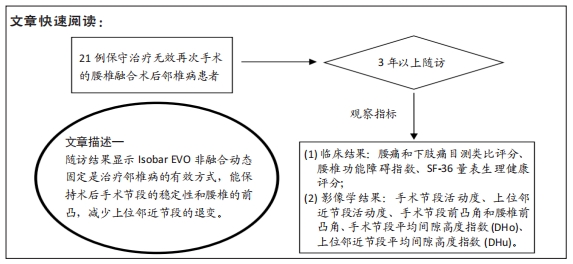
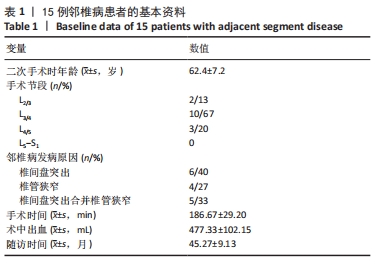
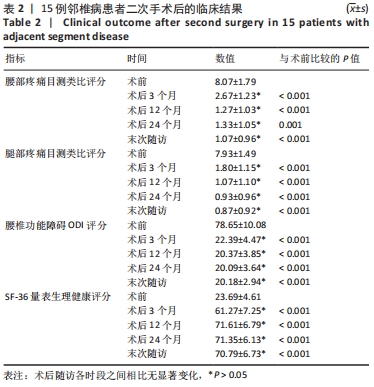
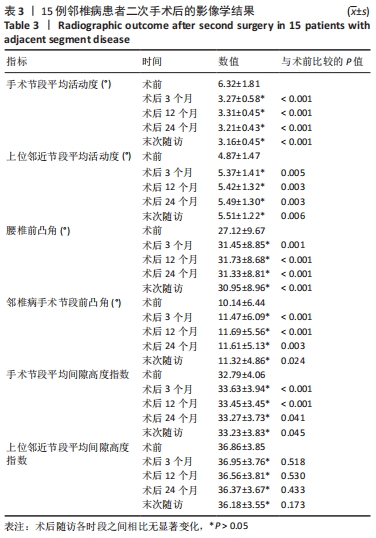
[1] PARK P, GARTON HJ, GALA VC, et al. Adjacent segment disease after lumbar or lumbosacral fusion: review of the literature. Spine. 2004;29:1938-1944.
[2] HASHIMOTO K, AIZAWA T, KANNO H, et al. Adjacent segment degeneration after fusion spinal surgery-a systematic review. Int Orthop. 2019;43:987-993.
[3] 刘明,勘武生,李鹏,等.髓核摘除联合Isobar非融合内固定治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(2):229-234.
[4] 张晓哲,王庆甫,赵子义,等.Isobar TTL系统治疗腰椎退行性疾病的疗效及术后融合率的探讨[J].中国骨伤,2019,32(10):914-918.
[5] OHNHAUS EE, ADLER R. Methodological problems in the measurement of pain: a comparison between the verbal rating scale and the visual analogue scale. Pain. 1975;1(4):379-384.
[6] FAIRBANK JC, PYNSENT PB. The Oswestry Disability Index. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(22):2940-2953.
[7] BRAZIER JE, HARPER R, JONES NM, et al. Validating the SF-36 health survey questionnaire: new outcome measure for primary care. BMJ. 1992;305(6846): 160-164.
[8] SASANI M, AYDIN AL, OKTENOGLU T, et al. The combined use of a posterior dynamic transpedicular stabilization system and a prosthetic disc nucleus device in treating lumbar degenerative disc disease with disc herniations. SAS J. 2008;2:130-136.
[9] FORMICA M, CAVAGNARO L, BASSO M, et al. Is it possible to preserve lumbar lordosis after hybrid stabilization? Preliminary results of a novel rigid-dynamic stabilization system in degenerative lumbar pathologies. Europ Spine J. 2015; 24 Suppl 7:849-854.
[10] XIA XP, CHEN HL, CHENG HB. Prevalence of adjacent segment degeneration after spine surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine. 2013;38: 597-608.
[11] SEARS WR, SERGIDES IG, KAZEMI N, et al. Incidence and prevalence of surgery at segments adjacent to a previous posterior lumbar arthrodesis. Spine J. 2011;11(1):11-20.
[12] OKUDA S, MIYAUCHI A, ODA T, et al. Surgical complications of posterior lumbar interbody fusion with total facetectomy in 251 patients. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006;4:304-309.
[13] TELFEIAN AE. Transforaminal Endoscopic Surgery for Adjacent Segment Disease After Lumbar Fusion. World Neurosurg. 2017;97:231-235.
[14] GREINER-PERTH R, SELLHAST N, PERLER G, et al. Dynamic posterior stabilization for degenerative lumbar spine disease: a large consecutive case series with long-term follow-up by additional postal survey. Eur Spine J. 2016;25:2563-2570.
