中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (9): 1913-1922.doi: 10.12307/2025.160
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的热点问题及应用前景
余 帅,刘家伟,朱 彬,潘 檀,李兴龙,孙广峰,于海洋,丁 亚,王宏亮
- 蚌埠医学院附属阜阳市人民医院骨科关节及创伤病区,安徽省阜阳市 236000
-
收稿日期:2024-02-02接受日期:2024-03-16出版日期:2025-03-28发布日期:2024-10-11 -
通讯作者:王宏亮,安徽省阜阳市人,主任医师,蚌埠医学院附属阜阳市人民医院骨科关节及创伤病区,安徽省阜阳市 236000 丁亚,安徽省六安市人,硕士,主治医师,蚌埠医学院附属阜阳市人民医院骨科关节及创伤病区,安徽省阜阳市 236000 -
作者简介:余帅,男,1999年生,河南省许昌市人,汉族,医师。 刘家伟,男,河南省安阳市人,汉族,医师。 -
基金资助:2022年安徽省脊柱畸形临床医学研究中心“医疗创新基金”项目(AHJZJX-GG2022-003),项目负责人:王宏亮;2022年安徽医科大学校科研基金立项资助项目(2022xkj084),项目负责人:丁亚;2022年度蚌埠医学院科研课题计划(2022byzdl70)项目负责人:朱彬;2020年度第二批蚌埠医学院科研项目计划(2020byzd352),项目负责人:潘檀
Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis
Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang
- Department of Orthopedics, Joint and Trauma, Fuyang People’s Hospital, Bengbu Medical University, Fuyang 236000, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2024-02-02Accepted:2024-03-16Online:2025-03-28Published:2024-10-11 -
Contact:Wang Hongliang, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Joint and Trauma, Fuyang People’s Hospital, Bengbu Medical University, Fuyang 236000, Anhui Province, China Ding Ya, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, Joint and Trauma, Fuyang People’s Hospital, Bengbu Medical University, Fuyang 236000, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Yu Shuai, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Joint and Trauma, Fuyang People’s Hospital, Bengbu Medical University, Fuyang 236000, Anhui Province, China Liu Jiawei, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, Joint and Trauma, Fuyang People’s Hospital, Bengbu Medical University, Fuyang 236000, Anhui Province, China Yu Shuai and Liu Jiawei contributed equally to this article. -
Supported by:“Medical Innovation Fund” Project of Anhui Spine Malformation Clinical Medical Research Center in 2022, No. AHJZJX-GG2022-003 (to WHL); Scientific Research Fund Project of Anhui Medical University in 2022, No. 2022xkj084 (to DY); Scientific Research Project of Bengbu Medical University in 2022, No. 2022byzdl70 (to ZB); The Second Batch of Scientific Research Project Plan of Bengbu Medical University in 2020, No. 2020byzd352 (to PT)
摘要:
文题释义:
小分子药物:主要是指分子质量小于1 kD的有机化合物,小分子药物结构具有良好的空间分散性,其通常是信号传导抑制剂,能够特异性地阻断肿瘤生长、增殖过程中所必需的信号传导通路,从而达到治疗的目的。骨关节炎:一种非炎症性的退行性关节病,表现为关节疼痛、僵硬,特别是长时间活动后。该病好发于50岁以上人群,女性多于男性,该病不同程度地影响中老年患者的生活质量。
摘要
背景:骨关节炎的病理生理过程中存在多种蛋白、信号通路及炎症递质等的参与,开发针对这些蛋白、信号通路及炎症递质等的小分子药物,可有效延缓骨关节炎的进展并改善其临床表现。
目的:基于骨关节炎的发病机制,对小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的研究进展作一综述。
方法:检索PubMed、中国知网和万方数据库,英文检索词为“osteoarthritis,arthritis,osteoarthrosis,degenerative,arthritides,deformans,small molecule drugs,small molecule inhibitors,small molecule agents”,中文检索词为“骨关节炎,小分子药物,小分子抑制剂”,按纳入和排除标准共纳入68篇文献进行总结。
结果与结论:①目前对于骨关节炎发病机制的研究尚不明确,骨关节炎的发生发展与蛋白质、细胞因子及信号转导通路的关系较为密切,因此其治疗机制较为复杂,当前通过小分子药物靶向骨关节炎相关的蛋白质、细胞因子及信号转导通路成为一大研究热点。②小分子药物通常具有明确的细胞内或细胞外靶点和疗效,包括增强软骨修复、抑制关节退化、减轻炎症和缓解疼痛,另外一些抗骨关节炎的小分子药物在促进干细胞软骨分化和软骨基质重建方面显示出前景。③目前对于小分子药物靶向骨关节炎的病理生理过程从而延缓骨关节炎的进展,还处于实验性阶段,但这些小分子药物在实验过程中大部分都表现出预期的结果,目前并无相关研究说明小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的疗效。④小分子药物治疗骨关节炎在基础实验阶段已经达到了预期的实验结果,大量研究表明,小分子药物可以靶向抑制引起骨关节炎的特定蛋白质、细胞因子及信号转导通路,从而治疗骨关节炎,但其安全性和有效性等问题还需要进一步的基础和临床研究进行验证,这一过程需要更多的学者进行探索和研究。⑤目前国内外有许多学者针对骨关节炎的治疗做出了贡献,比起传统治疗方式而言,小分子药物在基础实验阶段表现出更好的疗效和安全性,有望成为未来骨关节炎治疗的新兴方法,为骨关节炎患者摆脱痛苦。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
余 帅, 刘家伟, 朱 彬, 潘 檀, 李兴龙, 孙广峰, 于海洋, 丁 亚, 王宏亮. 小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的热点问题及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922.
Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922.
