,汪光蓉1,印 崇1,3
- 川北医学院附属医院,1检验科,2康复科,四川省南充市 637000;3川北医学院检验医学院转化医学研究中心,四川省南充市 637000
-
收稿日期:2025-06-16接受日期:2025-08-31出版日期:2026-08-08发布日期:2025-12-27 -
通讯作者:吴灵杰,女,1996年生,汉族,川北医学院在读硕士,主要从事分子生物学与骨质疏松症防治的研究。 -
作者简介:印崇,博士,副研究员,川北医学院附属医院检验科,四川省南充市 637000;川北医学院检验医学院转化医学研究中心,四川省南充市 637000 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金青年项目(32000924),项目负责人:印崇;四川省自然科学基金青年项目(23NSFSC6012),项目负责人:印崇;川北医附院2022年揭榜挂帅项目(2022JB007),项目负责人:印崇
Strategies for the application of miRNA-targeted therapy in the treatment of osteoporosis
Wu Lingjie1, Zheng Kaiyuan2, Wang Guangrong1, Yin Chong1, 3
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2Department of Rehabilitation, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China; 3Translational Medicine Research Center, School of Laboratory Medicine, North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2025-06-16Accepted:2025-08-31Online:2026-08-08Published:2025-12-27 -
Contact:Yin Chong, PhD, Associate researcher, Department of Laboratory Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China; Translational Medicine Research Center, School of Laboratory Medicine, North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Wu Lingjie, MS candidate, Department of Laboratory Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of North Sichuan Medical College, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (Youth Project), No. 32000924 (to YC); Sichuan Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Youth Project), No. 23NSFSC6012 (to YC); 2022 Best Candidate Project of North Sichuan Medical College Affiliated Hospital, No. 2022JB007 (to YC)
摘要:
文题释义:
miRNAs:是一种高度保守的非编码RNA分子,长度为20-25 nt,广泛存在于真核生物中(从植物、线虫到人类)。miRNAs本身不编码蛋白质,通过与靶mRNA碱基互补或不完全互补配对,切割mRNA或抑制靶mRNA翻译,以及介导mRNA脱腺苷化和衰变发挥调控作用。
骨质疏松症:是一种因骨形成与骨吸收失衡导致的代谢性骨病,严重威胁中老年人群的健康,多见于绝经后女性和老年男性。
背景:miRNA作为重要的基因转录后调控因子,在骨质疏松症的发生和发展过程中发挥着关键作用。通过对miRNA调节骨质疏松症生物学的深入探究,其潜在的疗愈机制得以揭示,此领域已成为当前研究的热门焦点。
目的:探讨miRNA在骨质疏松症发生中的调控作用及其分子机制,并对以miRNA为靶点的骨质疏松症治疗策略所遭遇的关键问题及其解决方案进行综述。
方法:以“miRNA,osteoporosis,angiogenesis,osteogenesis,gene therapy,drug delivery”为英文检索词,以“miRNA,
骨质疏松,基因治疗,核酸药物,递送载体”为中文检索词,检索PubMed、Web of Science数据库和中国知网2025年3月以前发表的文献。通过阅读文题和摘要进行初步筛选,排除相关性差、信息陈旧或观点重复且缺乏权威性的文献,最后纳入138篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①miRNA是一种高效的、应用范围广泛、可精准调控细胞活动的非编码RNA,在调控骨细胞功能与骨血管生成方面展现出显著的优势,在骨质疏松症的治疗中具有潜在价值;②尽管基于miRNA的靶向治疗药物在其他疾病领域已进入临床前研究阶段,但在临床转化过程中,仍面临核酸体内稳定性不足及脱靶效应的挑战;③针对miRNA疗法所面临的挑战,研究者们提出了多种应对策略,包括精准定位miRNA的靶基因降低脱靶效应;化学修饰提高核酸药物在体内的稳定性;降低核酸生产成本推进研究;利用病毒载体、外泌体和各类生物材料优化核酸药物的递送途径;④科技的进步在提升核酸药物载体性能上持续创新,未来终将达到精确而高效的药物递送及靶向治疗
效果。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8113-8911 (印崇)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
吴灵杰, 郑开元, 汪光蓉, 印 崇. miRNA靶向治疗骨质疏松症的应用策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(22): 5792-5803.
Wu Lingjie, Zheng Kaiyuan, Wang Guangrong, Yin Chong . Strategies for the application of miRNA-targeted therapy in the treatment of osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5792-5803.
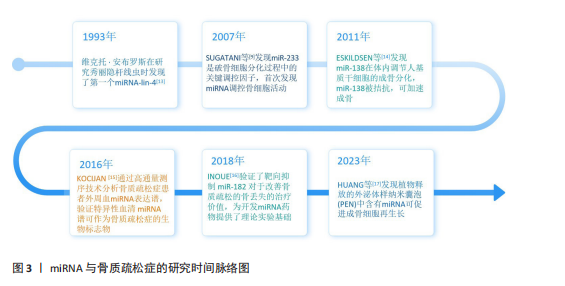
2.2 miRNA作为骨质疏松症治疗靶点的理论基础 miRNA对骨质疏松的调控研究始于2007年[9],至今为止已证明了多条与骨质疏松相关的miRNA,这些miRNA可以通过多方面机制调控骨质疏松的发生,如成骨细胞(骨形成)、破骨细胞(骨吸收)、血管生成等。miRNA作为骨质疏松调控的重要一环,可以作为骨质疏松治疗的重要靶点。此外,研究表明miRNA可以从细胞中分泌,在蛋白质复合物和细胞外囊泡保护下稳定存在于循环系统中[18],因此循环miRNA有可能成为一种骨质疏松的诊断标志物,通过qPCR、基因芯片/测序技术和新兴的等温扩增等技术对体液中miRNA进行检测,在未来可能会成为一种骨质疏松的筛查手段[19]。这里对miRNA从多个角度调控骨质疏松发生的机制进行了总结概述。
2.2.1 miRNA对成骨细胞的调控作用 成骨细胞来源于骨髓间充质干细胞,从骨髓间充质干细胞到成骨细胞的分化程序受多种信号通路[经典Wnt信号通路(Wnt/β-连环蛋白)、骨形态发生蛋白/Smad通路、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶通路/蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白通路、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶通路等]和转录因子(Runt相关转录因子2、同源转录因子DLX5、成骨细胞特异性转录因子Osterix、β-连环蛋白、转化生长因子β等)的调节[20]。其中研究最多的信号通路包括Wnt/β-连环蛋白、骨形态发生蛋白/Smad、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、Hedgehog和Notch信号通路。
大量研究表明,miRNA能够靶向作用于上述信号通路和转录因子,进而实现对成骨细胞分化的调节。例如:miR-29家族miR-29a/b在成骨细胞分化过程中可诱导Runt相关转录因子2和Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号传导来促进成骨分化;miR-29a/c负向调节许多细胞外基质基因表达,抑制成骨分化矿化阶段细胞外基质的组装沉积[21]。miR-21能靶向调控磷酸酶及张力蛋白同源物/磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶通路/蛋白激酶B/缺氧诱导因子1α通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移和成骨分化[22]。另外,miR-196b-5p可直接靶向信号素3a影响Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号传导,抑制骨形成[23]。研究发现miR-664-3p也可以直接靶Smad4和Osterix抑制成骨和骨形成[24]。更多关于miRNA调控成骨分化的信息见表1[21-36]。

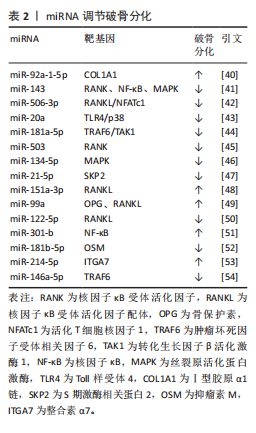
2.2.2 miRNA对破骨细胞的调控作用 破骨细胞源于骨髓中造血干细胞前体,髓系破骨细胞前体在巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和核因子κB受体活化因子配体共同作用下分化为单核破骨细胞,参与破骨细胞生成的主要信号通路有巨噬细胞集落刺激因子/集落刺激因子1受体、核因子κB受体活化因子配体/核因子κB受体活化因子/骨保护素、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、核因子κB[37]。核因子κB受体活化因子配体/核因子κB受体活化因子/骨保护素信号通路作为骨代谢平衡领域内备受关注的关键调控机制之一,在促进破骨细胞分化与功能活化方面发挥着显著效能[38]。miRNA在调控破骨细胞分化中发挥着重要作用[39]。例如:YU等[40]研究发现miR-92a-1-5p可直接作用于Ⅰ型胶原α1链,增强破骨细胞的分化。HE等[41]发现miR-143通过靶向核因子κB受体活化因子、核因子κB和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路抑制破骨细胞生成。DINESH等[42]表明,miR-506-3p通过抑制核因子κB受体活化因子配体/活化T细胞核因子1信号通路减少破骨细胞生成。KONG团队[43]研究揭示,miR-20a部分通过Toll样受体4/p38通路抑制破骨细胞的增殖和分化。更多参与破骨细胞分化的miRNA及其靶基因及作用机制总结见表2[40-54]。
2.2.3 miRNA对骨血管生成的调控 骨是高度血管化的组织,其内部的血管系统不仅输送氧气和必要的营养物质,还参与激素和细胞因子的合成,从而维持骨代谢的稳态[55]。H型血管内皮细胞通过多个信号通路与多种细胞因子的协同作用,刺激骨髓中骨祖细胞的增殖和分化,实现骨形成与血管生成的紧密耦合[56-57]。
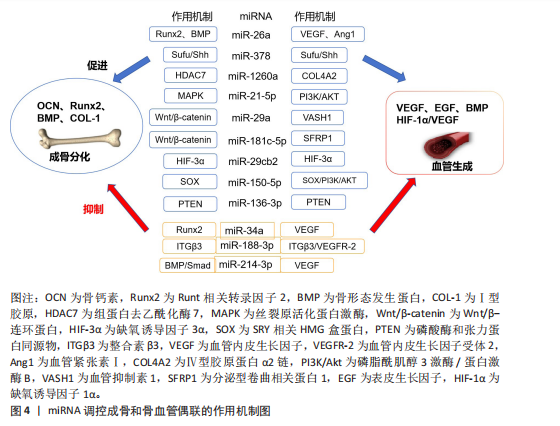
