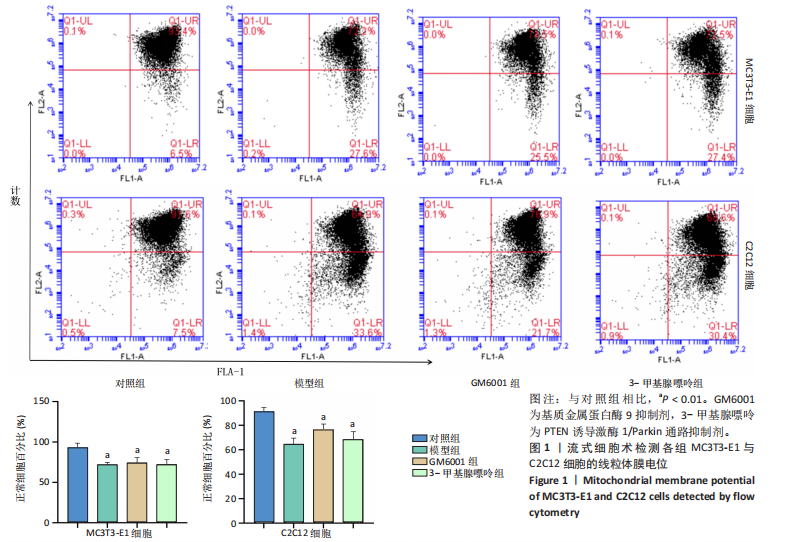
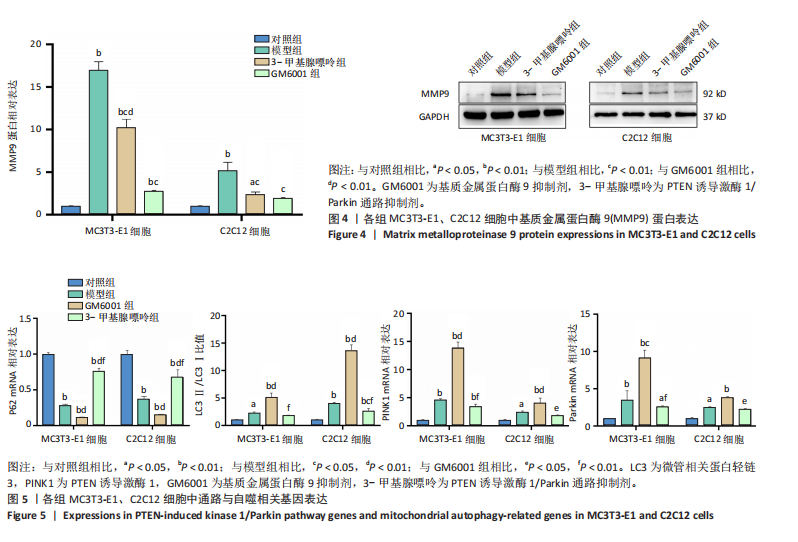
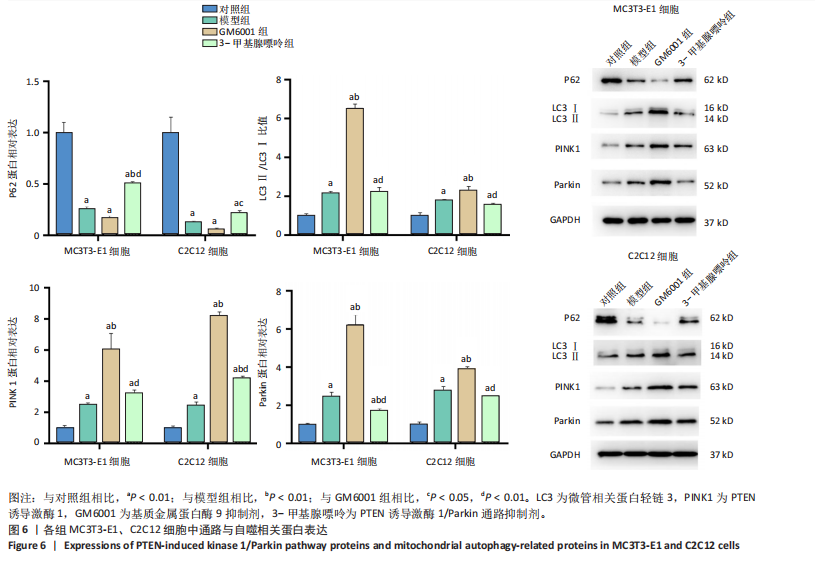
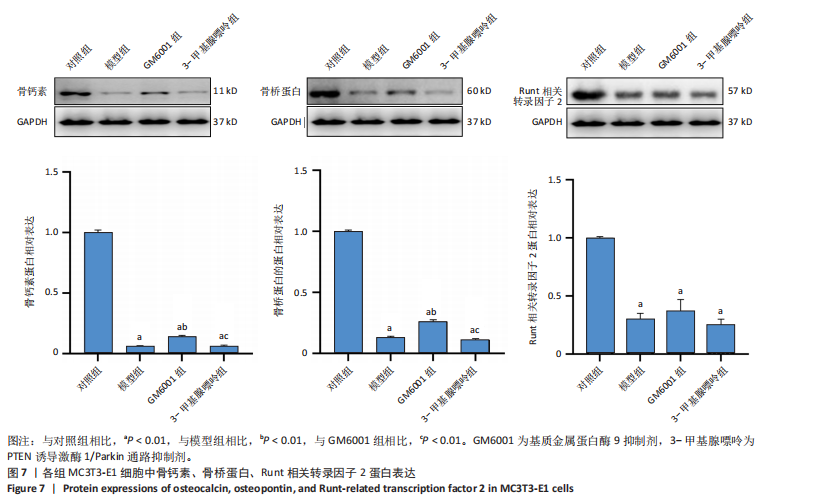
[1] LIJIE G, YUEYUE Z, NAN Z, et al. Mitsugumin 53 promotes mitochondrial autophagy through regulating Ambra1 expression in C2C12 myoblast cells. Cell Biol Int. 2019;43(3):290-298.
[2] LU Y, LI Z, ZHANG S, et al. Cellular mitophagy: Mechanism, roles in diseases and small molecule pharmacological regulation. Theranostics. 2023;13(2):736-766.
[3] DONG Y, ZHANG X. Targeting cellular mitophagy as a strategy for human cancers. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024;12:1431968.
[4] ZHENG F, ZHONG J, CHEN K, et al. PINK1-PTEN axis promotes metastasis and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer via non-canonical pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023;42(1):295.
[5] HAN R, LIU Y, LI S, et al. PINK1-PRKN mediated mitophagy: differences between in vitro and in vivo models. Autophagy. 2023;19(5):1396-1405.
[6] XIE W, CHEN M, LOOR JJ, et al. AMPK-endoplasmic reticulum stress axis contributes to lipopolysaccharide-caused mitochondrial dysfunction by regulating mitochondria-associated membrane function in bovine hepatocytes. J Dairy Sci. 2023;106(7):5146-5164.
[7] KAPOOR C, VAIDYA S, WADHWAN V, et al. Seesaw of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). J Cancer Res Ther. 2016;12(1):28-35.
[8] BHARATHA M, NANDANA MB, PRAVEEN R, et al. Unconjugated bilirubin and its derivative ameliorate IMQ-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice by inhibiting MMP9 and MAPK pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024;130:111679.