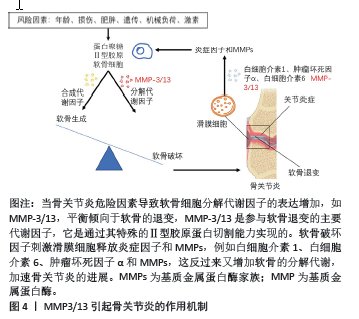
2.1 基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂 基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinases,MMP)是一个大家族,因其需要Ca2+,Zn2+等金属离子作为辅助因子而得名,MMP主要负责切割各种细胞外基质蛋白并参与软骨细胞外基质的降解和重塑。MMP包含25种亚型,编号分别为MMP1-25,其中MMP1,MMP2,MMP3,MMP8,MMP9,MMP10,
MMP13和MMP14,主要参与骨关节炎中细胞外基质的周转和关节软骨的相关破坏。尤其是MMP3/13起主导作用,MMP3/13可以降解关节软骨和骨骼中的Ⅱ型胶原[10]。值得注意的是,MMP3/13在骨关节炎患者的退行性软骨中特异性表达,但在正常成人软骨中不表达。因此,开发选择性MMP抑制剂是治疗骨关节炎的潜在策略。MMP3/13引起骨关节炎的作用机制见图4。
经过以往研究,目前有以下针对MMP的潜在小分子药物,这为骨关节炎的治疗带来了新的希望。Maresin-1是二十二碳六烯酸的代谢产物,具有潜在的抗炎作用,LU等[11]研究了Maresin-1对骨关节炎大鼠是否具有治疗作用,最终研究发现Maresin-1处理的骨关节炎大鼠中MMP13的表达降低,Maresin-1对骨关节炎大鼠具有一定的治疗效果。WANG等[12]利用白细胞介素1β刺激大鼠软骨细胞,观察到MMP13表达升高,随后该团队用芒果苷进行大鼠关节腔内注射,最终结果表明芒果苷可以降低骨关节炎大鼠模型中MMP13的表达,并且可以抑制软骨降解,表明芒果苷在治疗骨关节炎方面具有保护作用。Aflapin,也称为AprèsFlex,是作为齿叶乳香胶树脂增强生物利用度提取物而开发的,KARLAPUDI等[13]招募了35名受试者并随机分为安慰剂组和Aflapin组,受试者接受30 mg的Aflapin或安慰剂,使用标准工具评估所有受试者的疼痛和身体机能,并且还评估了软骨生物标志物MMP3在该过程中的变化,通过该项调查研究,最终证实Aflapin治疗骨关节炎具有一定临床疗效,并且还可以显著降低MMP3的表达。齐墩果酸(OLA)是五环三萜类化合物之一,是一种潜在的治疗骨关节炎的新型化合物,然而作用机制尚不清楚,MA等[14]通过体内和体外实验研究了OLA对细胞外基质降解的抗性机制及其在改善骨关节炎中的保护作用,研究发现OLA可以降低MMP3和MMP13的表达,抑制炎性细胞因子和软骨标志物水平,从而阻碍软骨的病理过程。染料木黄酮是一种天然存在的异黄酮,已被证明具有多种生物学效应,LOPEZ等[15]研究了染料木黄酮是否可以作为骨关节炎治疗的潜在因素,该团队让骨关节炎小鼠应用染料木黄酮12周来检测骨关节炎相关指标,最终研究表明染料木黄酮通过降低骨关节炎小鼠中MMP13 的表达从而延缓骨关节炎的进展。关于MMP抑制剂在骨关节炎治疗中的作用数据有限,研究者们需要进行更深一步临床研究,以尽可能避免MMP抑制剂所带来的不良反应,未来MMP抑制剂可能会为骨关节炎的治疗带来突破,见表1。
2.2 血小板反应蛋白整合素金属肽酶抑制剂 血小板反应蛋白整合素金属肽酶(a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs,ADAMTS)是一种分泌的锌内肽酶,其机制是降解蛋白聚糖,降低软骨细胞的稳定性,引起剧烈的形态变化,破坏软骨细胞,其中ADAMTS-4和ADAMTS-5是两个关键因素,ADAMTS-4/5是识别和缓解骨关节炎发展的一个有前途的靶点[16]。ADAMTS-4/5抑制剂已被证明可以减少骨关节炎模型中的滑膜关节损伤。因此,研究者们建立了活性ADAMTS-4/5的药物开发计划。ADAMTS-4/5引起骨关节炎的作用机制见图5。

查阅相关文献,文章归纳出以下靶向ADAMTS的小分子抑制剂。HO等[17]利用炎症刺激猪和人软骨细胞模型,以研究Cm-02和Ck-02对抗骨关节炎作用的分子机制,最终发现在经过炎症刺激的软骨细胞中Cm-02和Ck-02抑制了ADAMTS的表达,该项研究结果表明,Cm-02和Ck-02都具有强大的抗炎活性和保护骨关节炎细胞模型中软骨的能力,Cm-02和Ck-02具有进一步开发为用于骨关节炎治疗的潜力。SIEBUHR等[18]研究了一种新型抑制ADAMTS-5的纳米抗体(M6495)对体外软骨转换的影响,结果表明M6495通过剂量依赖方式抑制ADAMTS-5介导的软骨降解和抑制体外软骨退化,从而显示出软骨保护作用,并且纳米抗体M6495在健康男性受试者中进行了测试,显示出可接受的安全性和耐受性[19]。葛根素是从药用植物葛根中分离得到的异黄酮,MA等[20]研究了葛根素在大鼠骨关节炎模型中的抗炎和抗基质降解作用及其对关节的保护作用,该团队利用前交叉韧带横断术建立大鼠骨关节炎模型,手术诱导后2周,每日通过管饲法给予葛根素8周,最终发现葛根素降低了骨关节炎大鼠模型中ADAMTS-5的表达,抑制炎症因子的产生,增加Ⅱ型胶原含量,改变血清骨关节炎软骨降解及骨转换生物标志物的表达,该团队推测葛根素可以实现骨关节炎损伤的恢复。CLEMENT-LACROIX等[21]报道了GLPG1972/S201086的发现,这是一种新型的选择性口服ADAMTS-5抑制剂,已在膝骨关节炎患者中进行了Ⅱ期临床试验,研究结果表明GLPG1972/S201086可通过靶向抑制ADAMTS-5来延缓骨关节炎的进展,该药物有望成为骨关节炎治疗的方法。ZHAO等[22]发现了一种新型有效的ADAMTS-4/5抑制剂具有治疗骨关节炎的作用,即异吲哚啉酰胺,该团队发现在大鼠内侧半月板不稳定术的骨关节炎模型中,异吲哚啉酰胺显著抑制软骨变性,并以剂量依赖的方式改善关节损伤评分,这为骨关节炎的治疗提供了新方法。上述研究证实,靶向ADAMTS的小分子抑制剂在实验性骨关节炎中显示出可喜的结果,见表2。


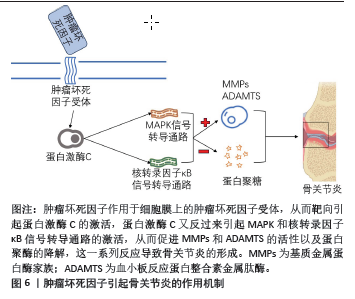
2.3 肿瘤坏死因子抑制剂 肿瘤坏死因子来源于巨噬细胞、成纤维细胞及软骨细胞等,是软骨基质降解的重要介质。开发靶向肿瘤坏死因子的小分子抑制剂也是骨关节炎治疗的一种合理策略[23-26]。肿瘤坏死因子引起骨关节炎的作用机制见图6。
根据以往研究,文章总结出下列几种靶向肿瘤坏死因子的小分子抑制剂。LIU等[27]从猪关节中分离出软骨细胞,并使用肿瘤坏死因子激活猪软骨细胞作为筛选工具,旨在合成和鉴定具有免疫调节作用的小分子抑制剂作为骨关节炎的治疗方法,最终研究发现,苯甲酰胺是肿瘤坏死因子刺激的猪软骨细胞中炎症递质的有效抑制剂,从而可以延缓骨关节炎的进展,苯甲酰胺抑制肿瘤坏死因子诱导的几种聚集酶的表达,并阻止肿瘤坏死因子介导的胶原Ⅱ减少,因此苯甲酰胺 可能是骨关节炎治疗的潜在疾病修饰药物。AZ-628是一种新型Raf抑制剂,在血管重塑和肿瘤疾病中具有好的治疗效果,GONG等[28]研究发现AZ-628可以通过抑制肿瘤坏死因子来抑制软骨细胞死亡和炎症,降低破骨细胞形成和骨吸收,从而减缓的软骨下骨的变化,逆转小鼠骨关节炎的进展,该研究结果表明AZ-628可通过抑制软骨细胞坏死性凋亡和调节破骨细胞形成来治疗骨关节炎。红花黄是红花的主要活性成分,红花是一种中药,具有抗凝、抗氧化、抗炎等多种药理作用,近年来红花黄介导的抗炎作用越来越受到关注,尽管红花黄是一种有效的炎症反应抑制剂,但其对关节软骨细胞的影响尚未在细胞或分子水平上进行研究,WANG等[29]研究了红花黄是否对肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的软骨细胞炎症反应和相关机制具有软骨保护作用,最终研究结果表明红花黄恢复了肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的各种炎症通路的下调,此外它通过抑制肿瘤坏死因子α来恢复软骨细胞增殖。CHEN等[30]研究发现,黄腐酚在内侧半月板不稳定术的小鼠模型中对骨关节炎的进展具有抑制作用,该团队又进行小鼠软骨细胞实验表明,黄腐酚可以显著降低小鼠骨关节炎模型中肿瘤坏死因子的表达,该实验表明黄腐酚可能是减缓和延缓骨关节炎发展的候选药物。简化α2-巨球蛋白作为一种新型的肿瘤坏死因子抑制剂,其机制是通过溶酶体降解来缓解炎症反应,该药对肿瘤坏死因子具有有效的生物活性抑制作用,ZHENG等[31]经过研究发现当在体内慢性炎症损伤中给药时,简化α2-巨球蛋白具有良好的治疗效果,其可以改善软骨变性从而缓解骨关节炎的炎症反应,这表明简化α2-巨球蛋白可能是骨关节炎治疗中靶向抑制肿瘤坏死因子的有前途的治疗方案。肿瘤坏死因子在骨关节炎中起着重要作用,因此希望未来更多靶向肿瘤坏死因子小分子抑制剂用于骨关节炎的临床治疗,见表3。

2.4 白细胞介素1β抑制剂 白细胞介素1β对骨关节炎具有全方位的作用,在改变正常软骨细胞结构和功能、促进软骨细胞凋亡、降解软骨细胞基质、参与滑脱膜性炎症性疾病及影响骨代谢等方面发挥着重要作用。因此,开发靶向白细胞介素1β的小分子抑制剂将是一个非常合适的选择[32-33]。