骨形成与血管生成的功能偶联受到血管内皮生长因子、骨形态发生蛋白、表皮生长因子样家族成员、缺氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子、Notch和Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号通路等的调节,研究发现一些miRNA调控血管的生成,参与成骨-血管生成耦合[58]。例如:miR-26a可诱导Runt相关转录因子2和骨形态发生蛋白2刺激成骨分化,也可以靶向骨形态发生蛋白/Smad1信号通路调控血管生成[59]。miR-378可促进骨髓间充质干细胞中的成骨-血管生成偶联,实现潜在的骨再生[60]。骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体中miR-1260a释放可直接靶向组蛋白去乙酰化酶7促进成骨和血管生成[61]。此外,还有许多参与调控血管和骨生成偶联的miRNA,见表3[59-70]。miRNA调控成骨和骨血管偶联的作用机制见图4。

2.3 miRNA靶向治疗骨质疏松症的潜力与挑战
2.3.1 miRNA疗法的应用潜力 miRNA疗法与传统小分子药物相比具有巨大优势,因为约80%疾病相关蛋白靶标是“不可成药”的,而核酸药物突破了蛋白质三维结构限制,miRNA旁分泌效应也提供了更广泛的靶标,使其覆盖整个信号通路[71]。miRNA疗法分为替代疗法(miRNA mimics)和抑制疗法(miRNA inhibitor)[72]。miRNA模拟物可提高胞内miRNA丰度[73]。miRNA抑制剂可特异性靶向内源miRNA,主要方式有miRNA的反义寡核苷酸(AMO),锁定核酸反义寡核苷酸(LNAs)、肽核酸(PNA)、miRNA海绵、miRNA诱饵等[74]。还有基因编辑技术CRISPR/Cas9可在基因水平切割miRNA的Drosha和Dicer加工位点,使miRNA基因组序列发生改变,抑制成熟miRNA合成[75]。
目前已有基于miRNA的多种靶向治疗药物进入临床试验阶段,例如MRX34(miR-34a模拟物)在晚期实体瘤中的Ⅰ期研究已完成[76];Cobomarsen(抗miR-155)针对皮肤T细胞淋巴瘤等肿瘤的Ⅱ期研究正在进行[77];RG-101(miR-122抑制剂)在丙型肝炎治疗中显示出显著病毒载量降低[78];CDR132L(抗miR-132)在心力衰竭治疗中表现出良好的安全性和疗效[79]。上述处于临床前阶段的几种miRNA药物的诞生,证明了miRNA疗法在疾病治疗中有着巨大的应用潜力。
2.3.2 miRNA疗法在骨质疏松症中的应用挑战 近10年关于miRNA与骨质疏松的研究呈快速增长趋势,miRNA作为骨质疏松症的基因治疗靶点展现出显著的潜力,是值得进一步研究的领域[80]。CHEN等[81]研究表明,miR-138-5p通过靶向微管肌动蛋白交联因子1负调控衰老成骨细胞的分化,转染其抑制剂至动物体内可减缓老龄动物的骨量流失。磁性纳米颗粒递送miR-15b-5p至破骨细胞,下调糖尿病骨质疏松大鼠体内神经胶质纤维酸性蛋白表达而抑制破骨细胞分化,减轻骨质疏松[82]。脂肪干细胞来源外泌体含miR-21-5p和let-7b-5p,能够抑制破骨细胞分化,静脉注射脂肪干细胞外泌体可减轻骨质疏松小鼠的骨质流失[83]。此外联合应用miRNA疗法与传统抗骨质疏松药物(如双膦酸盐)可能产生协同效应,为个体化治疗提供新思路,TAIPALEENM?KI等[84]研究表明,miR-19a/b负向调控骨重塑,其拮抗剂既可单独治疗低骨量,又能增强人甲状旁腺激素治疗骨质疏松的疗效。
基于miRNA促进骨再生来治疗骨质疏松症的可行性和有效性已经得到大量细胞和动物研究的支持。但是目前还没有miRNA疗法治疗骨质疏松症的临床研究,主要基于以下几项临床转化挑战,miRNA性质不稳定,易被核酸酶降解,缺乏靶向组织的能力,原料少和制备成本高等问题[85]。
2.4 miRNA靶向治疗骨质疏松症的应对策略 针对miRNA药物在骨质疏松症领域临床转化的挑战,现已开发出一些有效的应对策略,包括精准确定靶基因、化学修饰、利用CRISPR/Cas9编辑miRNA、优化递送系统以及降低生产成本[86]。miRNA的靶向治疗策略见图5。
2.4.1 miRNA靶基因确认 确保miRNA准确靶向其预期的mRNA是miRNA疗法特异性基础。生物信息学预测主要利用miRNA数据库(miRWalk、miRBase、TargetScan等)以及软件工具(MiRcode、Tools4miRs)快速确定miRNA序列和其靶基因;还有多种实验验证方法,包括荧光素酶报告基因实验(Luciferase Assay)、qPCR和Western blot、RNA免疫共沉淀(RIP)、交联免疫沉淀测序(CLIP-seq)等;还有靶向miRNA的CRISPR-Cas9敲除文库(lentiG-miR)有助于系统验证miRNA的作用靶点[87]。随着计算能力指数级的增长和可用数字数据的推动,由数据驱动的大型机器学习模型主导的AI适应不同生物的科学领域,一些用于准确预测人类miRNA靶标的机器学习模型诞生,例如:DeepMirTar(使用卷积神经网络分析miRNA和mRNA的序列特征)[88]。DANE-MDA(通过深度属性网络嵌入预测miRNA与疾病的关联)[89]、miRModuleNet(检测miRNA-mRNA调控模块)[90]。
2.4.2 化学修饰 化学修饰核酸,旨在保护核酸不被降解,增加分子的稳定性。目前,已广泛采用对核酸磷酸
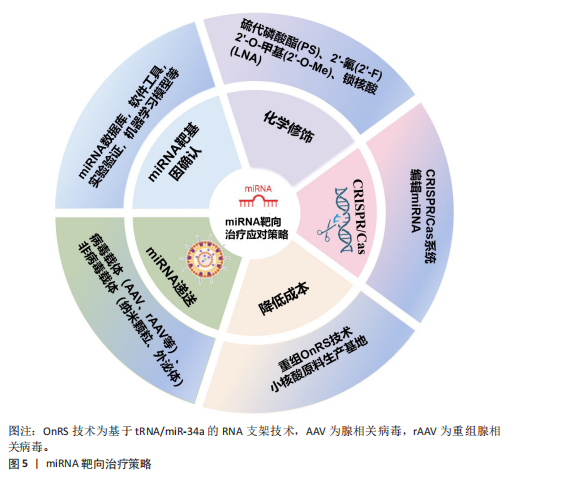
骨架和核糖、碱基的修饰。骨架修饰包括硫代磷酸酯(PS)、肽核酸(PNA)、二酰胺磷酸酯吗啉代(PMO)等;核糖修饰包括2’-O-甲基(2’-O-Me)、2’-氟(2’-F)和锁核酸(LNA)等,常用碱基修饰有2-硫尿苷、5-甲基胞苷等,不论是哪种修饰,均被证实能够有效抵抗核酸酶降解、降低毒性、增强靶点结合力[91]。其中锁核酸(LNA)作为常见的修饰手段,显著增强了对核糖核酸酶的耐药性,并改善了细胞摄取率。若与硫代磷酸酯修饰(PS)组合运用可以获得更好的治疗效果[92]。
2.4.3 CRISPR/Cas9编辑miRNA CRISPR/Cas系统是一种由向导RNA (gRNA)引导的基因编辑平台,可以精准靶向并编辑基因组特定位点。通过CRISPR/Cas技术可以在体内稳定切割miRNA序列以来敲除miRNA,也可以通过调控启动子的方式促进或抑制miRNA的表达[93]。
CRISPR/Cas系统有多种类型,其中最常见的是CRISPR/Cas9。它由Cas9核酸酶与crRNA和tracrRNA制成的嵌合单向导RNA(sgRNA)组成,设计简单、特异性高、操作简便。CRISPR/Cas9可以稳定且特异性地降低miRNA的表达高达96%,其瞬时编辑引起的miRNA敲低表型可在体内外模型中长期稳定维持(长达30 d)[94]。
CRISPR/Cas9系统不仅展现出优越的编辑效能和操作灵活性,还能与高通量测序、单细胞测序等前沿技术相结合,极大地丰富了其应用场景。例如:CRISPR/Cas9与转录组测序技术(RNA-seq)结合,在使用CRISPR/Cas9技术将miRNA敲除或点突变后,采用转录组测序技术分析基因编辑后细胞或模式动物的差异表达基因,同时也可以鉴定出有助于发掘疾病相关的关键突变位点,从而推进疾病的个体化精准治疗研究[95]。
尽管CRISPR/Cas9编辑miRNA具有优势和潜力,但仍面临一些挑战,例如:由于miRNA是短序列,可能出现序列缺失使向导RNA难以检测,向导RNA错配与错误靶标结合而导致的脱靶效应是制约CRISPR/Cas9临床应用的主要障碍之一;此外miRNA的调控机制网络较为复杂,单个miRNA可以调控数百个靶基因,多个miRNA也同时靶向单个基因,因此需要创建多个向导RNA,靶向不同的基因组位点或成熟的miRNA基因组序列才能获得完整的治疗效果;并且,如何将CRISPR/Cas9编辑工具递送到体内目标细胞同时避免或减少脱靶效应仍然是治疗应用的关键障碍。
2.4.4 降低miRNA制作成本 基于miRNA生产成本过高,产业化生产miRNA是目前亟需突破的技术瓶颈。目前RNA生产主要依赖于:①基于DNA的RNA合成;②化学合成的RNA;③体外转录合成的RNA;这些方式价格昂贵、产率低下。加州大学WANG开发了基于tRNA/miR-34a的RNA支架(OnRS)技术在大肠杆菌中合成携带各种小RNA的嵌合RNA的新方法[96],该方法具有高产量、低成本及安全高效的特点[97]。该技术生产的重组miR-129-5p抑制剂能缓解卵巢切除小鼠骨质疏松,效果优于化学合成的抑制剂[98]。另外,国内的瑞博生物公司已投入建成符合GMP标准的小核酸原料公斤级生产基地,能够大幅度降低生产RNA的成本,有利于推动小核酸药物的发展进程。
2.4.5 优化miRNA递送系统 核酸药物的给药方式主要分为全身系统性给药和局部给药(组织特异性递送),miRNA被细胞摄取后,它在细胞质中的生物活性受到多种因素的影响,包括亚细胞定位、与靶标分子的相互作用、细胞微环境等,与药物递送载体偶联是实现miRNA递送的既定方法[99]。常用的递送载体主要分为病毒载体和非病毒载体。
(1)病毒载体:病毒载体主要包括慢病毒(Lentivirus,LV)、腺病毒(Adenovirus,AD)、腺相关病毒(Adeno-associated virus,AAV)及重组腺相关病毒(rAAV)。病毒载体具有优异靶向性和高效转染效率,能有效增加治疗剂在靶细胞浓度,但部分有安全隐患。慢病毒载体包膜或衣壳蛋白易诱导免疫反应限制了疗效。腺病毒免疫原性最强,可致强烈炎症甚至多器官衰竭[100]。腺相关病毒安全性高,宿主基因组整合率极低[101],迄今为止未发现野生型腺相关病毒(wtAAV)致病[102],已获批用于治疗先天性失明(Luxturna)、脊髓性肌萎缩症及血友病B[103]。但是腺相关病毒搭载容量极小(≤4.7 kb),限制了其携带大基因或复杂调控元件的能力。
重组腺相关病毒通过精简腺相关病毒基因组提升安全性,工程改造后可增强组织靶向性,还可通过策略扩大载量[104]。目前OH等[105]使用骨靶向重组腺相关病毒搭载miRNA,降低了Wnt抑制剂schnurri-3和硬化蛋白的表达水平,促进骨生成。在病毒载体方面,重组病毒载体因低免疫原性和高转染效率占据优势,正从实验室走向大规模临床应用,有望应用于骨质疏松症的基因治疗。但重组腺相关病毒无法通过再感染进行自我扩增,生产需要同时表达辅助病毒基因,大规模生产高质量重组腺相关病毒还受到技术限制,通过静脉注射高剂量的重组腺相关病毒会导致肝毒性[104]。
(2)非病毒载体:非病毒载体较病毒载体有多种优势,如原料广泛、化学成分灵活、高载样量可功能化,但也存在转染率低和半衰期短问题,主要有脂质纳米颗粒(lipid nanoparticle,LNP)、聚合物纳米颗粒(Polymeric nanoparticles,PNPs)、无机纳米材料(Inorganic nanomaterials,INP)和外泌体(Exosomes)等[106]。
脂质纳米颗粒:脂质纳米颗粒是由阳离子/可电离脂质、辅助脂质、聚乙二醇脂质、胆固醇4种脂质合成,成分与结构可控,适合规模化生产。不同组合可调节药代动力学与细胞靶向性[107]。脂质纳米颗粒的复杂结构赋予高稳定性,其中阳离子脂质体纳米颗粒可与核酸阴离子结合成稳定复合物,是核酸递送载体中应用最广泛的选择之一[108]。脂质纳米颗粒能控制药物在体内释放的位置和时间,广泛用于疫苗开发,但其靶向性有限,易聚集在肝脏[109]。WANG等[110]发现通过脂质成分优化、靶向配体修饰和微环境响应设计等策略,可制备选择性器官靶向性脂质纳米颗粒以实现组织特异性核酸递送。LIU等[111]发现天冬氨酸(D-Asp8)与羟基磷灰石高度亲和,将天冬氨酸与脂质体偶联,封装miR-148a拮抗剂(抑制破骨细胞生成),可减少骨质疏松小鼠骨吸收。脂质纳米颗粒作为药物递送载体,具有易量产、应用广泛的优势,但存在化学与物理方面的不稳定性,其脂质易水解或封装药物发生泄漏[112]。
