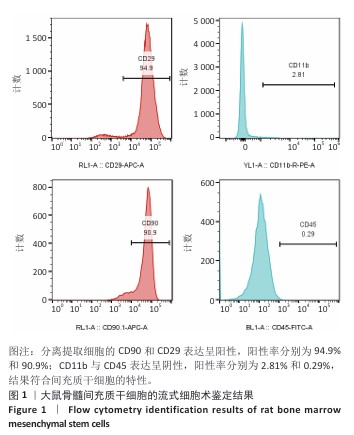
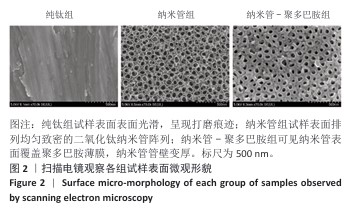
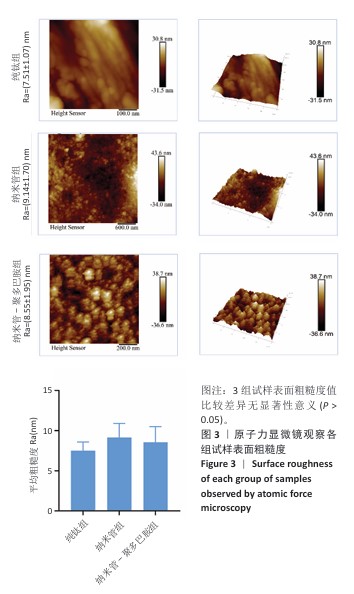
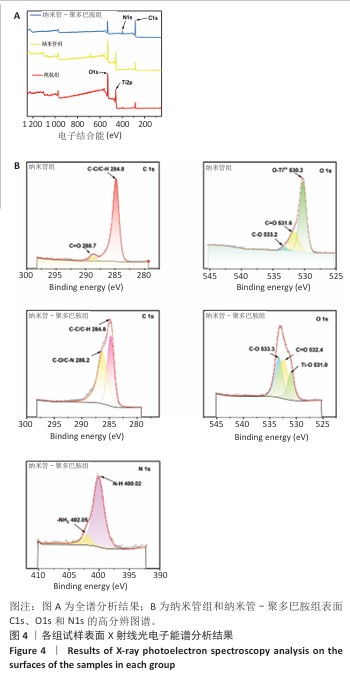
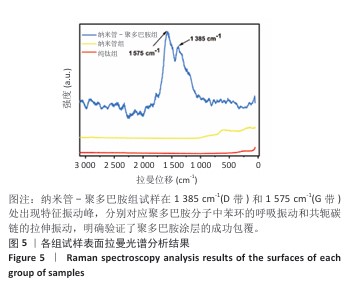
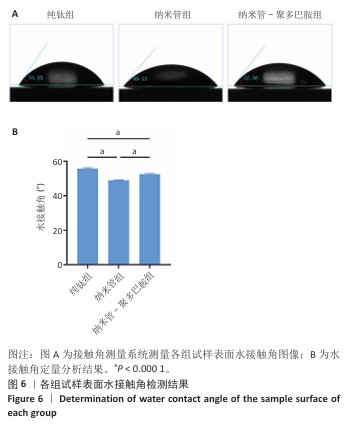
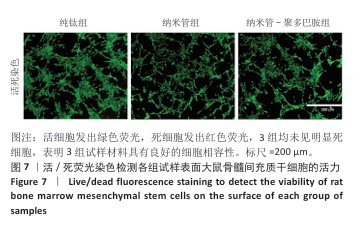
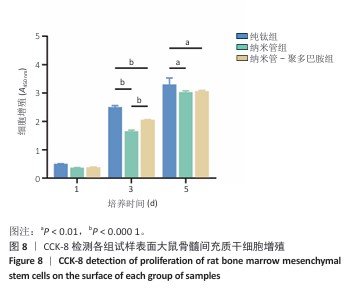
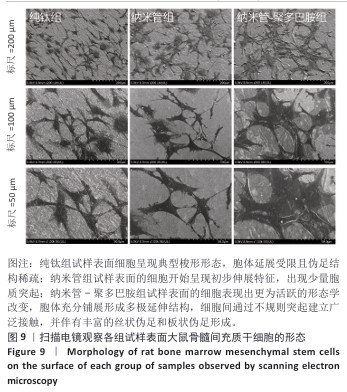
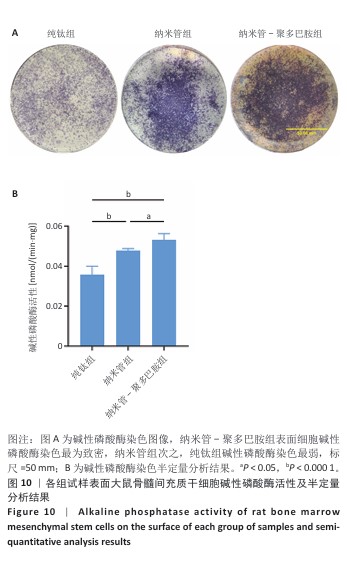
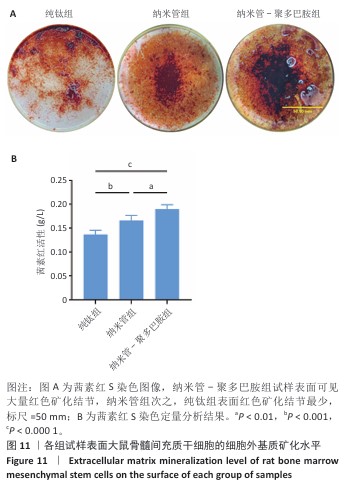
[1] YUAN P, CHEN M, LU X, et al. Application of advanced surface modification techniques in titanium-based implants: latest strategies for enhanced antibacterial properties and osseointegration. J Mater Chem B. 2024;12(41):10516-10549.
[2] HAN X, MA J, TIAN A, et al. Surface modification techniques of titanium and titanium alloys for biomedical orthopaedics applications: A review. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2023;227:113339.
[3] HUO SC, YUE B. Approaches to promoting bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis on orthopedic implant surface. World J Stem Cells. 2020;12(7):545-561.
[4] SOTOVA C, YANUSHEVICH O, KRIHELI N, et al. Dental Implants: Modern Materials and Methods of Their Surface Modification. Materials. 2023;16(23):7383.
[5] WANG S, ZHAO X, HSU Y, et al. Surface modification of titanium implants with Mg-containing coatings to promote osseointegration. Acta Biomater. 2023;169:19-44.