通过文献检索,文章总结出了以下几种靶向白细胞介素1β的小分子药物。丁酸盐是一种短链脂肪酸,被认为是结肠细胞维持肠道稳态和功能的主要能量来源,PIROZZI等[34]在存在或不存在丁酸盐的情况下,用白细胞介素1β刺激小鼠软骨细胞24 h,随后进行RT-PCR和Western blot分析,以评估炎症递质和结构蛋白的表达,结果发现,丁酸盐降低了白细胞介素1β刺激的软骨细胞中典型促炎递质(Nos2、环氧化酶2、白细胞介素6)、促炎脂肪因子(脂质运载蛋白2和nesfatin-1)和黏附分子(VCAM-1和ICAM-1)的表达,并且抑制了炎症信号通路,综上所述,该实验数据证明丁酸盐作为治疗软骨细胞炎症和软骨退行性过程的多靶点方法中的潜在应用。海葵素是一种从是从包括铁线莲在内的草药中分离出来的天然小分子,已被证明具有抗炎特性,WANG等[35]研究了海葵素是否可以通过抑制白细胞介素1β通路激活来减弱骨关节炎的进展,在10周龄雄性小鼠中进行内侧半月板不稳定术,然后将海葵素注射到关节囊中,持续8,12周,将白细胞介素1β攻击的人关节软骨细胞和软骨外植体用海葵素处理,最终发现海葵素在体外和体内都延迟了关节软骨变性,海葵素处理还减轻了用白细胞介素1β离体处理的人软骨外植体中的蛋白多糖损失,海葵素是一种有效的骨关节炎保护分子,它通过抑制白细胞介素1β激活来部分抑制细胞外基质丢失和软骨细胞肥大,从而延缓骨关节炎进展。OHZONO等[36]发现腹膜内注射帕比司他可以抑制关节内注射白细胞介素1β诱导的骨关节炎发病介质的表达,在小鼠骨关节炎模型中,帕比司他降低了软骨、滑膜和软骨下骨组织学变化的严重程度,并改善了疼痛行为。综上所述,靶向白细胞介素1β的小分子抑制剂是一种很有前途的骨关节炎治疗方法,与白细胞介素1β相关的小分子抑制剂分为与白细胞介素1β直接结合的抑制剂和与白细胞介素1β受体联合使用的小分子抑制剂,不同的类别呈现出不同的机制、常规给药和治疗效果,因此需要进行更多的研究来确定其是否存在差异。
2.5 Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路抑制剂 Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路是调节发育、生长、稳态和疾病中的关键生物过程,尤其是在关节和骨骼中。Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路在软骨细胞中上调可促进其增殖和肥大,并对软骨细胞的稳态产生负面影响。关节软骨中Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路的过度激活与骨关节炎的发生和严重程度有显著关系,并且越来越多的证据表明该通路在骨关节炎的发生发展过程中具有一定的作用。因此,抑制Wnt/β-Catenin信号已被探索作为骨关节炎的潜在治疗方法[37-39]。
针对以往研究,主要有以下几种靶向Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路的小分子药物。XAV-939是一种Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的小分子抑制剂,LIETMAN等[40]将小鼠进行了内侧半月板不稳定术,并在小鼠关节内注射XAV-939进行治疗,旨在检验Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对滑膜成纤维细胞和关节软骨细胞的影响以及抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对骨关节炎疾病严重程度的治疗作用,最终结果表明,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在小鼠滑膜成纤维细胞以及骨关节炎衍生的人滑膜成纤维细胞中高度激活;XAV-939改善了体内软骨退行性变和滑膜炎从而减轻骨关节炎的严重程度。盐霉素是一种抗肿瘤药物,可以改善肿瘤免疫微环境,研究表明其在胃肠道肉瘤、骨肉瘤和结直肠癌中具有显著的抗癌活性[41-42]。CHEN等[43]发现盐霉素对小鼠软骨细胞没有细胞毒性,并且对小鼠软骨细胞和软骨外植体具有保护作用,在内侧半月板不稳定术诱导的小鼠骨关节炎模型中,盐霉素降低了骨关节炎相关变化的严重程度,并延迟了软骨破坏、软骨下骨硬化和骨赘形成。从机制上讲,低盐霉素浓度通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,从而诱导软骨细胞的合成代谢并抑制分解代谢,研究结果表明,盐霉素可能是一种潜在的针对骨关节炎发病机制的疾病改善疗法。SM04690是一种首创的小分子Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制剂,用于局部关节内注射治疗膝关节骨关节炎,体外研究表明,SM04690能有效抑制Wnt/β-catenin通路[44],YAZICI等[45]招募了61名受试者评估SM04690作为新型Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制剂对骨关节炎治疗的安全性、药代动力学和探索性疗效,最终研究表明,SM04690具有安全且耐受性良好的优点,可有效改善骨关节炎疼痛。综合上述研究发现,通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的激活可以对骨关节炎的治疗产生一定的帮助,并且有越来越多的证据表明Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制剂在骨关节炎中的病理作用,因此抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路已被探索成为骨关节炎具有前途的治疗方法。
2.6 核转录因子κB信号通路抑制剂 核转录因子κB是一种诱导转录因子,在免疫反应、炎症反应、细胞分化以及正常细胞和恶性细胞的存活中起着重要作用,关节炎、癌症和自身免疫性疾病等多种病变均存在核转录因子κB信号通路功能失调的现象。它在骨关节炎中起重要作用,骨关节炎的炎症过程和机械负荷可以激活核转录因子κB信号通路,加速软骨细胞的分解代谢。因此,核转录因子κB信号通路包括协同因子和下游效应因子,被认为是骨关节炎治疗干预的潜在靶点[46-48]。
以下靶向核转录因子κB信号通路的小分子药物可为骨关节炎治疗提供新的思路。Nepetin是一种具有细胞外基质和炎症调节功能的小型天然化合物,XU等[49]探讨了Nepetin对小鼠软骨细胞炎症的治疗作用,在软骨细胞中,用Nepetin处理可抑制促炎细胞因子和介质的过表达,经研究发现Nepetin通过抑制软骨细胞中的核转录因子κB信号通路,从而对小鼠骨关节炎模型展现出保护和治疗作用,因此,上述研究提示Nepetin在骨关节炎中具有新的潜在治疗选择。SC75741是一种新型的核转录因子κB抑制剂,WENG等[50]研究了核转录因子κB抑制剂SC75741在骨关节炎模型中的治疗潜力,该团队用SC75741处理骨关节炎小鼠模型48 h后发现核转录因子κB信号通路的表达显著降低,最终研究证明了核转录因子κB信号通路在骨关节炎进展中的作用,以及SC75741作为核转录因子κB信号通路抑制剂对骨关节炎的治疗潜力。奈拉替尼作为一种具有抗炎和抗肿瘤特性的小分子化合物[51],是一种非常有效的白细胞介素1β诱导的软骨细胞炎症和合成代谢抑制剂,QIU等[52]通过研究奈拉替尼对软骨细胞的影响,最终发现奈拉替尼可以抑制核转录因子κB信号通路来减少炎症,该团队还研究了奈拉替尼对破骨细胞的影响,结果显示奈拉替尼在体外也是一种抗破骨细胞药物,该药物可以抑制核转录因子κB信号通路,从而抑制破骨细胞生成,体内动物实验结果支持了体外实验的结论。奈拉替尼同时抑制内侧半月板破坏诱导的软骨退化和破骨细胞形成,证明奈拉替尼具有保护软骨和抑制破骨细胞形成的双重作用,这表明奈拉替尼可以成为治疗骨关节炎的全新潜在策略。综合上述研究可知,对于核转录因子κB信号通路的小分子抑制剂在一定程度上可以缓解骨关节炎的症状,因此开发更为安全有效的核转录因子κB信号通路抑制剂已经成为骨关节炎的潜在治疗方法。
2.7 转化生长因子β信号通路抑制剂 转化生长因子β已被证明是软骨和骨形成的关键因素之一,研究发现转化生长因子β过表达会促进骨关节炎的发生与发展[53]。因此,靶向抑制转化生长因子β是治疗骨关节炎发生和发展的潜在机制。
通过对以往研究的探索,以下几种小分子药物可能成为未来骨关节炎治疗的新希望。Noggin是骨形态发生蛋白的拮抗剂,据报道可通过保护软骨和防止病理性软骨下骨重塑来有效缓解骨关节炎进展,然而,其基本机制尚未完全阐明,WEN等[54]研究了Noggin是否可以直接与转化生长因子β相互作用,结果表明Noggin可以拮抗转化生长因子β,从而对骨关节炎有一定的疗效,该团队还发现Noggin在拮抗转化生长因子β的同时不抑制间充质干细胞增殖和软骨生成;因此,其对骨关节炎治疗似乎很有希望 。TissueGene-C是一种用于治疗骨关节炎的新型细胞和基因疗法,由人同种异体软骨细胞和经过改造的过表达转化生长因子β1的辐照细胞组成[55],LEE等[56]利用骨关节炎模型,研究TissueGene-C是否可以改善大鼠骨关节炎症状和软骨结构,结果表明,TissueGene-C
为骨关节炎模型提供了疼痛缓解和软骨结构改善,使用TissueGene-C的细胞疗法可能是靶向骨关节炎的潜在致病机制、减轻疼痛、改善功能和创造促合成代谢微环境的有前途的策略,这种环境支持软骨结构再生,值得在未来的临床试验中进一步评估。
2.8 组织蛋白酶K抑制剂 组织蛋白酶K是半胱氨酸蛋白酶家族的一部分,其参与体内多种生理过程,包括骨吸收过程中Ⅰ型胶原蛋白和弹性蛋白的降解。组织蛋白酶K的水平变化与多种病理状况有关,主要与骨和软骨退化有
关[57]。经过长期研究人们发现,在骨关节炎中组织蛋白酶K呈现出高表达状态,开发靶向抑制组织蛋白酶K的小分子药物有助于延缓骨关节炎的发展。
