[1] VOELKER R. What Are Diabetic Foot Ulcers? JAMA. 2023;330(23):2314.
[2] HUANG F, LU X, YANG Y, et al. Microenvironment-Based Diabetic Foot Ulcer Nanomedicine. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(2):e2203308.
[3] ARMSTRONG DG, TAN TW, BOULTON AJM, et al. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Review. JAMA. 2023;330(1):62-75.
[4] ZHU D, WEI W, ZHANG J, et al. Mechanism of damage of HIF-1 signaling in chronic diabetic foot ulcers and its related therapeutic perspectives. Heliyon. 2024;10(3):e24656.
[5] 李文惠,柳国斌.国际糖尿病足研究知识图谱:基于CiteSpace的文献可视化分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(20):3178-3184.
[6] SENNEVILLE É, ALBALAWI Z, VAN ASTEN SA, et al. IWGDF/IDSA guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes-related foot infections (IWGDF/IDSA 2023). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2024;40(3):e3687.
[7] TIAN W, ZHANG L, WANG Y, et al. Tibial transverse transport promotes wound healing in diabetic foot ulcers by stimulating endothelial progenitor cell mobilization and homing mediated neovascularization. Ann Med. 2024;56(1):2404186.
[8] WEI W, JIANG T, HU F, et al. Tibial transverse transport combined with platelet-rich plasma sustained-release microspheres activates the VEGFA/VEGFR2 pathway to promote microcirculatory reconstruction in diabetic foot ulcer. Growth Factors. 2024;42(3):128-144.
[9] OU S, XU C, YANG Y, et al. Transverse Tibial Bone Transport Enhances Distraction Osteogenesis and Vascularization in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(9):2170-2179.
[10] 刘杰,花奇凯,李山郎,等.骨膜牵张技术用于糖尿病足治疗的理论基础及临床结果验证[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(32):5236-5241.
[11] CHEN LL. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(8):475-490.
[12] YAO R, YAO Y, LI C, et al. Circ-HIPK3 plays an active role in regulating myoblast differentiation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;155: 1432-1439.
[13] ZHONG G, ZHAO Q, CHEN Z, et al. TGF-β signaling promotes cervical cancer metastasis via CDR1as. Mol Cancer. 2023;22(1):66.
[14] ASHRAFIZADEH M, ZARRABI A, MOSTAFAVI E, et al. Non-coding RNA-based regulation of inflammation. Semin Immunol. 2022;59:101606.
[15] HUANG Q, CHU Z, WANG Z, et al. circCDK13-loaded small extracellular vesicles accelerate healing in preclinical diabetic wound models. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):3904.
[16] MISIR S, WU N, YANG BB. Specific expression and functions of circular RNAs. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(3):481-491.
[17] ULSHÖFER CJ, PFAFENROT C, BINDEREIF A, et al. Methods to study circRNA-protein interactions. Methods. 2021;196:36-46.
[18] HWANG HJ, KIM YK. Molecular mechanisms of circular RNA translation. Exp Mol Med. 2024;56(6):1272-1280.
[19] LI X, LI N, LI B, et al. Noncoding RNAs and RNA-binding proteins in diabetic wound healing. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021;50:128311.
[20] WANG Y, ZHAO R, SHEN C, et al. Exosomal CircHIPK3 Released from Hypoxia-Induced Cardiomyocytes Regulates Cardiac Angiogenesis after Myocardial Infarction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:8418407.
[21] GAREEV I, KUDRIASHOV V, SUFIANOV A, et al. The role of long non-coding RNA ANRIL in the development of atherosclerosis. Noncoding RNA Res. 2022;7(4):212-216.
[22] ZHANG S, TU D, LIU W, et al. circELP2 reverse-splicing biogenesis and function as a pro-fibrogenic factor by targeting mitochondrial quality control pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2024;28(3):e18098.
[23] LI Z, ZHANG W, ZHANG H. Hsa_circ_0000129 knockdown attenuates proliferation and migration in keloid fibroblasts by targeting miR-485-3p/SGMS2 pathway. Burns. 2023;49(8):2007-2017.
[24] YANG L, FU J, HAN X, et al. Hsa_circ_0004287 inhibits macrophage-mediated inflammation in an N6-methyladenosine-dependent manner in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;149(6):2021-2033.
[25] ZHOU JL, DENG S, FANG HS, et al. Circular RNA circANKRD36 regulates Casz1 by targeting miR-599 to prevent osteoarthritis chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(1):120-131.