聚合物纳米颗粒:聚合物纳米颗粒分为天然和合成两种。天然聚合物包括多糖大分子、蛋白质和透明质酸等,例如:壳聚糖是多糖大分子,因其生物降解性、高生物相容性及功能化特性,有制作可降解骨诱导膜的潜力[113]。合成聚合物为结构可控高分子,分为可生物降解[如聚乙醇酸(PGA)、聚乳酸(PLA)及聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物(PLGA)],获FDA/EMA批准和不可生物降解[如聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)、聚酰胺胺(PAMAM)和聚丙烯亚胺(PPI)]两类[114],可生物降解类在降低免疫原性与细胞毒性方面优势显著。现阶段由聚合物结合无机/有机材料组成的杂化聚合物材料,广泛用于临床试验,包括纳米胶囊、纳米纤维、胶束多种形式,能够结合聚合物和其他分子优势,改变生物分布、溶解度、增强生物相容性[115]。例如:GARCíA-GARCíA等[116]利用脂质-聚合物复合纳米颗粒靶向递送Sfrp-1(Wnt信号抑制剂),促进骨质疏松小鼠骨形成。当前研究聚焦“智能”聚合物纳米颗粒,可响应内/外源性刺激并靶向特定部位,显著提升临床前疗效[117]。实施机器学习可帮助预测聚合物药物的细胞毒性和释放曲线[118]。聚合物纳米颗粒具有高稳定性、低免疫原性及持续递送特性,可功能化设计,广泛应用于生物医学,但制备工艺复杂,在体内代谢清除具有不确定性。
无机纳米颗粒:无机纳米颗粒主要包括金属、碳基、磁性、二氧化硅和磷酸钙等材料,骨骼系统中运用较多的有以下几种,例如:介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒带正电荷,具有高表面积、有序介孔结构,可控药物释放,表面易功能化修饰,可促进细胞黏附与增殖刺激骨再生[119],对其表面修饰(蛋白涂层和聚合物)可增强稳定性、分散性和生物相容性,对其硅质骨架改造能调节机械强度、降解性能[120];磁性纳米颗粒如Fe3O4和γ-Fe2O3,具有超顺磁性和强磁响应能力,在静磁场作用下可促进骨再生及血管生成[121];磷酸钙纳米颗粒为天然骨矿物质,体内可降解为钙离子参与骨矿化,其优异生物相容性和可降解性使它成为骨科药物递送的理想载体[122];羟基磷灰石钙是骨骼的主要成分,兼具生物相容性、骨传导性及诱导性,带正电荷羟基磷灰石钙纳米颗粒可高效负载核酸,实现骨组织靶向递送[123-124],还可通过掺杂锌、锶、镁等离子进行材料改性,改善成骨和抗菌活性[125]。此外,还有氧化石墨烯[126]、金纳米颗粒[127]、黑鳞纳米片等[128]。无机纳米颗粒通过表面修饰可赋予多功能特性,例如:XIANG等[129]利用抗菌鱼精蛋白修饰磷酸钙纳米颗粒,抗菌的同时可高效递送。仿生纳米技术利用细胞膜包被无机纳米颗粒,具备免疫逃避、长循环及靶向能力[130]。无机纳米颗粒具有亲水性、易修饰、生物相容性和高度稳定性等优点,但不易被机体代谢,有潜在的生物毒性风险[131]。
外泌体:外泌体是直径30-150 nm的细胞外囊泡,由质膜融合释放,参与细胞因子、miRNA等生物分子转运,在细胞通讯中起关键作用,作为天然纳米载体,其低免疫原性、高生物相容性、可穿透多种屏障(血脑屏障),适用于核酸递送[132]。例如:间充质干细胞来源外泌内含多种miRNA和蛋白质,具有天然成骨和血管生成能力,调节免疫反应,倾向于归巢至骨组织,在骨质疏松症治疗中显示出诱人的应用前景[133]。然而天然外泌体的靶向能力通常不够精准,内部成分复杂,治疗效果有限,限制了其临床应用,通过工程化可提高治疗效果,例如:用特定的靶向分子(包括肽)修饰外泌体可实现更精准靶送,通过药物共孵育或基因工程修饰提升载药能力和疗效[134]。例如:WANG等[135]加载骨靶向肽(AspSerSer)6至外泌体构成F6-(DSS)6-exo靶向递送姜黄素至骨组织,恢复骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力。外泌体凭借生物安全、低免疫原性、可工程化,在药物开发和基因治疗领域表现突出,但面临规模化生产、质控与保存等挑战[136]。随着技术的进展,目前已有人工外泌体结合天然与合成材料,提升载药效率并突破天然细胞外囊泡局限[137],以及人工智能技术优化外泌体分离提纯方法,推动精准递送系统开发,为外泌体治疗开辟新方向,例如:LIM等[138]将人工智能算法与超分辨率显微镜相结合,可显著提高外泌体分析的通量和准确性,提取各种特征参数,并通过统计分析揭示囊泡群体的分布规律和异质性,发现潜在的生物标志物或药物靶点。
各种类型药物递送载体的优缺点及应用,见表4。

| [1] WU D, CLINE-SMITH A, SHASHKOVA E, et al. T-Cell Mediated Inflammation in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:687551. [2] LIANG B, BURLEY G, LIN S, et al. Osteoporosis pathogenesis and treatment: existing and emerging avenues. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022;27(1):72. [3] ADEJUYIGBE B, KALLINI J, CHIOU D, et al. Osteoporosis: Molecular Pathology, Diagnostics, and Therapeutics. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(19):14583. [4] SINDEL D. Osteoporosis: Spotlight on current approaches to pharmacological treatment. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2023;69(2):140-152. [5] KOMATSU S, KITAI H, SUZUKI HI. Network Regulation of microRNA Biogenesis and Target Interaction. Cells. 2023;12(2):306. [6] ALEXANDRI C, DANIEL A, BRUYLANTS G, et al. The role of microRNAs in ovarian function and the transition toward novel therapeutic strategies in fertility preservation: from bench to future clinical application. Hum Reprod Update. 2020;26(2):174-196. [7] HILL M, TRAN N. miRNA interplay: mechanisms and consequences in cancer. Dis Model Mech. 2021;14(4):dmm047662. [8] NAQVI RA, DATTA M, KHAN SH, et al. Regulatory roles of MicroRNA in shaping T cell function, differentiation and polarization. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022; 124:34-47. [9] SUGATANI T, HRUSKA KA. MicroRNA-223 is a key factor in osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2007;101(4):996-999. [10] EMCH MJ, WICIK Z, ASPROS KGM, et al. Estrogen-regulated miRs in bone enhance osteoblast differentiation and matrix mineralization. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023;33:28-41. [11] SHEN X, ZHU W, ZHANG P, et al. Macrophage miR-149-5p induction is a key driver and therapeutic target for BRONJ. JCI Insight. 2022;7(16):e159865. [12] DEL REAL A, RIANCHO-ZARRABEITIA L, LÓPEZ-DELGADO L, et al. Epigenetics of Skeletal Diseases. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018;16(3):246-255. [13] LEE RC, FEINBAUM RL, AMBROS V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75(5):843-854. [14] ESKILDSEN T, TAIPALEENMÄKI H, STENVANG J, et al. MicroRNA-138 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human stromal (mesenchymal) stem cells in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(15):6139-6144. [15] KOCIJAN R, MUSCHITZ C, GEIGER E, et al. Circulating microRNA Signatures in Patients With Idiopathic and Postmenopausal Osteoporosis and Fragility Fractures. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016;101(11):4125-4134. [16] INOUE K, DENG Z, CHEN Y, et al. Bone protection by inhibition of microRNA-182. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4108. [17] HWANG JH, PARK YS, KIM HS, et al. Yam-derived exosome-like nanovesicles stimulate osteoblast formation and prevent osteoporosis in mice. J Control Release. 2023;355:184-198. [18] MATSUZAKI J, OCHIYA T. Circulating microRNAs and extracellular vesicles as potential cancer biomarkers: a systematic review. Int J Clin Oncol. 2017;22(3):413-420. [19] TAKIZAWA S, MATSUZAKI J, OCHIYA T. Circulating microRNAs: Challenges with their use as liquid biopsy biomarkers. Cancer Biomark. 2022;35(1):1-9. [20] CAPULLI M, PAONE R, RUCCI N. Osteoblast and osteocyte: games without frontiers. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014;561:3-12. [21] HORITA M, FARQUHARSON C, STEPHEN LA. The role of miR-29 family in disease. J Cell Biochem. 2021;122(7):696-715. [22] OKA S, LI X, ZHANG F, et al. MicroRNA-21 facilitates osteoblast activity. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2020;25:100894. [23] XIE Y, ZHOU J, TIAN L, et al. miR-196b-5p Regulates Osteoblast and Osteoclast Differentiation and Bone Homeostasis by Targeting SEMA3A. J Bone Miner Res. 2023;38(8):1175-1191. [24] XU Y, JIN Y, HONG F, et al. MiR-664-3p suppresses osteoblast differentiation and impairs bone formation via targeting Smad4 and Osterix. J Cell Mol Med. 2021; 25(11):5025-5037. [25] WANG CG, HU YH, SU SL, et al. LncRNA DANCR and miR-320a suppressed osteogenic differentiation in osteoporosis by directly inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp Mol Med. 2020; 52(8):1310-1325. [26] XUE J, LIU L, LIU H, et al. LncRNA SNHG14 activates autophagy via regulating miR-493-5p/Mef2c axis to alleviate osteoporosis progression. Commun Biol. 2023;6(1):1120. [27] HE P, YANG Z, LI H, et al. miR-18a-5p promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSC by inhibiting Notch2. Bone. 2024; 188:117224. [28] LI R, RUAN Q, YIN F, et al. MiR-23b-3p promotes postmenopausal osteoporosis by targeting MRC2 and regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Pharmacol Sci. 2021;145(1):69-78. [29] GU Z, XIE D, HUANG C, et al. MicroRNA-497 elevation or LRG1 knockdown promotes osteoblast proliferation and collagen synthesis in osteoporosis via TGF-β1/Smads signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(21):12619-12632. [30] MA H, LI M, JIA Z, et al. MicroRNA-455-3p promotes osteoblast differentiation via targeting HDAC2. Injury. 2022;53(11):3636-3641. [31] SONG CY, GUO Y, CHEN FY, et al. Resveratrol Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Through miR-193a/SIRT7 Axis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2022;110(1):117-130. [32] LIU J, CHANG X, DONG D. MicroRNA-181a-5p Curbs Osteogenic Differentiation and Bone Formation Partially Through Impairing Runx1-Dependent Inhibition of AIF-1 Transcription. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2023;38(1):156-173. [33] WANG J, GAO Z, GAO P. MiR-133b Modulates the Osteoblast Differentiation to Prevent Osteoporosis Via Targeting GNB4. Biochem Genet. 2021;59(5):1146-1157. [34] REN LR, YAO RB, WANG SY, et al. MiR-27a-3p promotes the osteogenic differentiation by activating CRY2/ERK1/2 axis. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):43. [35] WU M, WANG H, KONG D, et al. miR-452-3p inhibited osteoblast differentiation by targeting Smad4. PeerJ. 2021;9:e12228. [36] JIN SL, BAI YM, ZHAO BY, et al. Silencing of miR-330-5p stimulates osteogenesis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and inhibits bone loss in osteoporosis by activating Bgn-mediated BMP/Smad pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020; 24(8):4095-4102. [37] ANWAR A, SAPRA L, GUPTA N, et al. Fine-tuning osteoclastogenesis: An insight into the cellular and molecular regulation of osteoclastogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2023; 238(7):1431-1464. [38] TOBEIHA M, MOGHADASIAN MH, AMIN N, et al. RANKL/RANK/OPG Pathway: A Mechanism Involved in Exercise-Induced Bone Remodeling. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 2020:6910312. [39] 赵瑞,潘静,裴雪冬,等.破骨细胞相关非编码RNA介导的表观遗传学骨质疏松研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2024, 30(4):588-594. [40] YU L, SUI B, FAN W,et al. Exosomes derived from osteogenic tumor activate osteoclast differentiation and concurrently inhibit osteogenesis by transferring COL1A1-targeting miRNA-92a-1-5p.Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(3):e12056. [41] HE X, ZHU L, AN L, et al. MiR-143 Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis by Targeting RANK and NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2020;13(3):224-232. [42] DINESH P, KALAISELVAN S, SUJITHA S, et al. miR-506-3p alleviates uncontrolled osteoclastogenesis via repression of RANKL/NFATc1 signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(12):9497-9509. [43] KONG XH, SHI SF, HU HJ, et al. MicroRNA-20a suppresses RANKL-modulated osteoclastogenesis and prevents bone erosion in mice with rheumatoid arthritis through the TLR4/p38 pathway. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2021;35(3):921-931. [44] XUE HY, LIU MW, YANG G. Resveratrol suppresses lipopolysaccharide-mediated activation of osteoclast precursor RAW 264.7 cells by increasing miR-181a-5p expression. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2023;37:3946320231154995. [45] HUANG MZ, ZHUANG Y, NING X, et al. Artesunate inhibits osteoclastogenesis through the miR-503/RANK axis. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(7):BSR20194387. [46] HUANG M, WANG Y, WANG Z, et al. miR-134-5p inhibits osteoclastogenesis through a novel miR-134-5p/Itgb1/MAPK pathway. J Biol Chem. 2022;298(7):102116. [47] HUANG Y, YANG Y, WANG J, et al. miR-21-5p targets SKP2 to reduce osteoclastogenesis in a mouse model of osteoporosis. J Biol Chem. 2021;296:100617. [48] HE Y, CHEN D, GUO Q, et al. MicroRNA-151a-3p Functions in the Regulation of Osteoclast Differentiation: Significance to Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Clin Interv Aging. 2021;16:1357-1366. [49] MOURA SR, BRAS JP, FREITAS J, et al. miR-99a in bone homeostasis: Regulating osteogenic lineage commitment and osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 2020;134:115303. [50] CHOI JH, SUNG SE, KANG KK, et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppress RANKL-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation via miR122-5p. Biochem Genet. 