目前研究已经发现的靶向组织蛋白酶K的小分子抑制剂主要有以下几种。MIV-711是一种新型选择性组织蛋白酶K抑制剂,已经被证明在骨关节炎模型中对骨骼和软骨有益,CONAGHAN等[58]评估了MIV-711对骨关节炎患者的疗效,该团队招募了244例患有骨关节炎的参与者分为注射MIV-711组和注射安慰剂组,结果显示与安慰剂相比,MIV-711显著降低了股骨内侧软骨变薄,并显著降低了骨和软骨生物标志物水平,该研究表明MIV-711通过抑制组织蛋白酶K从而有助于骨关节炎的治疗。L-006235是选择性组织蛋白酶K抑制剂,NWOSU等[59]研究了L-006235对骨关节炎模型中疼痛行为和关节病理学的影响,研究表明用L-006235口服治疗大鼠骨关节炎模型显著减弱了该模型中疼痛行为和关节病理学的发展。PELLETIER等[60]探讨了雷奈酸锶在治疗剂量下对关节结构变化和主要病理生理途径的改善作用,该团队对狗采取了前交叉韧带横断术,手术后4周每天接受25,50或
75 mg/kg的雷奈酸锶或安慰剂治疗12周,雷奈酸锶治疗在所有测试剂量下均显著减少了骨关节炎软骨病变,并且雷奈酸锶在骨关节炎软骨中显著降低了组织蛋白酶K基因的表达。这些研究表明,在骨关节炎中通过靶向抑制组织蛋白酶K可以保护软骨下骨的完整性以及防止软骨退化,这为骨关节炎患者提供了潜在治疗靶点。
2.9 靶向骨关节炎的激活剂
2.9.1 成纤维细胞生长因子 成纤维细胞生长因子信号通路参与多种生理过程,如细胞增殖、迁移和分化,成纤维细胞生长因子信号通路在骨骼和软骨发育中也起着关键作用。既往研究表明,成纤维细胞生长因子1,2,7,8,9,18和23是与骨关节炎发病机制相关的主要因素,尤其是成纤维细胞生长因子18。在肌肉骨骼系统中,成纤维细胞生长因子18参与软骨的发育和成熟,具有增强成熟软骨再生和修复的功。Sprifermin是一种有效的疾病修饰性骨关节炎药物,它是一种重组人成纤维细胞生长因子18蛋白分子,它可以促进关节软骨细胞的增殖和细胞外基质的合成,以剂量依赖性的方式增加软骨的厚度,并且也可以抑制蛋白水解酶的活性,显著缓解软骨的变性[61-63],GIGOUT等[64]证明Sprifermin具有促进软骨生长和修复软骨的潜力,从而延缓骨关节炎的进展并改善患者的病情,虽然Sprifermin可以被视为骨关节炎患者的潜在治疗药物,但其有效性和安全性仍需要更多的证据,综合评价Sprifermin在促进软骨修复中的具体作用,并评价其潜在的分子机制,有利于Sprifermin的进一步改进。
2.9.2 腺苷酸激活蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)信号通路 AMPK信号通路是一种丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,它是一种高度保守的能量传感器,可对真核细胞中ATP水平的变化作出反应。研究表明,AMPK在骨关节炎患者中的反应性降低,这会引起关节自我修复和再生能力的缺失,从而加速骨关节炎进展[65]。二甲双胍已被证明可以激活AMPK信号通路,它是能量平衡和代谢的主要调节剂,LI等[66]将10周龄的雄性C57野生小鼠进行内侧半月板不稳定术,旨在确定二甲双胍对骨关节炎发生和发展的影响,结果发现二甲双胍上调了关节软骨组织中AMPK的表达,以及在内侧半月板不稳定术后导致软骨退化显著减少;在AMPK信号通路敲除的小鼠中未观察到二甲双胍对骨关节炎发育的保护作用,表明二甲双胍的软骨保护作用是由AMPK信号传导介导的。Sestrin2是一种新型应激诱导蛋白,被证明可以减少活性氧的产生,SUN等[67]研究了Sestrin2对骨关节炎大鼠模型中线粒体的影响,结果显示Sestrin2的过表达减轻了骨关节炎大鼠的疼痛行为,此外Sestrin2的过表达增加了AMPK信号通路的活性,并显著恢复了线粒体功能,这表明Sestrin2通过增加AMPK信号通路的活性而延缓了骨关节炎的症状。姜黄素是一种从姜黄根茎中提取的多酚色素,它可以缓解患者的炎症和退行性疾病,JIN等[68]建立了大鼠膝关节的骨关节炎模型和骨关节炎软骨细胞模型,以验证姜黄素对骨关节炎的作用和机制,结果发现,姜黄素对骨关节炎的软骨保护作用是由AMPK信号通路介导,姜黄素可能作为骨关节炎治疗的潜在新药。这些研究结果表明,靶向激活AMPK信号通路的小分子药物有助于骨关节炎治疗,AMPK信号通路可能会是骨关节炎治疗的下一个靶点,这需要更进一步的研究和试验。

| [1] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组,中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨关节炎学组,湘雅医院国家老年疾病临床医学研究中心,等.中国骨关节炎诊疗指南(2021年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(18):1291-1314. [2] DA CB, PEREIRA TV, SAADAT P, et al. Effectiveness and safety of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and opioid treatment for knee and hip osteoarthritis: network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2021;375:n2321. [3] WANG J, ZENG J, LIU Z, et al. Promising strategies for transdermal delivery of arthritis drugs: microneedle systems. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(8):1736. [4] JACKSON RW. Memories of the early days of arthroscopy: 1965-1975. The formative years. Arthroscopy. 1987;3(1):1-3. [5] KRUEGER FJ. A vitallium replica arthroplasty on the shoulder; a case report of aseptic necrosis of the proximal end of the humerus. Surgery. 1951; 30(6):1005-1011. [6] COVENTRY MB. Osteotomy of the upper portion of the tibia for degenerative arthritis of the knee. A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1965;47:984-990. [7] 中华医学会骨科学分会.骨关节炎诊治指南(2007年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2007,27(10):793-796. [8] CHERIAN JJ, KAPADIA BH, MCELROY MJ, et al. Knee osteoarthritis: does transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation work? Orthopedics. 2016;39(1): e180-e186. [9] SHI Y, HU X, CHENG J, et al. A small molecule promotes cartilage extracellular matrix generation and inhibits osteoarthritis development. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1914. [10] HU Q, ECKER M. Overview of MMP13 as a promising target for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1742. [11] LU J, FENG X, ZHANG H, et al. Maresin-1 suppresses IL-1beta-induced MMP13 secretion by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway and inhibiting the NF-kappaB pathway in synovioblasts of an osteoarthritis rat model with treadmill exercise. Connect Tissue Res. 2021;62(5):508-518. [12] WANG Y, GUO X, FAN X, et al. The protective effect of mangiferin on osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo study. Physiol Res. 2022;71(1):135-145. [13] KARLAPUDI V, SUNKARA KB, KONDA PR, et al. Efficacy and safety of aflapin(R), a novel boswellia serrata extract, in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a short-term 30-day randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2023;42(2):159-168. [14] MA T, RUAN H, LV L, et al. Oleanolic acid, a small-molecule natural product, inhibits ECM degeneration in osteoarthritis by regulating the Hippo/YAP and Wnt/beta-catenin pathways. Food Funct. 