[6] DONOHOE E, KAHATAB R, BARRAK F. A systematic review comparing the macrophage inflammatory response to hydrophobic and hydrophilic sandblasted large grit, acid‐etched titanium or titanium–zirconium surfaces during in vitro studies. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2023;9(3):437-448.
[7] WEN X, LIU Y, XI F, et al. Micro-arc oxidation (MAO) and its potential for improving the performance of titanium implants in biomedical applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1282590.
[8] CHHABRA K, RAJASEKAR A. Comparison of Roughness, Wettability, and SEM Features between Sandblasted Acid-Etched and Oxidized Titanium Dental Implants. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2024;34(4):57-63.
[9] ALEMAYEHU DB, TODOH M, HSIEH JH, et al. Improving Pure Titanium’s Biological and Mechanical Characteristics through ECAP and Micro-Arc Oxidation Processes. Micromachines. 2023;14(8):1541.
[10] LI J, CUI X, HOOPER GJ, et al. Rational design, bio-functionalization and biological performance of hybrid additive manufactured titanium implants for orthopaedic applications: A review. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;105:103671.
[11] JACOBS TW, DILLON JT, COHEN DJ, et al. Different Methods to Modify the Hydrophilicity of Titanium Implants with Biomimetic Surface Topography to Induce Variable Responses in Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. Biomimetics. 2024;9(4):227.
[12] KIDO D, KOMATSU K, SUZUMURA T, et al. Influence of Surface Contaminants and Hydrocarbon Pellicle on the Results of Wettability Measurements of Titanium. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(19):14688.