[9] XIA Q, DU Z, CHEN M, et al. A protein complex of LCN2, LOXL2 and MMP9 facilitates tumour metastasis in oesophageal cancer. Mol Oncol. 2023;17(11):2451-2471.
[10] GAAFAR NAG, ASLANI M, AGHAZADEH Z, et al. The Oral Administration Effect of Drug Mannuronic Acid (M2000) on Gene Expression of Matrix and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2020;17(5):704-710.
[11] RASHID ZA, BARDAWEEL SK. Novel Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) Inhibitors in Cancer Treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(15):12133.
[12] ZHU G, CHEN W, TANG CY, et al. Knockout and Double Knockout of Cathepsin K and Mmp9 reveals a novel function of Cathepsin K as a regulator of osteoclast gene expression and bone homeostasis. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(14):5522-5538.
[13] COFFEY EC, ASTUMIAN M, ALROWAISHED SS, et al. Lysosomal Function Impacts the Skeletal Muscle Extracellular Matrix. J Dev Biol. 2021;9(4):52.
[14] YAN C, SHI Y, YUAN L, et al. Mitochondrial quality control and its role in osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1077058.
[15] LEE SY, AN HJ, KIM JM, et al. PINK1 deficiency impairs osteoblast differentiation through aberrant mitochondrial homeostasis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):589.
[16] LEDUC-GAUDET JP, REYNAUD O, HUSSAIN SN, et al. Parkin overexpression protects from ageing-related loss of muscle mass and strength. J Physiol. 2019;597(7):1975-1991.
[17] SU X, YANG D, HU Y, et al. Berberine suppressed sarcopenia insulin resistance through SIRT1-mediated mitophagy. Open Life Sci. 2023; 18(1):20220648.