2024;62(4):2830-2852. [51] ZHU J, WANG H, LIU H. Osteoclastic miR-301-b knockout reduces ovariectomy (OVX)-induced bone loss by regulating CYDR/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;529(1):35-42. [52] HAN Z, ZHAN R, CHEN S, et al. miR-181b/Oncostatin m axis inhibits prostate cancer bone metastasis via modulating osteoclast differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(2):1664-1674. [53] LIU LL, XIAO YS, HUANG WM, et al. ATF1/miR-214-5p/ITGA7 axis promotes osteoclastogenesis to alter OVX-induced bone absorption. Mol Med. 2022;28(1):56. [54] MINAMI S, FUJII Y, YOSHIOKA Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles from mouse bone marrow macrophages-derived osteoclasts treated with zoledronic acid contain miR-146a-5p and miR-322-3p, which inhibit osteoclast function. Bone. 2025;190:117323. [55] SHANMUGAVADIVU A, BALAGANGADHARAN K, SELVAMURUGAN N. Angiogenic and osteogenic effects of flavonoids in bone regeneration. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2022;119(9):2313-2330. [56] ZHU Y, RUAN Z, LIN Z, et al. The association between CD31hiEmcnhi endothelial cells and bone mineral density in Chinese women. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019;37(6): 987-995. [57] 董晤讯,袁翰,马勇,等.骨血管生成机制与功能的研究进展[J].中国现代医学杂志,2017,27(27):51-58. [58] JIN L, LONG Y, ZHANG Q, et al. MiRNAs regulate cell communication in osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling during bone regeneration. Mol Biol Rep. 2023;50(10):8715-8728. [59] SADOWSKA JM, ZIMINSKA M, FERREIRA C, et al. Development of miR-26a-activated scaffold to promote healing of critical-sized bone defects through angiogenic and osteogenic mechanisms. Biomaterials. 2023;303:122398. [60] NAN K, ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Exosomes from miRNA-378-modified adipose-derived stem cells prevent glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by enhancing angiogenesis and osteogenesis via targeting miR-378 negatively regulated suppressor of fused (Sufu). Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):331. [61] WU D, CHANG X, TIAN J, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cells stimulation by magnetic nanoparticles and a static magnetic field: release of exosomal miR-1260a improves osteogenesis and angiogenesis. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021; 19(1):209. [62] QI L, HONG S, ZHAO T, et al. DNA Tetrahedron Delivering miR-21-5p Promotes Senescent Bone Defects Repair through Synergistic Regulation of Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024; 13(30):e2401275. [63] HE WZ, YANG M, JIANG Y, et al. miR-188-3p targets skeletal endothelium coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis during ageing. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(5):494. [64] LU GD, CHENG P, LIU T, et al. BMSC-Derived Exosomal miR-29a Promotes Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020; 8:608521. [65] ZHA X, SUN B, ZHANG R, et al. Regulatory effect of microRNA-34a on osteogenesis and angiogenesis in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(1):417-424. [66] YU X, RONG PZ, SONG MS, et al. lncRNA SNHG1 induced by SP1 regulates bone remodeling and angiogenesis via sponging miR-181c-5p and modulating SFRP1/Wnt signaling pathway. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):141. [67] OUYANG L, SUN Y, LV D, et al. miR-29cb2 promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis by inhibiting HIF-3α in bone. iScience. 2021;25(1):103604. [68] WANG X, LI X, LI J, et al. Mechanical loading stimulates bone angiogenesis through enhancing type H vessel formation and downregulating exosomal miR-214-3p from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. FASEB J. 2021;35(1):e21150. [69] WU F, SONG C, ZHEN G, et al. Exosomes derived from BMSCs in osteogenic differentiation promote type H blood vessel angiogenesis through miR-150-5p mediated metabolic reprogramming of endothelial cells. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024;81(1):344. [70] CHEN Y, YU H, ZHU D, et al. miR-136-3p targets PTEN to regulate vascularization and bone formation and ameliorates alcohol-induced osteopenia. FASEB J. 2020;34(4):5348-5362. [71] HUANG CK, KAFERT-KASTING S, THUM T. Preclinical and Clinical Development of Noncoding RNA Therapeutics for Cardiovascular Disease. Circ Res. 2020; 126(5):663-678. [72] LAGGERBAUER B, ENGELHARDT S. MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease. J Clin Invest. 2022; 132(11):e159179. [73] JIN HY, GONZALEZ-MARTIN A, MILETIC AV, et al. Transfection of microRNA Mimics Should Be Used with Caution. Front Genet. 2015;6:340. [74] LIMA JF, CERQUEIRA L, FIGUEIREDO C, et al. Anti-miRNA oligonucleotides: A comprehensive guide for design. RNA Biol. 2018;15(3):338-352. [75] HUSSEN BM, RASUL MF, ABDULLAH SR, et al. Targeting miRNA by CRISPR/Cas in cancer: advantages and challenges. Mil Med Res. 2023;10(1):32. [76] HONG DS, KANG YK, BORAD M, et al. Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br J Cancer. 