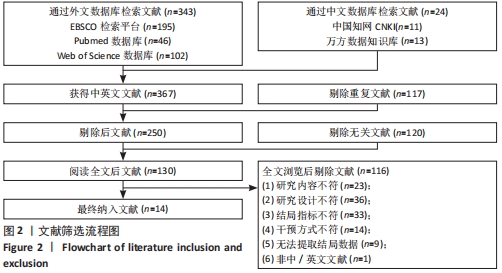
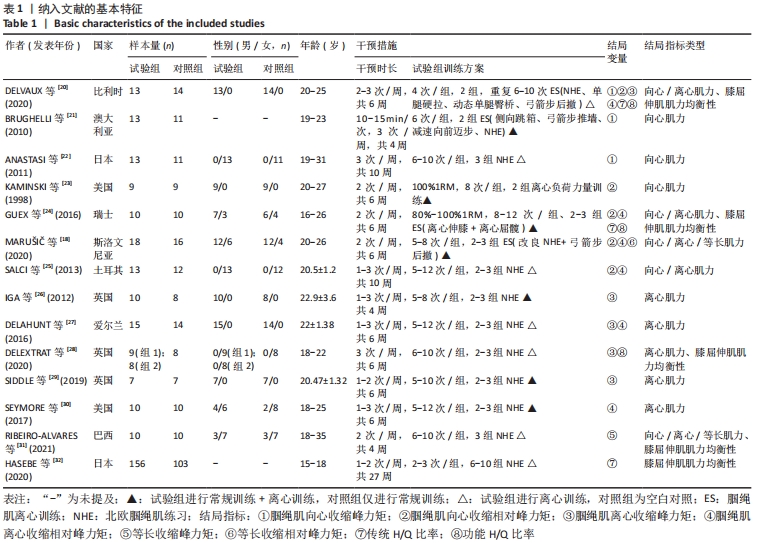
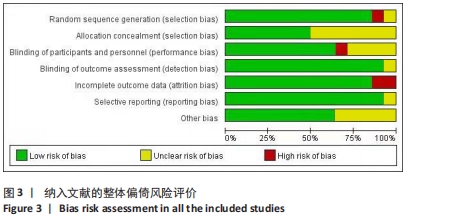
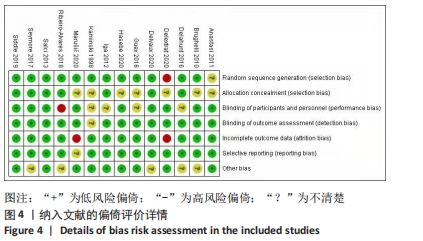
[1] FREEMAN BW, TALPEY SW, JAMES LP, et al. Sprinting and Hamstring Strain Injury: Beliefs and Practices of Professional Physical Performance Coaches in Australian Football. Phys Ther Sport. 2021;48:12-19.
[2] ZACHAZEWSKI J, SILVERS H, LI B, et al. Prevalence of Hamstring Injuries in Summer League Baseball Players. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2019;14(6): 885.
[3] ROE M, MURPHY JC, GISSANE C, et al. Hamstring Injuries in Elite Gaelic Football: An 8-Year Investigation to Identify Injury Rates, Time-Loss Patterns and Players at Increased Risk. Br J Sports Med. 2018; 52(15):982-988.
[4] EDUARD B, OLEG T, MIKHAIL B, et al. The Prevalence of Non-contact Muscle Injuries of the Lower Limb in Professional Soccer Players who Perform Salah Regularly: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):1-6.
[5] MALLIAROPOULOS N, BIKOS G, MEKE M, et al. Higher Frequency of Hamstring Injuries in Elite Track and Field Athletes who Had a Previous Injury to the Ankle-a 17 Years Observational Cohort Study. J Foot Ankle Res. 2018;11(1):1-8.
[6] OKOROHA KR, CONTE S, MAKHNI EC, et al. Hamstring Injury Trends in Major and Minor League Baseball: Epidemiological Findings From the Major League Baseball Health and Injury Tracking System. Orthop J Sports Med. 2019;7(7):1-7.
[7] BUCKTHORPE M, WRIGHT S, BRUC-LOW S, et al. Recommendations for Hamstring Injury Prevention in Elite Football: Translating Research into Practice. Br J Sports Med. 2019;53(7):449-456.
[8] HUYGAERTS S, COS F, COHEN DD, et al. Mechanisms of Hamstring Strain Injury: Interactions between Fatigue, Muscle Activation and Function. Sports (Basel). 2020;8(5):65.
[9] ERTELT T, GRONWALD T. Hamstring Injury Risk Factors in Elite Sports: The Role of Muscle Geometry and Function. Acta Physiol. 2019;227(1):e13253-e13253.