[13] REN B, WAN Y, LIU C, et al. Improved osseointegration of 3D printed Ti-6Al-4V implant with a hierarchical micro/nano surface topography: An in vitro and in vivo study. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021; 118:111505.
[14] WU N, GAO H, WANG X, et al. Surface Modification of Titanium Implants by Metal Ions and Nanoparticles for Biomedical Application. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(6):2970-2990.
[15] ZHOU S, XIAO C, FAN L, et al. Injectable ultrasound-powered bone-adhesive nanocomposite hydrogel for electrically accelerated irregular bone defect healing. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024;22(1):54.
[16] LI Y, XU C, LEI C. The Delivery and Activation of Growth Factors Using Nanomaterials for Bone Repair. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(3):1017.
[17] YU YM, LU YP, ZHANG T, et al. Biomaterials science and surface engineering strategies for dental peri-implantitis management. Mil Med Res. 2024;11(1):29.
[18] BANDYOPADHYAY A, SHIVARAM A, MITRA I, et al. Electrically polarized TiO2 nanotubes on Ti implants to enhance early-stage osseointegration. Acta Biomater. 2019;96:686-693.
[19] LI J, MUTREJA I, TREDINNICK S, et al. Hydrodynamic control of titania nanotube formation on Ti-6Al-4V alloys enhances osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;109:110562.
[20] MA QL, FANG L, JIANG N, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell secretion of sRANKL/OPG/M-CSF in response to macrophage-mediated inflammatory response influences osteogenesis on nanostructured Ti surfaces. Biomaterials. 2018;154:234-247.
[21] GUO Q, CHEN J, WANG J, et al. Recent progress in synthesis and application of mussel-inspired adhesives. Nanoscale. 2020;12(3):1307-1324.
[22] JINSHENG L, QING D, JUNHAO C, et al. Micro/nano topological modification of TiO nanotubes activates Thy-1 signaling to control osteogenic differentiation of stem cells. SLAS Discov. 2024;29(3): 100139.
[23] GUO X, BAI J, GE G, et al. Bioinspired peptide adhesion on Ti implants alleviates wear particle-induced inflammation and improves interfacial osteogenesis. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;605:410-424.
[24] SAMYN P. A platform for functionalization of cellulose, chitin/chitosan, alginate with polydopamine: A review on fundamentals and technical applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;178:71-93.
[25] XIA S, LIU D, JIANG K, et al. Photothermal driven BMSCs osteogenesis and M2 macrophage polarization on polydopamine-coated TiC nanosheets/poly(vinylidene fluoride trifluoroethylene) nanocomposite coatings. Mater Today Bio. 2024;27:101156.
[26] LEE H, DELLATORE SM, MILLER WM, et al. Mussel-Inspired Surface Chemistry for Multifunctional Coatings. Science. 2007;318(5849): 426-430.
[27] MA Q, JIANG N, LIANG S, et al. Functionalization of a clustered TiO nanotubular surface with platelet derived growth factor-BB covalent modification enhances osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2020;230:119650.
[28] YANG X, WANG Q, YAN C, et al. A dual-functional strontium-decorated titanium implants that guides the immune response for osseointegration of osteoporotic rats. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2024;233:113643.
[29] DING C, LU Y, XIANG M, et al. Internal electric field-assisted copper ions chelated polydopamine/titanium dioxide nano-thin film heterojunctions activate peroxymonosulfate under visible light to catalyze degradation of gatifloxacin: Theoretical calculations and biotoxicity analysis. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023;646:275-289.
[30] CHEN J, CHEN T, FANG Q, et al. Gd2 O3 /b‐TiO2 composite nanoprobes with ultra‐high photoconversion efficiency for MR image‐guided NIR‐II photothermal therapy. Exploration. 2022;2(6):20220014.
[31] WEBSTER TJ. Reduced adhesion of macrophages on anodized titanium with select nanotube surface features. Int J Nanomedicine. Published online August 2011;6:1765-1771.
[32] SEREDIN P, GOLOSHCHAPOV D, BUYLOV N, et al. A Study of the Peculiarities of the Formation of a Hybrid Interface Based on Polydopamine between Dental Tissues and Dental Composites, Using IR and Raman Microspectroscopy, at the Submicron Level. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(14):11636.