[15] VERESCIAGINA K, MEHRKENS A, SCHAREN S, et al. Minimum ten-year follow-up of spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis treated with decompression and dynamic stabilization. J Spine Surg. 2018;4:93-101.
[16] KANER T, OZER AF. Dynamic stabilization for challenging lumbar degenerative diseases of the spine: a review of the literature. Adv Orthop. 2013;2013: 753470.
[17] NAKASHIMA H, KAWAKAMI N, TSUJI T, et al. Adjacent Segment Disease After Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Based on Cases With a Minimum of 10 Years of Follow-up. Spine. 2015;40:E831-841.
[18] CHOI KC, KIM JS, SHIM HK, et al. Changes in the adjacent segment 10 years after anterior lumbar interbody fusion for low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472:1845-1854.
[19] BYDON M, MACKI M, KEREZOUDIS P, et al. The incidence of adjacent segment disease after lumbar discectomy: A study of 751 patients. J Clin Neurosci. 2017;35:42-46.
[20] CARREON LY, GLASSMAN SD, HOWARD J. Fusion and nonsurgical treatment for symptomatic lumbar degenerative disease: a systematic review of Oswestry Disability Index and MOS Short Form-36 outcomes. Spine J. 2008;8:747-755.
[21] LEE JC, KIM Y, SOH JW, et al. Risk factors of adjacent segment disease requiring surgery after lumbar spinal fusion: comparison of posterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterolateral fusion. Spine 2014;39:E339-345.
[22] PAN A, HAI Y, YANG J, et al. Adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar spinal fusion compared with motion-preservation procedures: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25:1522-1532.
[23] HEO Y, PARK JH, SEONG HY, et al. Symptomatic adjacent segment degeneration at the L3-4 level after fusion surgery at the L4-5 level: evaluation of the risk factors and 10-year incidence. Eur Spine J. 2015;24:2474-2480.
[24] KAITO T, HOSONO N, FUJI T, et al. Disc space distraction is a potent risk factor for adjacent disc disease after PLIF. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131:1499-1507.
[25] AIKI H, OHWADA O, KOBAYASHI H, et al. Adjacent segment stenosis after lumbar fusion requiring second operation. J Orthop Sci. 2005;10:490-495.
[26] CHEN BL, WEI FX, UEYAMA K, et al. Adjacent segment degeneration after single-segment PLIF: the risk factor for degeneration and its impact on clinical outcomes. Eur Spine J. 2011;20:1946-1950.
[27] BAE JS, LEE SH, KIM JS, et al. Adjacent segment degeneration after lumbar interbody fusion with percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for adult low-grade isthmic spondylolisthesis: minimum 3 years of follow-up. Neurosurgery. 2010;67:1600-1607; discussion 1607-1608.
[28] DISCH AC, SCHMOELZ W, MATZIOLIS G, et al. Higher risk of adjacent segment degeneration after floating fusions: long-term outcome after low lumbar spine fusions. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2008;21:79-85.
[29] LU K, LILIANG PC, WANG HK, et al. Reduction in adjacent-segment degeneration after multilevel posterior lumbar interbody fusion with proximal DIAM implantation. Journal of neurosurgery. Spine. 2015;23:190-196.
[30] PARKER SL, MENDENHALL SK, SHAU D, et al. Determination of minimum clinically important difference in pain, disability, and quality of life after extension of fusion for adjacent-segment disease. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16:61-67.
[31] MASHALY H, PASCHEL EE, KHATTAR NK, et al. Posterior lumbar dynamic stabilization instead of arthrodesis for symptomatic adjacent-segment degenerative stenosis: description of a novel technique. Neurosurg Focus. 2016;40:E5.
[32] BERTAGNOLI R, YUE JJ, FENK-MAYER A, et al. Treatment of symptomatic adjacent-segment degeneration after lumbar fusion with total disc arthroplasty by using the prodisc prosthesis: a prospective study with 2-year minimum follow up. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006;4:91-97.
[33] BARREY C, PERRIN G, CHAMPAIN S. Pedicle-Screw-Based Dynamic Systems and Degenerative Lumbar Diseases: Biomechanical and Clinical Experiences of Dynamic Fusion with Isobar TTL. ISRN Orthop. 2013;2013:183702.
[34] LI Z, LI F, YU S, et al. Two-year follow-up results of the Isobar TTL Semi-Rigid Rod System for the treatment of lumbar degenerative disease. J Clin Neurosci. 2013;20:394-399.
[35] JI ZS, YANG H, YANG YH, et al. Analysis of clinical effect and radiographic outcomes of Isobar TTL system for two-segment lumbar degenerative disease: a retrospective study. BMC Surgery. 2020;20(1):15.
[36] 曹宗锐,郑博,屈波,等.ISObar TTL动态固定系统治疗双节段腰椎椎间盘突出症:8年随访[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(32):5110-5116.
|