[10] 杜建平,任薇,夏能能,等.等速肌力训练对改善膝骨关节炎肌肉功能的Meta分析[J].中国康复,2020,35(11):594-599.
[11] Kenneally-Dabrowski CJB, Brown NAT, Lai AKM, et al. Late Swing or Early Stance? A Narrative Review of Hamstring Injury Mechanisms during High-Speed Running. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2019;29(8):1083-1091.
[12] 卢志泉,夏正亮,李玉章,等.肌肉力量的神经生物力学基础及诊断[J].上海体育学院学报,2019,43(3):113-120,126.
[13] 谭恺,张春合,吕海龙. Nordic Hamstring跪姿前倾离心训练的生理效应及其对腘绳肌拉伤的预防效果[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(7):601-610.
[14] ABDEL-AZIEM AA, SOLIMAN ES, ABDELRAOUF OR. Isokinetic Peak Torque and Flexibility Changes of the Hamstring Muscles after Eccentric Training: Trained versus Untrained Subjects. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2018;52(4):308-314.
[15] HEGYI A, PÉTER A, FINNI T, et al. Region-Dependent Hamstrings Activity in Nordic Hamstring Exercise and Stiff-Leg Deadlift Defined with High-Density Electromyography. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018;28(3):992-1000.
[16] VANGSGAARD S, TAYLOR JL, HANSEN EA, et al. Changes in H Reflex and Neuromechanical Properties of the Trapezius Muscle after 5 weeks of Eccentric Training: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2014; 116(12):1623-1631.
[17] TØIEN T, PEDERSEN HAGLO H, UNHJEM R, et al. Maximal Strength Training: the Impact of Eccentric Overload. J Neurophysiol. 2018; 120(6):2868-2876.
[18] MARUŠIČ J, VATOVEC R, MARKOVIĆ G, et al. Effects of Eccentric Training at Long-Muscle Length on Architectural and Functional Characteristics of the Hamstrings. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2020;30(11):2130-2142.
[19] 谷鸿秋,王杨,李卫.Cochrane偏倚风险评估工具在随机对照研究Meta分析中的应用[J].中国循环杂志,2014,29(2):147-148.
[20] DELVAUX F, SCHWARTZ C, DECREQUY T, et al. Influence of a Field Hamstring Eccentric Strengthening on Muscle Strength and Flexibility. Int J Sports Med. 2020;41(4): 233-241.
[21] BRUGHELLI M, MENDIGUCHIA J, NOSAKA K, et al. Effects of Eccentric Exercise on Optimum Length of the Knee Flexors and Extensors during the Preseason in Professional Soccer Players. Phys Ther Sport. 2010;11(2):50-55.
[22] ANASTASI SM, HAMZEH MAL. Does the Eccentric Nordic Hamstring Exercise Have an Effect on Isokinetic Muscle Strength Imbalance and Dynamic Jumping Performance in Female Rugby Union Players?. Isokinet Exerc Sci. 2011; 19(4):251-260.
[23] Kaminski TW, Wabbersen CV, Murphy RM. Concentric versus Enhanced Eccentric Hamstring Strength Training: Clinical Implications. J Athl Train. 1998;33(3):216-221.
[24] GUEX KJ, LUGRIN V, BORLOZ S, et al. Influence on Strength and Flexibility of a Swing Phase-Specific Hamstring Eccentric Program in Sprinters’ General Preparation. J Strength Cond Res. 2016;30(2):525-532.
[25] SALCI Y, YILDIRIM A, CELIK O, et al. The Effects of Eccentric Hamstring Training on Lower Extremity Strength and Landing Kinetics in Recreational Female Athletes. Isokinet Exerc Sci. 2013;21(1):11-18.
[26] IGA J, FRYER CS, DEIGHAN M, et al. ‘Nordic’ Hamstrings Exercise Engagement Characteristics and Training Responses. Int J Sports Med. 2012;33(12):1000-1004.
[27] DELAHUNT E, McGROARTY M, De VITO G, et al. Nordic Hamstring Exercise Training Alters Knee Joint Kinematics and Hamstring Activation Patterns in Young Men. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2016;116(4):663-672.
[28] DELEXTRAT A, BATEMAN J, ROSS C, et al. Changes in Torque-Angle Profiles of the Hamstrings and Hamstrings-to-Quadriceps Ratio after Two Hamstring Strengthening Exercise Interventions in Female Hockey Players. J Strength Cond Res. 2020;34(2):396-405.
[29] SIDDLE J, GREIG M, WEAVER K, et al. Acute Adaptations and Subsequent Preservation of Strength and Speed Measures Following a Nordic Hamstring Curl Intervention: A Randomised Controlled Trial. J Sports Sci. 2019;37(8):911-920.