[26] 周俊丽,王小俊,王海焦,等.新型医用敷料治疗糖尿病足溃疡疗效比较的网状Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(16):2562-2569.
[27] 邓晓慧,张增增,张执华,等.间充质干细胞外泌体基因修饰microRNA治疗糖尿病足的机制及应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究, 2022,26(31):5076-5084.
[28] JIN Y, MENG M, ZHANG Y, et al. Comparative study on the efficacy of PRP gel and UC-MSCs gel as adjuvant therapies in the treatment of DFU wounds. Skin Res Technol. 2024;30(1):e13549.
[29] LO ZJ, HARISH KB, TAN E, et al. A feasibility study on the efficacy of a patient-owned wound surveillance system for diabetic foot ulcer care (ePOWS study). Digit Health. 2023;9:20552076231205747.
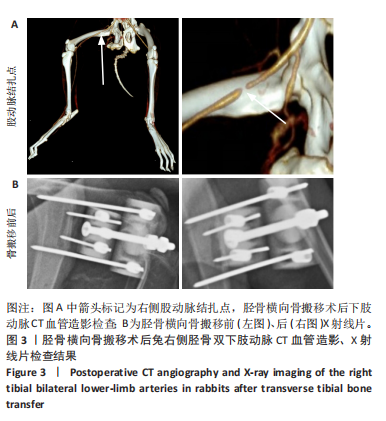
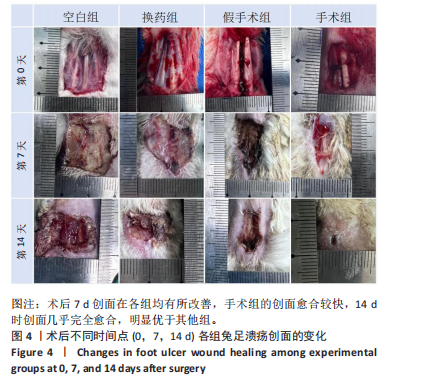
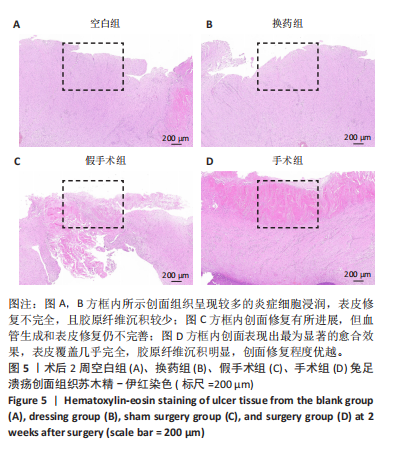
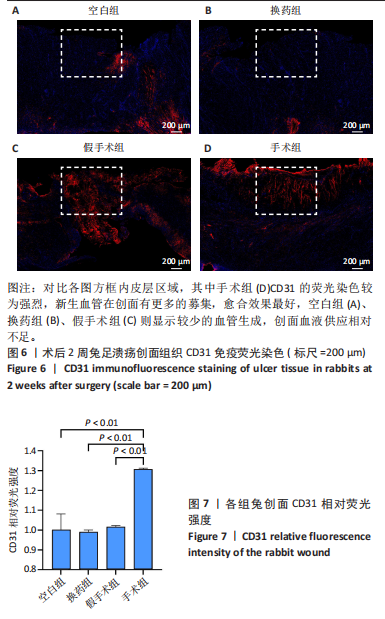
[30] 郭国庆,陈林海,郭明君,等.胫骨横向骨搬移技术对糖尿病兔下肢溃疡创面促细胞趋化水平的研究[J].中国医疗美容,2021, 11(7):50-53.
[31] WANG F, ZHANG X, ZHANG J, et al. Recent advances in the adjunctive management of diabetic foot ulcer: Focus on noninvasive technologies. Med Res Rev. 2024;44(4):1501-1544.
[32] 刘星余,刘日光,李光第,等.内源性竞争RNA调控骨性关节炎的发生[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(28):4559-4565.
[33] WANG XF, YU CQ, YOU ZH, et al. A feature extraction method based on noise reduction for circRNA-miRNA interaction prediction combining multi-structure features in the association networks. Brief Bioinform. 2023;24(3):bbad111.
[34] JIANG Z, JIANG Y. Circular RNA CircPDS5B impairs angiogenesis following ischemic stroke through its interaction with hnRNPL to inactivate VEGF-A. Neurobiol Dis. 2023;181:106080.
|