2020;122(11):1630-1637. [77] SETO AG, BEATTY X, LYNCH JM, et al. Cobomarsen, an oligonucleotide inhibitor of miR-155, co-ordinately regulates multiple survival pathways to reduce cellular proliferation and survival in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2018;183(3): 428-444. [78] VAN DER REE MH, DE VREE JM, STELMA F, et al. Safety, tolerability, and antiviral effect of RG-101 in patients with chronic hepatitis C: a phase 1B, double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017; 389(10070):709-717. [79] TÄUBEL J, HAUKE W, RUMP S, et al. Novel antisense therapy targeting microRNA-132 in patients with heart failure: results of a first-in-human Phase 1b randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur Heart J. 2021;42(2):178-188. [80] YUN L, WANG L, PAN Y, et al. Current status and development trend of miRNAs in osteoporosis-related research: A bibliometric analysis. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2021;59(4):203-211. [81] CHEN Z, HUAI Y, CHEN G, et al. MiR-138-5p Targets MACF1 to Aggravate Aging-related Bone Loss. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(13):4837-4852. [82] XU C, WANG Z, LIU Y, et al. Delivery of miR-15b-5p via magnetic nanoparticle-enhanced bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles mitigates diabetic osteoporosis by targeting GFAP. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024;40(1):52. [83] LEE KS, LEE J, KIM HK, et al. Extracellular vesicles from adipose tissue-derived stem cells alleviate osteoporosis through osteoprotegerin and miR-21-5p. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(12):e12152. [84] TAIPALEENMÄKI H, SAITO H, SCHRÖDER S, et al. Antagonizing microRNA-19a/b augments PTH anabolic action and restores bone mass in osteoporosis in mice. EMBO Mol Med. 2022;14(11):e13617. [85] DAMMES N, PEER D. Paving the Road for RNA Therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2020;41(10):755-775. [86] BRILLANTE S, VOLPE M, INDRIERI A. Advances in MicroRNA Therapeutics: From Preclinical to Clinical Studies. Hum Gene Ther. 2024;35(17-18):628-648. [87] MERK DJ, PAUL L, TSIAMI F, et al. CRISPR-Cas9 screens reveal common essential miRNAs in human cancer cell lines. Genome Med. 2024;16(1):82. [88] WEN M, CONG P, ZHANG Z, et al. DeepMirTar: a deep-learning approach for predicting human miRNA targets. Bioinformatics. 2018;34(22):3781-3787. [89] JI BY, YOU ZH, WANG Y, et al. DANE-MDA: Predicting microRNA-disease associations via deep attributed network embedding. iScience. 2021;24(6):102455. [90] YOUSEF M, GOY G, BAKIR-GUNGOR B. miRModuleNet: Detecting miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Modules. Front Genet. 2022;13:767455. [91] KHVOROVA A, WATTS JK. The chemical evolution of oligonucleotide therapies of clinical utility. Nat Biotechnol. 2017; 35(3):238-248. [92] WANG J, TAN M, WANG Y, et al. Advances in modification and delivery of nucleic acid drugs. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023;52(4):417-428. [93] YI B, LARTER K, XI Y. CRISPR/Cas9 System to Knockdown MicroRNA In Vitro and In Vivo. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2300:133-139. [94] CHUNG PJ, CHUNG H, OH N, et al. Efficiency of Recombinant CRISPR/rCas9-Mediated miRNA Gene Editing in Rice. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9606. [95] SELVAKUMAR SC, PREETHI KA, ROSS K, et al. CRISPR/Cas9 and next generation sequencing in the personalized treatment of Cancer. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):83. [96] WANG WP, HO PY, CHEN QX, et al. Bioengineering Novel Chimeric microRNA-34a for Prodrug Cancer Therapy: High-Yield Expression and Purification, and Structural and Functional Characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015;354(2):131-141. [97] CHEN QX, WANG WP, ZENG S, et al. A general approach to high-yield biosynthesis of chimeric RNAs bearing various types of functional small RNAs for broad applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(7):3857-3869. [98] YIN C, TIAN Y, YU Y, et al. miR-129-5p Inhibits Bone Formation Through TCF4. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:600641. [99] RUSESKA I, ZIMMER A. Cellular uptake and trafficking of peptide-based drug delivery systems for miRNA. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2023;191:189-204. [100] WANG X, MA C, RODRÍGUEZ LABRADA R, et al. Recent advances in lentiviral vectors for gene therapy. Sci China Life Sci. 2021;64(11):1842-1857. [101] AL-HEETI OM, CATHRO HP, ISON MG. Adenovirus Infection and Transplantation. Transplantation. 2022;106(5):920-927. [102] COSTA VERDERA H, KURANDA K, MINGOZZI F. AAV Vector Immunogenicity in Humans: A Long Journey to Successful Gene Transfer. Mol Ther. 2020;28(3):723-746. [103] MENDELL JR, AL-ZAIDY SA, RODINO-KLAPAC LR, et al. Current Clinical Applications of In Vivo Gene Therapy with AAVs. Mol Ther. 2021;29(2):464-488. [104] WANG JH, GESSLER DJ, ZHAN W, et al. Adeno-associated virus as a delivery vector for gene therapy of human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024;9(1):78. [105] OH WT, YANG YS, XIE J, et al. WNT-modulating gene silencers as a gene therapy for osteoporosis, bone fracture, and critical-sized bone defects. Mol Ther. 2023;31(2):435-453. [106] WANG C, PAN C, YONG H, et al. Emerging non-viral vectors for gene delivery. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):272. [107] PAUNOVSKA K, LOUGHREY D, DAHLMAN JE. Drug delivery systems for RNA therapeutics. Nat Rev Genet. 2022;23(5):265-280. [108] KOYNOVA R, TENCHOV B. Cationic lipids: molecular structure/ transfection activity relationships and interactions with biomembranes. Top Curr Chem. 2010; 296:51-93. [109] SCHOENMAKER L, WITZIGMANN D, KULKARNI JA, et al. mRNA-lipid nanoparticle COVID-19 vaccines: Structure and stability. Int J Pharm. 