[30] SEYMORE KD, DOMIRE ZJ, DEVITA P, et al. The Effect of Nordic Hamstring Strength Training on Muscle Architecture, Stiffness, and Strength. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2017;117(5):943-953.
[31] RIBEIRO-ALVARES JB, OLIVEIRA GDS, De LIMA-E-SILVA FX, et al. Eccentric Knee Flexor Strength of Professional Football Players with and without Hamstring Injury in the Prior Season. Eur J Sport Sci. 2021;21(1):131-139.
[32] HASEBE Y, AKASAKA K, OTSUDO T, et al. Effects of Nordic Hamstring Exercise on Hamstring Injuries in High School Soccer Players: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int J Sports Med. 2020;41(3):154-160.
[33] 尚玢,曹峰锐,陈静. 男子水球守门员膝、踝关节屈伸肌群等速肌力实验测量[J].太原理工大学学报,2019,50(1):135-140.
[34] DEMETS DL. Methods for Combining Randomized Clinical Trials: Strengths and Limitations. Stat Med. 1987;6(3):341-34.
[35] ROUIS M, COUDRAT L, JAAFAR H, et al. Assessment of Isokinetic Knee Strength in Elite Young Female Basketball Players: Correlation with Vertical Jump. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2015;55(12):1502-1508.
[36] SUNDBY OH, GORELICK ML. Relationship Between Functional Hamstring: Quadriceps Ratios and Running Economy in Highly Trained and Recreational Female Runners. J Strength Cond Res. 2014;28(8):2214-2227.
[37] 曹峰锐.“腘绳肌离心收缩力矩/股四头肌向心收缩力矩”在预防腘绳肌运动性拉伤和膝关节前交叉韧带损伤方面的应用[J].中国体育科技,2017,53(2):43-52+63.
[38] 杨洪杰,王艳,刘善云.男大学生功能动作表现与健康体适能的关系[J].中国学校卫生,2020,41(12):1863-1867.
[39] DORNELLES MP, FRITSCH CG, SONDA FC, et al. Photobiomodulation Therapy as a Tool to Prevent Hamstring Strain Injuries by Reducing Soccer-induced Fatigue on Hamstring Muscles. Lasers Med Sci. 2019; 34(6):1177-1184.
[40] BURIGO RL, SCOZ RD, ALVES BMO, et al. Concentric and Eccentric Isokinetic Hamstring Injury Risk Among 582 Professional Elite Soccer Players: A 10-Years Retrospective Cohort Study. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2020;6(1):e000868.
[41] CORREIA P, SANTOS P, MIL-HOMENS P, et al. Rapid Hamstrings to Quadriceps Ratio at Long Muscle Lengths in Professional Football Players with Previous Hamstring Strain Injury. Eur J Sport Sci. 2020;20(10):1405-1413.
[42] DE OLIVEIRA NT, MEDEIROS TM, VIANNA KB, et al. A Four-week Training Program With the Nordic Hamstring Exercise During Preseason Increases Eccentric Strength of Male Soccer Players. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2020;15(4):571-578.
[43] ALTALT T, SEVERIN J, KOMNIK I, et al. Nordic Hamstring Exercise Training Induces Improved Lower-limb Swing Phase Mechanics and Sustained Strength Preservation in Sprinters. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2021;31(4):826-838.
[44] ALT T, KNICKER AJ, STRUDER HK. Assessing Thigh Muscle Balance of Male Athletes with Special Emphasis on Eccentric Hamstring Strength. Phys Sportsmed. 2020;48(3):327-334.
[45] PIETERS D, WITVROUW E, WEZENBEEK E, et al. Value of Isokinetic Strength Testing for Hamstring Injury Risk Assessment: Should the ‘Strongest’ Mates Stay Ashore?. Eur J Sport Sci. 2020;1-12.
[46] GURUHAN S, KAFA N, ECEMIS ZB, et al. Muscle Activation Differences During Eccentric Hamstring Exercises. Sports Health. 2021;13(2):181-186.
[47] 杜东,范建中,尹瑞雪. 不同角速度下等速躯干屈伸训练对腰痛患者核心肌群的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019, 25(4):381-384.
[48] 成鹏,毕霞,郎海涛,等. 速度因素对躯干等速肌力测试影响的研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2004,19(8):578-580.
[49] 黄婷婷,范利华,高东,等.等速肌力测试与训练技术在肌肉功能评定中的研究进展[J].法医学杂志,2013,29(1):49-52.
[50] Croisier JL, Ganteaume S, Binet J, et al. Strength Imbalances and Prevention of Hamstring Injury in Professional Soccer Players: A Prospective Study. Am J Sports Med. 2008;36(8):1469-1475.
|