[18] BADRELDIN AA, BAGHERI L, ZHANG B, et al. Relative mRNA and protein stability of epigenetic regulators in musculoskeletal cell culture models. Gene. 2021;766:145032.
[19] WALKER CL, POMATTO LCD, TRIPATHI DN, et al. Redox Regulation of Homeostasis and Proteostasis in Peroxisomes. Physiol Rev. 2018; 98(1):89-115.
[20] DONG Y, HOU Q, LEI J, et al. Quercetin Alleviates Intestinal Oxidative Damage Induced by H2O2 via Modulation of GSH: In Vitro Screening and In Vivo Evaluation in a Colitis Model of Mice. ACS Omega. 2020; 5(14):8334-8346.
[21] 陶乐维,韩煦,陈清光,等.基于FOXO1的抗氧化作用探讨六味地黄方对去卵巢大鼠及H2O2诱导的氧化损伤MC3T3-E1细胞的干预作用[J].上海中医药杂志,2023,57(7):13-20.
[22] CHEN T, WANG H, JIANG C, et al. PKD1 alleviates oxidative stress-inhibited osteogenesis of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through TAZ activation. J Cell Biochem. 2021;122(11):1715-1725.
[23] DENG W, DING Z, WANG Y, et al. Dendrobine attenuates osteoclast differentiation through modulating ROS/NFATc1/ MMP9 pathway and prevents inflammatory bone destruction. Phytomedicine. 2022; 96:153838.
[24] ZHU L, TANG Y, LI XY, et al. Proteolytic regulation of a galectin-3/Lrp1 axis controls osteoclast-mediated bone resorption. J Cell Biol. 2023;222(4):e202206121.
[25] ZHANG H, LIU L, JIANG C, et al. MMP9 protects against LPS-induced inflammation in osteoblasts. Innate Immun. 2020;26(4):259-269.
[26] HU C, JI F, LV R, et al. Putrescine promotes MMP9-induced angiogenesis in skeletal muscle through hydrogen peroxide/METTL3 pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2024;212:433-447.
[27] PHAN TTT, LIN YC, CHOU YT, et al. Tumor suppressor p53 restrains cancer cell dissemination by modulating mitochondrial dynamics. Oncogenesis. 2022;11(1):26.
[28] LIU C, LIU R, CAO Z, et al. Identification of MMP9 as a Novel Biomarker to Mitochondrial Metabolism Disorder and Oxidative Stress in Calcific Aortic Valve Stenosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:3858871.
[29] CAO L, LIU J, ZHANG L, et al. Curcumin inhibits H2O2-induced invasion and migration of human pancreatic cancer via suppression of the ERK/NF-κB pathway. Oncol Rep. 2016;36(4):2245-2251.
[30] 王思微,姚啸生,戚晓楠,等.线粒体相关蛋白IGF-1、MMP9、PKM的在骨质疏松症患者中临床意义及诊断价值[J/OL].重庆医科大学学报,1-6[2025-05-29].https://doi.org/10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.003764.
[31] ASHRAFI G, SCHWARZ TL. The pathways of mitophagy for quality control and clearance of mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20(1): 31-42.
[32] ZHOU TY, MA RX, LI J, et al. Review of PINK1-Parkin-mediated mitochondrial autophagy in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 2023;959:176057.
[33] NARENDRA DP, YOULE RJ. The role of PINK1-Parkin in mitochondrial quality control. Nat Cell Biol. 2024;26(10):1639-1651.
[34] BARODIA SK, CREED RB, GOLDBERG MS. Parkin and PINK1 functions in oxidative stress and neurodegeneration. Brain Res Bull. 2017;133:51-59.
[35] KANE LA, LAZAROU M, FOGEL AI, et al. PINK1 phosphorylates ubiquitin to activate Parkin E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. J Cell Biol. 2014;205(2): 143-153.
[36] YI J, WANG HL, LU G, et al. Spautin-1 promotes PINK1-PRKN-dependent mitophagy and improves associative learning capability in an alzheimer disease animal model. Autophagy. 2024;20(12):2655-2676.
[37] HUANG T, ZUO L, WALCZYŃSKA KS, et al. Essential roles of matrix metalloproteinases in axolotl digit regeneration [published correction appears in Cell Tissue Res. 2021;386(1):207.
[38] 朱汉民,王松,肖文琳,等.线粒体自噬调控骨代谢[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(8):1676-1683.
[39] LI Y, ZHANG H, YU C, et al. New Insights into Mitochondria in Health and Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(18):9975.
|