2021;601:120586. [110] WANG X, LIU S, SUN Y, et al. Preparation of selective organ-targeting (SORT) lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) using multiple technical methods for tissue-specific mRNA delivery. Nat Protoc. 2023;18(1):265-291. [111] LIU J, DANG L, LI D, et al. A delivery system specifically approaching bone resorption surfaces to facilitate therapeutic modulation of microRNAs in osteoclasts. Biomaterials. 2015;52:148-160. [112] FAN Y, MARIOLI M, ZHANG K. Analytical characterization of liposomes and other lipid nanoparticles for drug delivery. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2021;192:113642. [113] FARJAMINEJAD S, FARJAMINEJAD R, GARCIA-GODOY F. Nanoparticles in Bone Regeneration: A Narrative Review of Current Advances and Future Directions in Tissue Engineering. J Funct Biomater. 2024;15(9):241. [114] CHENTHAMARA D, SUBRAMANIAM S, RAMAKRISHNAN SG, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of nanoparticles and routes of administration. Biomater Res. 2019;23:20. [115] FERREIRA SOARES DC, DOMINGUES SC, VIANA DB, et al. Polymer-hybrid nanoparticles: Current advances in biomedical applications. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131:110695. [116] GARCÍA-GARCÍA P, REYES R, GARCÍA-SÁNCHEZ D, et al. Nanoparticle-mediated selective Sfrp-1 silencing enhances bone density in osteoporotic mice. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):462. [117] BEACH MA, NAYANATHARA U, GAO Y, et al. Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Chem Rev. 2024;124(9):5505-5616. [118] GREENBERG ZF, GRAIM KS, HE M. Towards artificial intelligence-enabled extracellular vesicle precision drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023;199:114974. [119] PINNA A, TORKI BAGHBADERANI M, VIGIL HERNÁNDEZ V, et al. Nanoceria provides antioxidant and osteogenic properties to mesoporous silica nanoparticles for osteoporosis treatment. Acta Biomater. 2021;122:365-376. [120] KANKALA RK, HAN YH, NA J, et al. Nanoarchitectured Structure and Surface Biofunctionality of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Adv Mater. 2020; 32(23):e1907035. [121] XIA Y, SUN J, ZHAO L, et al. Magnetic field and nano-scaffolds with stem cells to enhance bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2018;183:151-170. [122] KHALIFEHZADEH R, ARAMI H. Biodegradable calcium phosphate nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2020;279:102157. [123] KAWSAR M, SAHADAT HOSSAIN M, ALAM MK, et al. Synthesis of pure and doped nano-calcium phosphates using different conventional methods for biomedical applications: a review. J Mater Chem B. 2024;12(14):3376-3391. [124] MUNIR MU, SALMAN S, JAVED I, et al. Nano-hydroxyapatite as a delivery system: overview and advancements. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2021;49(1):717-727. [125] SHOKRI M, KHARAZIHA M, TAFTI HA, et al. Synergic role of zinc and gallium doping in hydroxyapatite nanoparticles to improve osteogenesis and antibacterial activity. Biomater Adv. 2022;134:112684. [126] ITOO AM, VEMULA SL, GUPTA MT, et al. Multifunctional graphene oxide nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer. J Control Release. 2022;350:26-59. [127] GUPTA A, SINGH S. Multimodal Potentials of Gold Nanoparticles for Bone Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: Avenues and Prospects. Small. 2022;18(29): e2201462. [128] XU Y, CHEN S, ZHANG Y, et al. Antibacterial black phosphorus nanosheets for biomedical applications. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(30):7069-7093. [129] XIANG C, TENKUMO T, OGAWA T, et al. Gene transfection achieved by utilizing antibacterial calcium phosphate nanoparticles for enhanced regenerative therapy. Acta Biomater. 2021;119:375-389. [130] SONG W, JIA P, ZHANG T, et al. Cell membrane-camouflaged inorganic nanoparticles for cancer therapy. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):289. [131] 秦灿,梁爱玲,刘勇军.纳米载体在抗癌肽递送中的应用[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2025,41(6):833-842. [132] ESCUDÉ MARTINEZ DE CASTILLA P, TONG L, HUANG C, et al. Extracellular vesicles as a drug delivery system: A systematic review of preclinical studies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;175:113801. [133] LI X, SI Y, LIANG J, et al. Enhancing bone regeneration and immunomodulation via gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel-encapsulated exosomes from osteogenic pre-differentiated mesenchymal stem cells. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2024;672:179-199. [134] ZHANG M, HU S, LIU L, et al. Engineered exosomes from different sources for cancer-targeted therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):124. [135] WANG Y, SUN L, DONG Z, et al. Targeted inhibition of ferroptosis in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by engineered exosomes alleviates bone loss in smoking-related osteoporosis. Mater Today Bio. 2025;31:101501. [136] ISAAC R, REIS FCG, YING W, et al. Exosomes as mediators of intercellular crosstalk in metabolism. Cell Metab. 2021;33(9):1744-1762. [137] LI YJ, WU JY, LIU J, et al. Artificial exosomes for translational nanomedicine. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):242. [138] LIM HJ, KIM GW, HEO GH, et al. Nanoscale single-vesicle analysis: High-throughput approaches through AI-enhanced super-resolution image analysis. Biosens Bioelectron. 2024;263:116629. |