[33] LU R, WANG C, WANG X, et al. Effects of hydrogenated TiO2 nanotube arrays on protein adsorption and compatibility with osteoblast-like cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:2037-2049.
[34] SUN XD, LIU TT, WANG QQ, et al. Surface Modification and Functionalities for Titanium Dental Implants. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(8):4442-4461.
[35] LI X, COMBS JD, SALAITA K, et al. Polarized focal adhesion kinase activity within a focal adhesion during cell migration. Nat Chem Biol. 2023;19(12):1458-1468.
[36] XING B, LEI Z, WANG Z, et al. A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 22 activates integrin β 1 through its disintegrin domain to promote the progression of pituitary adenoma. Neuro-Oncol. 2024;26(1):137-152.
[37] OLIVEIRA WF, ARRUDA IRS, SILVA GMM, et al. Functionalization of titanium dioxide nanotubes with biomolecules for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;81:597-606.
[38] MA T, WANG C, GE X, et al. Applications of Polydopamine in Implant Surface Modification. Macromol Biosci. 2023;23(10):2300067.
[39] HE R, SUI J, WANG G, et al. Polydopamine and hyaluronic acid immobilisation on vancomycin-loaded titanium nanotube for prophylaxis of implant infections. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022; 216:112582.
[40] OMIDIAN H, WILSON RL. Polydopamine Applications in Biomedicine and Environmental Science. Materials. 2024;17(16):3916.
[41] ZHANG Q, PAN RL, WANG H, et al. Nanoporous Titanium Implant Surface Accelerates Osteogenesis via the Piezo1/Acetyl-CoA/β-Catenin Pathway. Nano Lett. 2024;24(27):8257-8267.
[42] LIU C, LI Y, WANG J, et al. Improving Hydrophilicity and Inducing Bone-Like Apatite Formation on PPBES by Polydopamine Coating for Biomedical Application. Molecules. 2018;23(7):1643.
[43] WANG H, YUAN C, LIN K, et al. Modifying a 3D-Printed Ti6Al4V Implant with Polydopamine Coating to Improve BMSCs Growth, Osteogenic Differentiation, and In Situ Osseointegration In Vivo. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:761911.
[44] ZHANG Y, DONG C, YANG S, et al. Enhanced silver loaded antibacterial titanium implant coating with novel hierarchical effect. J Biomater Appl. 2018;32(9):1289-1299.
[45] XIANG Y, LIN D, ZHOU Q, et al. Elucidating the Mechanism of Large-Diameter Titanium Dioxide Nanotubes in Protecting Osteoblasts Under Oxidative Stress Environment: The Role of Fibronectin and Albumin Adsorption. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024;19:10639-10659.
[46] JIA L, HAN F, WANG H, et al. Polydopamine-assisted surface modification for orthopaedic implants. J Orthop Transl. 2019;17:82-95.
[47] VIMALRAJ S. Alkaline phosphatase: Structure, expression and its function in bone mineralization. Gene. 2020;754:144855.
[48] BERNAR A, GEBETSBERGER JV, BAUER M, et al. Optimization of the Alizarin Red S Assay by Enhancing Mineralization of Osteoblasts. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):723.
[49] MORANDINI RODRIGUES L, LIMA ZUTIN EA, SARTORI EM, et al. Nanoscale hybrid implant surfaces and Osterix ‐mediated osseointegration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2022;110(3):696-707.
[50] FARJAMINEJAD S, FARJAMINEJAD R, GARCIA-GODOY F. Nanoparticles in Bone Regeneration: A Narrative Review of Current Advances and Future Directions in Tissue Engineering. J Funct Biomater. 2024;15(9):241.
[51] KULKARNI M, MAZARE A, GONGADZE E, et al. Titanium nanostructures for biomedical applications. Nanotechnology. 2015;26(6):062002.
[52] ZHAN J, LI L, YAO L, et al. Evaluation of sustained drug release performance and osteoinduction of magnetron-sputtered tantalum-coated titanium dioxide nanotubes. RSC Adv. 2024;14(6):3698-3711. |