2023;14(22):9999-10013. [15] LOPEZ J, AL-NAKKASH L, BRODERICK TL, et al. Genistein suppresses IL-6 and MMP13 to attenuate osteoarthritis in obese diabetic mice. Metabolites. 2023;13(9):1014. [16] LI T, PENG J, LI Q, et al. The mechanism and role of ADAMTS protein family in osteoarthritis. Biomolecules. 2022;12(7):959. [17] HO YJ, LU JW, HO LJ, et al. Anti-inflammatory and anti-osteoarthritis effects of Cm-02 and Ck-02. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;517(1):155-163. [18] SIEBUHR AS, WERKMANN D, BAY-JENSEN AC, et al. The Anti-ADAMTS-5 nanobody((R)) M6495 protects cartilage degradation Ex Vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(17):5992. [19] LI H, WEI Y, YANG Z, et al. Safety, Tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of alirocumab in healthy chinese subjects: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, ascending single-dose study. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2020;20(5):489-503. [20] MA TW, WEN YJ, SONG XP, et al. Puerarin inhibits the development of osteoarthritis through antiinflammatory and antimatrix-degrading pathways in osteoarthritis-induced rat model. Phytother Res. 2021;35(5):2579-2593. [21] CLEMENT-LACROIX P, LITTLE CB, SMITH MM, et al. Pharmacological characterization of GLPG1972/S201086, a potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of ADAMTS5. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):291-301. [22] ZHAO P, LIU D, SONG C, et al. Discovery of isoindoline amide derivatives as potent and orally bioavailable ADAMTS-4/5 inhibitors for the treatment of osteoarthritis. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2022;5(7):458-467. [23] ZHONG G, LONG H, CHEN F, et al. Oxoglaucine mediates Ca(2+) influx and activates autophagy to alleviate osteoarthritis through the TRPV5/calmodulin/CAMK-II pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 2021;178(15):2931-2947. [24] ZHANG Y, LIN Z, CHEN D, et al. CY-09 attenuates the progression of osteoarthritis via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;553:119-125. [25] ZHANG X, DONG Y, DONG H, et al. Telmisartan mitigates TNF-alpha-Induced type II collagen reduction by upregulating SOX-9. ACS Omega. 2021;6(17): 11756-11761. [26] ALLAEYS I, RIBEIRO DVF, BOURGOIN SG, et al. Human inflammatory neutrophils express genes encoding peptidase inhibitors: production of elafin mediated by NF-kappaB and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta. J Immunol. 2021;206(8):1943-1956. [27] LIU FC, HUANG HS, HUANG CY, et al. A benzamide-linked small molecule HS-Cf inhibits TNF-alpha-induced interferon regulatory factor-1 in porcine chondrocytes: a potential disease-modifying drug for osteoarthritis therapeutics. J Clin Immunol. 2011;31(6):1131-1142. [28] GONG Y, QIU J, YE J, et al. AZ-628 delays osteoarthritis progression via inhibiting the TNF-alpha-induced chondrocyte necroptosis and regulating osteoclast formation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;111:109085. [29] WANG C, GAO Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Safflower yellow alleviates osteoarthritis and prevents inflammation by inhibiting PGE2 release and regulating NF-kappaB/SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathways. Phytomedicine. 2020;78:153305. [30] CHEN X, LI Z, HONG H, et al. Xanthohumol suppresses inflammation in chondrocytes and ameliorates osteoarthritis in mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;137:111238. [31] ZHENG W, ZHOU T, ZHANG Y, et al. Simplified alpha(2)-macroglobulin as a TNF-alpha inhibitor for inflammation alleviation in osteoarthritis and myocardial infarction therapy. Biomaterials. 