| [1] | 温广伟, 甄颖豪, 郑泰铿, 周淑怡, 莫国业, 周腾鹏, 李海山, 赖以毅. 异银杏素对破骨细胞分化的影响和机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(6): 1348-1358. |
| [2] | 许嘉木, 杨 城, 李玮民, 王春庆. 细胞焦亡与炎症因子在骨质疏松症发生中的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(3): 691-700. |
| [3] | 高佳斌, 李天奇, 徐 坤, 朱汉民, 周 茜, 李 微. 线粒体自噬调控破骨细胞:骨质疏松症治疗的新视角[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(23): 5982-5991. |
| [4] | 王 岩, 吕 浩, 胡芷苜, 周 瑶, 刘 强, 杨玉祥, 衣海茹, 王久香, 江 渟. 复方补肾活血颗粒干预骨质疏松症模型小鼠:TRIB3/β-catenin轴的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(23): 6142-6149. |
| [5] | 韩 杰, 胡天发, 吴亚超, 农 彬, 玉开龙. 叉头框转录因子O3影响骨代谢及参与多类骨相关疾病的病理进程[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(22): 5770-5781. |
| [6] | 张 也, 安哲庆, 席 歆, 刘晓妍, 洪 伟, 廖 健. 载唑来膦酸可溶性微针贴片抑制脂多糖诱导破骨细胞的分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5115-5124. |
| [7] | 王馨跃, 李红丽, 郭春辉, 陈继冰, 玉 华. 卵巢早衰动物模型卵巢组织与卵巢早衰患者外周血中6种miRNAs的表达变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(18): 4675-4684. |
| [8] | 李佳音, 隋 磊, 李彦静. 微小RNA-146a调节骨代谢在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(18): 4702-4712. |
| [9] | 王思微, 姚啸生, 戚晓楠, 王 禹, 崔海舰, 赵佳萱. 基质金属蛋白酶9介导线粒体自噬调控成骨及成肌[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(18): 4557-4567. |
| [10] | 赵 宇, 薛 云, 黄家俊, 吴迪友, 杨 彬, 黄俊卿. 菟丝子总黄酮抑制激素性股骨头坏死的成骨细胞凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(17): 4289-4298. |
| [11] | 傅璟玥, 周勤峰, 李沐哲, 马 勇, 潘娅岚, 孙 杰, 黄项阳, 郭 杨. 骨质疏松症与骨关节炎共病模型大鼠的制备与评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(17): 4299-4308. |
| [12] | 孙 龙, 吴海洋, 仝林建, 刘 睿, 杨伟光, 肖 剑, 刘立策, 孙志明. 瘦素调控骨代谢的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(12): 3100-3108. |
| [13] | 齐 鲁, 王俊杰, 邓钦高, 王 星. 敲低Linc00052表达对成骨细胞增殖、迁移和凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(12): 2949-2956. |
| [14] | 石腾博, 倘艳锋, 张孟瑜, 王幸飞, 李晨阳, 师锦玉, 郭超韡, 李彦州, 贺自克, 王上增. 高剂量低分子量肝素对股骨干骨折愈合的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(12): 2957-2964. |
| [15] | 于漫亚, 崔 兴. 骨髓微环境中不同细胞对多发性骨髓瘤骨病外泌体环状RNA的贡献及相互作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(1): 101-110. |
miRNA是真核生物中长度19-24 nt的非编码单链RNA分子,主要通过与靶mRNA的3’-非翻译区结合调节基因表达[5]。miRNA参与多种细胞生物学事件和疾病的病理生理过程[6-8]。2007年SUGATANI等[9]发现miR-223是破骨细胞分化过程中的关键因子,开启了miRNA调控骨代谢的研究。随着研究的持续进展,发现大量miRNA通过调节骨代谢相关的转录因子及信号通路,对骨重塑起到调控作用。同时某些激素和药物影响miRNA表达干预骨质疏松症的发展,例如:雌激素可通过存在于骨细胞中的多种miRNA影响骨形成[10]。唑来膦酸可在巨噬细胞中促进miR-149-5p转录进而抑制破骨细胞分化[11]。
鉴于miRNA独特的调控机制及其与骨质疏松症发病机制的高度相关性,采用miRNA靶向治疗策略有望实现对骨质疏松的精准干预。但目前miRNA的靶向治疗仍存在一些局限性(如靶向递送效率、脱靶效应等),制约了其临床转化和应用。此文章系统阐述了miRNA在骨质疏松发生发展中的分子调控机制,总结了基于miRNA治疗骨质疏松症所面临的主要挑战及潜在应对策略,以期加速miRNA药物转化医学突破,为相关研究提供新的思路和参考。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2024年6月进行检索,并实时更新。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 各数据库建库至2025年3月,主要集中于近10年。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed数据库(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)、Web of Science数据库(https://webofscience.clarivate.cn/wos/alldb/basic-search)、中国知网(https://www.cnki.net/)。
1.1.4 检索途径 主题词、关键词、标题/摘要及部分全文检索。
1.1.5 检索词 中文检索词为“miRNA,骨质疏松,基因治疗,核酸药物,递送载体”。英文检索词为“miRNA,osteoporosis,angiogenesis,osteogenesis,gene therapy,drug delivery”。
1.1.6 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述、荟萃分析等。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例,见图1。
1.2 入选标准 ①miRNA与骨质疏松、骨细胞活动相关的研究和综述;②基于miRNA治疗的相关研究和综述;③相关性、可靠性高,创新性较为突出的文献;④英文文献主要来源于PubMed核心集。
1.3 排除标准 ①与研究主题无关的文献;②观点陈旧的文章;③缺乏创新性、可读性较低的文章。
1.4 资料整合 共检索到3 863篇相关文献,其中排除3 725篇文献,实际纳入138篇文献,中文3篇,英文135篇。文献筛选流程图见图2。
3.1 既往他人在该领域研究的贡献和存在的问题 近年来随着分子生物学和遗传学的快速发展,人们对于骨重建周期有了更详细的了解,大量研究已证明miRNA能通过调节某些细胞因子、转录因子和信号中间体的表达来调节骨稳态,一些已知功能的
miRNA构成了骨代谢疾病潜在的治疗靶点。许多研究团队和研究人员也为基于miRNA靶向治疗骨质疏松症作出了突出的贡献,然而仍存在一些局限性:首先基于miRNA治疗骨质疏松症的研究多数停留于动物实验,miRNA药物结合药物递送载体进入机体后,面临着血液屏障、网状内皮系统清除、溶酶体降解、核酸释放与功能发挥障碍、补体系统的激活等阻碍,然而,如何协助核酸药物在体内发挥作用的具体分子机制尚未完全阐明,不同材料的核酸药物递送载体进入体内后,其清除机制以及药物代谢动力学还缺乏足够的实验数据,目前还没有关于器官选择性的具体机制的明确结论。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 文章采用严格的筛选标准选取近5年内的高质量期刊文章,综述了miRNA作为一种组织特异性强和敏感性高的内源性分子,通过表观遗传的方式调控骨重塑过程中的成骨-破骨平衡,以及骨血管与骨再生偶联的机制,进而在骨质疏松发生发展中发挥着重要作用,深入探讨了miRNA治疗骨质疏松症的应用潜能,分析了目前miRNA靶向治疗骨质疏松症面临的挑战,着重探讨了如何推进miRNA靶向治疗骨质疏松症的相应策略,聚焦于miRNA核酸药物在体内递送是可选择的不同生物递送载体及优化载体的技术策略。
3.3 综述的局限性 基于篇幅原因,该综述存在一定的局限性,miRNA不仅参与调控骨质疏松症的成骨分化、破骨分化和血管生成,同时对间充质干细胞成脂分化、细胞自噬等具有调控作用,在此未能详细阐述。另随着基因编辑技术CRISPR/Cas9在核酸药物治疗中的应用正在快速发展,CRISPR/Cas9具有精准靶向性可编辑miRNA的加工位点,可改造核酸药物的递送载体或宿主细胞,解决递送效率低和脱靶效应问题,受内容的限制在此未能详细展开介绍。
3.4 综述的重要意义 相比传统的治疗方法,基于miRNA的核酸疗法潜能巨大,能从多角度抑制疾病的发展,包括抑制病理蛋白质的产生(基因沉默)、产生治疗性蛋白质(基因表达)和引导基因编辑。因此,基于miRNA的核酸药物疗法被提出,这些药物潜能巨大,能从多角度更有效地维持骨重建中的动态平衡,抑制疾病的发展。在某些疾病中以miRNA作为靶点进行治疗已经进入临床阶段,但在骨质疏松症领域,鉴于骨靶向性和miRNA稳定性等问题,尚无直接用于人类骨质疏松症治疗的以miRNA作为靶点的研究。因此,大量学者针对靶向miRNA的核酸药物挑战进行了大量研究,随着化学修饰、递送系统和miRNA生产技术的不断发展,阻碍核酸药物临床转化的障碍在正在逐渐被克服。因此,开发治疗骨质疏松的miRNA治疗剂具有广泛的前景。
相信在不久的将来,随着技术的发展,核酸药物在体内的稳定性能够得到较大的提升,通过不断地优化生物材料,适合大规模生产、靶向精准、生物相容性高、药物控释灵敏的“智能”药物载体有望诞生,miRNA靶向治疗的核酸药物有望成为治疗骨骼系统疾病的主力军。
3.5 课题组专家对未来的建议 基于miRNA对骨质疏松症发生发展的调控机制,以及核酸药物临床转化的障碍,未来的研究可聚焦于以下几个方面:优化核酸药物递送系统,深入不同药物载体在体内代谢方式,选择最优的给药途径;设计多模态递送载体,例如结合外泌体与聚合物或其他材料的优势,进行核酸药物递送;优化材料生产技术,提高材料产量的同时严格把握质控标准;借助人工智能等技术辅助预测核酸序列与载体最优组合和精准递送。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
近年来,核酸药物(包括siRNA、miRNA等)在疾病治疗领域取得突破性进展,其研究热点主要集中在靶向递送、化学修饰、适应证拓展及临床转化等方面。本文聚焦于miRNA调控骨代谢的分子机制(miRNA调控成骨分化、破骨分化及骨血管耦联),突出了miRNA在骨质疏松症的紧密联系。详细列举了miRNA靶向治疗所遇到的临床转化挑战与应对策略(CRISPR-Cas9编辑miRNA、化学修饰、优化递送等)。本文综述核酸药物的最新研究进展,分析当前面临的挑战,并展望未来发展方向。未来可能通过多学科交叉策略,通过智能化递送、联合疗法等措施突破miRNA靶向治疗临床转化瓶颈,为骨质疏松症提供精准干预手段。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||