2023,301:122247. [32] WANG F, LIU J, CHEN X, et al. IL-1beta receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) combined with autophagy inducer (TAT-Beclin1) is an effective alternative for attenuating extracellular matrix degradation in rat and human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):171. [33] CONAGHAN PG, COOK AD, HAMILTON JA, et al. Therapeutic options for targeting inflammatory osteoarthritis pain. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(6):355-363. [34] PIROZZI C, FRANCISCO V, GUIDA FD, et al. Butyrate Modulates Inflammation in Chondrocytes via GPR43 Receptor. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(1): 228-243. [35] WANG Z, HUANG J, ZHOU S, et al. Anemonin attenuates osteoarthritis progression through inhibiting the activation of IL-1beta/NF-kappaB pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(12):3231-3243. [36] OHZONO H, HU Y, NAGIRA K, et al. Targeting FoxO transcription factors with HDAC inhibitors for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(2):262-271. [37] CHERIFI C, MONTEAGUDO S, LORIES RJ. Promising targets for therapy of osteoarthritis: a review on the Wnt and TGF-beta signalling pathways. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2021;13:1759720X211006959. [38] LORIES RJ, MONTEAGUDO S. Review article: is wnt signaling an attractive target for the treatment of osteoarthritis? Rheumatol Ther. 2020;7(2):259-270. [39] HUANG J, CHEN C, LIANG C, et al. Dysregulation of the Wnt signaling pathway and synovial stem cell dysfunction in osteoarthritis development. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(7):401-413. [40] LIETMAN C, WU B, LECHNER S, et al. Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling ameliorates osteoarthritis in a murine model of experimental osteoarthritis. JCI Insight. 2018;3(3):e96308. [41] YU SM, KIM SJ. Salinomycin causes dedifferentiation via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway in rabbit articular chondrocytes. J Pharmacol Sci. 2015;127(2):196-202. [42] ZHOU J, LIU S, WANG Y, et al. Salinomycin effectively eliminates cancer stem-like cells and obviates hepatic metastasis in uveal melanoma. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):159. [43] CHEN J, LIU J, CHEN S, et al. Salinomycin alleviates osteoarthritis progression via inhibiting Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022; 112:109225. [44] DESHMUKH V, HU H, BARROGA C, et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway (SM04690) as a potential disease modifying agent for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018; 26(1):18-27. [45] YAZICI Y, MCALINDON TE, FLEISCHMANN R, et al. A novel Wnt pathway inhibitor, SM04690, for the treatment of moderate to severe osteoarthritis of the knee: results of a 24-week, randomized, controlled, phase 1 study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(10):1598-1606. [46] XU Y, ZHANG M, YANG W, et al. Nootkatone protects cartilage against degeneration in mice by inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;100:108119. [47] LEE KT, CHEN BC, LIU SC, et al. Nesfatin-1 facilitates IL-1beta production in osteoarthritis synovial fibroblasts by suppressing miR-204-5p synthesis through the AP-1 and NF-kappaB pathways. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(18):22490-22501. [48] CATHELINE SE, BELL RD, OLUOCH LS, et al. IKKbeta-NF-kappaB signaling in adult chondrocytes promotes the onset of age-related osteoarthritis in mice. Sci Signal. 2021;14(701):eabf3535. [49] XU Z, SHEN Z H, WU B, et al. Small molecule natural compound targets the NF-kappaB signaling and ameliorates the development of osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(11):7298-7307. [50] WENG PW, YADAV VK, PIKATAN NW, et al. Novel NFkappaB inhibitor SC75741 mitigates chondrocyte degradation and prevents activated fibroblast transformation by modulating miR-21/GDF-5/SOX5 signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(20):11082. [51] GUO L, SHAO W, ZHOU C, et al. Neratinib for HER2-positive breast cancer with an overlooked option. Mol Med. 2023;29(1):134. [52] QIU J, JIANG T, YANG G, et al. Neratinib exerts dual effects on cartilage degradation and osteoclast production in osteoarthritis by inhibiting the activation of the MAPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022;205:115155. [53] YAO Q, WU X, TAO C, et al. Osteoarthritis: pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):56. [54] WEN L, GAO M, HE Z, et al. Noggin, an inhibitor of bone morphogenetic protein signaling, antagonizes TGF-beta1 in a mouse model of osteoarthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021;570:199-205. [55] YOON HJ, KIM SB, SOMAIYA D, et al. Type II collagen and glycosaminoglycan expression induction in primary human chondrocyte by TGF-beta1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:141. [56] LEE H, KIM H, SEO J, et al. TissueGene-C promotes an anti-inflammatory micro-environment in a rat monoiodoacetate model of osteoarthritis via polarization of M2 macrophages leading to pain relief and structural improvement. Inflammopharmacology. 2020;28(5):1237-1252. [57] DELL’ACCIO F, CAILOTTO F. Pharmacological blockade of the WNT-beta-catenin signaling: a possible first-in-kind DMOAD. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(1):4-6. [58] CONAGHAN PG, BOWES MA, KINGSBURY SR, et al. Disease-modifying effects of a novel cathepsin k inhibitor in osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 2020;172(2):86-95. [59] NWOSU LN, GOWLER P, BURSTON JJ, et al. Analgesic effects of the cathepsin K inhibitor L-006235 in the monosodium iodoacetate model of osteoarthritis pain. Pain Rep. 2018;3(6):e685. [60] PELLETIER JP, KAPOOR M, FAHMI H, et al. Strontium ranelate reduces the progression of experimental dog osteoarthritis by inhibiting the expression of key proteases in cartilage and of IL-1beta in the synovium. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(2):250-257. [61] ANTUNES BP, VAINIERI ML, ALINI M, et al. Enhanced chondrogenic phenotype of primary bovine articular chondrocytes in fibrin-hyaluronan hydrogel by multi-axial mechanical loading and FGF18. Acta Biomater. 2020;105:170-179. [62] MULLER S, LINDEMANN S, GIGOUT A. Effects of sprifermin, IGF1, IGF2, BMP7, or CNP on bovine chondrocytes in monolayer and 3D culture. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(3):653-662. [63] HOCHBERG MC, GUERMAZI A, GUEHRING H, et al. Effect of intra-articular sprifermin vs placebo on femorotibial joint cartilage thickness in patients with osteoarthritis: the FORWARD randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019; 322(14):1360-1370. [64] GIGOUT A, GUEHRING H, FROEMEL D, et al. Sprifermin (rhFGF18) enables proliferation of chondrocytes producing a hyaline cartilage matrix. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(11):1858-1867. [65] WANG J, LI J, SONG D, et al. AMPK: implications in osteoarthritis and therapeutic targets. Am J Transl Res. 2020;12(12):7670-7681. [66] LI J, ZHANG B, LIU W X, et al. Metformin limits osteoarthritis development and progression through activation of AMPK signalling. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(5):635-645. [67] SUN J, SONG FH, WU JY, et al. Sestrin2 overexpression attenuates osteoarthritis pain via induction of AMPK/PGC-1alpha-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and suppression of neuroinflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 2022;102:53-70. [68] JIN Z, CHANG B, WEI Y, et al. Curcumin exerts chondroprotective effects against osteoarthritis by promoting AMPK/PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;151:113092. |
| [1] | 张艺博, 卢健棋, 毛美玲, 庞 延, 董 礼, 杨尚冰, 肖 湘. 类风湿关节炎与冠状动脉粥样硬化的因果关系:GWAS数据库血清代谢物和炎症因子数据[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(在线): 1-9. |
| [2] | 马 驰, 王 宁, 陈 拥, 魏志晗, 刘逢纪, 朴成哲. 3D打印个体化截骨导板结合定制钢板在开放楔形胫骨高位截骨中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [3] | 赵济宇, 王少伟. 叉头框转录因子O1信号通路与骨代谢[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [4] | 孙韫頔, 程露露, 万海丽, 常 赢, 熊雯娟, 夏 渊. 神经肌肉训练对膝骨关节炎患者疼痛和功能影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [5] | 邓柯淇, 李光第, GOSWAMI ASHUTOSH, 刘星余, 何孝勇. 基于生物信息学对骨关节炎铁超载关键基因的筛选与验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [6] | 尹 路, 蒋川锋, 陈俊杰, 易 明, 王子赫, 石厚银, 汪国友, 沈骅睿. 沙苑子苷A对关节软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [7] | 王文涛, 侯振扬, 王熠军, 徐耀增. Apelin-13抑制巨噬细胞M1极化缓解全身炎症性骨丢失[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1548-1555. |
| [8] | 陈 帅, 金 杰, 韩化伟, 田宁晟, 李志伟. 两样本孟德尔随机化分析循环炎症细胞因子与骨密度的因果关联[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1556-1564. |
| [9] | 王佩光, 张小文, 麦美斯, 黎璐茜, 黄 浩. 广义估计方程评估浮针法联合穴位埋线治疗不同分期膝骨关节炎的疗效[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [10] | 李开颖, 魏晓歌, 宋 斐, 杨 楠, 赵振宁, 王 燕, 穆 静, 马惠昇. 理筋手法调控兔骨骼肌损伤修复中瘢痕形成的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1600-1608. |
| [11] | 于经邦, 吴亚云. 非编码RNA在肺纤维化过程中的调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [12] | 王秋月, 靳 攀, 蒲 锐. 运动干预与细胞焦亡在骨关节炎中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [13] | 袁维勃, 刘 婵, 余丽梅. 肝脏类器官在肝脏疾病模型与移植治疗中的应用潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [14] | 赵嘉诚, 任诗齐, 祝 秦, 刘佳佳, 朱 翔, 杨 洋. 原发性骨质疏松潜在生物标志物的生物信息学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [15] | 陈跃平, 陈 锋, 彭清林, 陈荟伊, 董盼锋. 三七治疗骨关节炎机制:基于UHPLC-QE-MS、网络药理学及分子动力学模拟[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
1 kD的有机化合物,小分子药物具有使用广泛、理论成熟等优势。据统计,在常用药物中,小分子药物的数量可占总量的98%。小分子药物结构具有良好的空间分散性,其化学性质决定了它们良好的成药性能和药物代谢动力学性质,这些特点就使得小分子药物在药物研发过程及其它药物领域中表现出巨大优势。小分子药物通常是信号传导抑制剂,能特异性地阻断肿瘤生长、增殖过程中所必需的信号传导通路,从而达到治疗目的。与其他治疗相比,小分子药物具有成分明确、药理作用和药代动力学参数明确、不良反应少及耐受性好等诸多优点[2-3]。最重要的是,小分子药物不仅可以缓解症状,还能重建正常的软骨结构,恢复关节功能,这为彻底治愈骨关节炎带来了希望,这种特性使得小分子药物成为骨关节炎治疗领域的研究热点。
目前对于早期骨关节炎的治疗仍局限于抗炎药物或关节腔内注射玻璃酸钠等,但这些传统治疗方式并不能完全阻止骨关节炎的进展,以至于骨关节炎患者发展到终末阶段只能面临关节置换。小分子药物可以靶向特定的蛋白质和信号转导通路,目前临床上使用的大多数药物的主要成分都是小分子抑制剂,治疗骨关节炎的小分子药物正在不断研究中。文章认为,未来基于小分子药物的骨关节炎临床治疗应与骨关节炎的预后因素和运动疗法等多种模式相结合,其可以准确评估患者的临床异质性。总之,小分子药物的开发和治疗方案正在骨关节炎领域出现,未来十年可能会看到骨关节炎治疗的重大变化,这有望成为减轻骨关节炎患者巨大负担的一种新兴潜在方法。
综合上述原因,文章主要阐述了与骨关节炎发病机制相关的最新治疗方式,并就近年来国内外学者对它们的研究结果进行整合汇总,列举了各种发病机制相关的治疗方式和基础实验研究结果,并且预测了这些治疗方式在未来面临的挑战,这对于未来更进一步探索针对骨关节炎的治疗提供了帮助。该综述以其为将来开发治疗骨关节炎的方式、进行相关研究作依据。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2023年11月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2013年1月至2023年12月的文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、中国知网和万方数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“osteoarthritis,arthritis,osteoarthrosis,degenerative,arthritides,deformans,small molecule drugs,small molecule inhibitors,small molecule agents”,中文检索词为“骨关节炎,小分子药物,小分子抑制剂”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述、述评和荟萃分析。
1.1.6 检索策略 见图1。
1.2 纳入及排除标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①与骨关节炎有关的文献;②与小分子抑制剂和小分子药物有关的文献;同一领域的相关研究选择近年发表的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①研究目的及内容与此研究无关的文献;②重复性研究;③Meta分析。
1.3 文献质量评估和数据的提取 共检索到文献1 274篇,英文文献1 175篇,中文文献99篇,排除与研究目的相关性差及内容陈旧、质量不高及重复的文献1 206篇,纳入68篇符合标准的文献进行综述。文献检索流程见图2。
动物实验和临床试验突出了针对各种骨关节炎的新治疗靶点,针对其中一些靶点开发的小分子抑制剂在Ⅱ-Ⅲ期临床试验中显示出有希望的结果。前文所介绍的靶向骨关节炎的小分子抑制剂在镇痛和软骨保护方面显示出有希望的效果。因此,它们是疾病修饰性骨关节药物的可靠候选者,为骨关节炎患者带来了新的希望。此外,疾病修饰性骨关节药物通过合理设计给药系统,在有效治疗骨关节炎方面具有巨大潜力。目前对于骨关节炎的小分子药物治疗,还需要进一步去完善以下几点:①探索骨关节炎的发病机制可以为针对骨关节炎治疗的小分子抑制剂的开发提供更有效的靶点;②评估新型药物在治疗骨关节炎的同时是否存在长期慢性毒性,以确保其长期安全性;③针对多个部位/症状的联合治疗可能是骨关节炎治疗更有效的策略。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 文章总结了近年来与骨关节炎相关的小分子药物治疗的研究进展,同时结合在该领域相关的临床研究和基础实验后发现,通过小分子药物靶向骨关节炎相关的发病机制是比较热门且有前景的疗法,与以往综述不同的是,研究者们更加关注对于小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的靶点及疗效。通过蛋白酶、细胞因子和信号转导通路治疗骨关节炎进行阐述,希望将来能为相关的临床及基础实验研究提供依据,也为从现代医学角度阐述其治疗骨关节炎提供参考。
3.3 综述的局限性 ①作者通过检索国内外相关文献,发现目前小分子药物对于骨关节炎的作用疗效并未完全阐明,以及其相关治疗方式大多未应用于临床,尤其是国内的临床试验和基础研究较少,难以对中国的临床患者进行更加详细的比较研究,国内外总体也缺乏临床研究数据来进行对比,需要更多的主客观数据,如影像学及病理学资料等。②与骨关节炎相关的治疗方式较多,因为其治疗方式的机制不同,所以难以评价各个治疗方式之间的疗效。同时作者也未检索到上述小分子药物治疗对于不同治疗方式的对比研究,使得综述对比不够全面。
3.4 综述的重要意义 目前临床应用较为广泛的骨关节炎治疗方式主要以抗炎镇痛药物、关节腔内注射药物和缓解骨关节炎症状药物等,这些方式只能缓解骨关节炎的症状而不能彻底治愈,最终疾病发展到一定程度还要接受手术治疗。近年来,人们对于骨关节炎的治疗及发病机制研究从未停止过,许多学者都致力于从骨关节炎的发病机制入手,从而研究出可以逆转软骨变形的方式。因此,通过小分子药物靶向骨关节炎的发病机制从而治疗骨关节炎的研究具有十分重要的意义。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 目前,小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的主要限制因素有治疗效果的不确定性、潜在的不良因素和探索更有效的靶点。骨关节炎是一个较为复杂的疾病,其发病机制常常涉及多种蛋白酶、细胞因子和信号通路的参与,如果单单靶向抑制某个机制在理论上很难起到较为满意的效果。尽管骨关节炎很常见,且骨关节炎患者并不存在致命性问题,但心理负担和生活上的局限性已经对患者的生活产生了较大的阻碍。总之,目前的研究表明骨关节炎的小分子药物相关治疗在未来有较好的趋势,探索更为安全有效的骨关节炎靶点是值得期待的,在将来骨关节炎的治疗有望实现进一步的飞跃。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
骨关节炎的病理生理过程中存在多种蛋白、信号通路及炎症介质等的参与,开发针对这些蛋白、信号通路及炎症介质等的小分子药物,可有效地延缓骨关节炎的进展并改善其临床表现。
#br#
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||