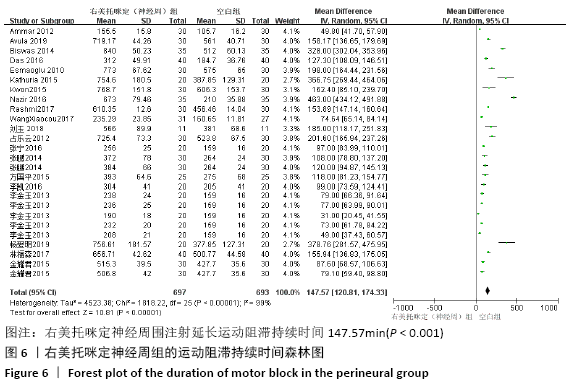
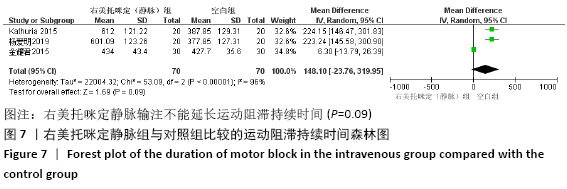
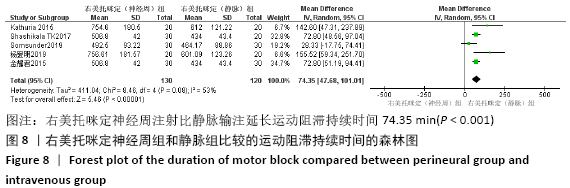
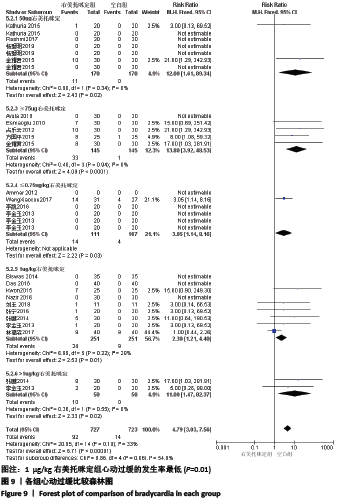
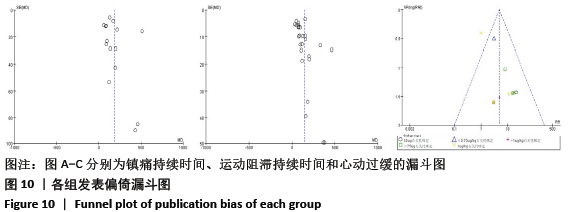
[1] BRUMMETT CM, HONG EK, JANDA AM, et al. Perineural dexmedetomidine added to ropivacaine for sciatic nerve block in rats prolongs the duration of analgesia by blocking the hyperpolarization-activated cation current. Anesthesiology. 2011; 115(4):836-843.
[2] KAUR M, KAUR R, KAUR S, et al. A study to compare the analgesic efficacy of dexmedetomidine and fentanyl as adjuvants to levobupivacaine in ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Anesth Essays Res. 2018;12(3):669-673.
[3] ALISTE J, LAYERA S, LAYERA S, et al. Randomized comparison between perineural dexamethasone and dexmedetomidine for ultrasound-guided infraclavicular block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2019. doi:10.1136/rapm-2019-100680.
[4] LIU Z, JIANG M, XU T, et al. Analgesic effect of ropivacaine combined with dexmedetomidine on brachial plexus block. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018; 18(1):107.
[5] KANG R, JEONG JS, YOO JC, et al. Effective dose of intravenous dexmedetomidine to prolong the analgesic duration of interscalene brachial plexus block: a single-center, prospective, double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2018;43(5):488-495.
[6] ABDALLAH FW, BRULL R. Facilitatory effects of perineural dexmedetomidine on neuraxial and peripheral nerve block: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2013;110(6):915-925.
[7] 代坤吾,莫均,王念念.右美托咪定复合局部麻醉药在臂丛神经阻滞中疗效的Meta分析[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2019,25(11):837-843.
[8] AVULA RR, VEMURI NN, PUTHI S, et al. Ultrasound-guided subclavian perivascular brachial plexus block using 0.5% bupivacaine with dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Anesth Essays Res. 2019;13(4):615-619.
[9] RASHMI HD, KOMALA HK. Effect of dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to 0.75% ropivacaine in interscalene brachial plexus block using nerve stimulator: a prospective, randomized double-blind study.Anesth Essays Res. 2017;11(1):134-139.
[10] WANG X, YU F, LI K. Which is the better adjuvant to ropivacaine in brachial plexus block: Dexmedetomidine or morphine? A prospective, randomized, double-blinded, comparative study (Article). Int J Clin Exp Med. 2017;10(7): 10813-10819.
[11] NAZIR N, JAIN S. A randomized controlled trial study on the effect of adding dexmedetomidine to bupivacaine in supraclavicular block using ultrasound guidance. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2016;26(6):561-566.
[12] DAS B, LAKSHMEGOWDA M, SHARMA M, et al. Supraclavicular brachial plexus block using ropivacaine alone or combined with dexmedetomidine for upper limb surgery: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded, comparative study. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2016;63(3):135-140.
[13] KATHURIA S, GUPTA S, DHAWAN I. Dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to ropivacaine in supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Saudi J Anaesth. 2015;9(2):148-154.
[14] KWON Y, HWANG SM, LEE JJ, et al. The effect of dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to ropivacaine on the bispectral index for supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2015;68(1):32-36.
[15] BISWAS S, DAS RK, MUKHERJEE G, et al. Dexmedetomidine an adjuvant to levobupivacaine in supraclavicular brachial plexus block: a randomized double blind prospective study. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2014;24(3):203-208.
[16] AMMAR AS, MAHMOUD KM. Ultrasound-guided single injection infraclavicular brachial plexus block using bupivacaine alone or combined with dexmedetomidine for pain control in upper limb surgery: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Saudi J Anaesth. 2012;6(2):109-114.
[17] ESMAOGLU A, YEGENOGLU F, AKINET A, et al. Dexmedetomidine added to levobupivacaine prolongs axillary brachial plexus block. Anesth Analg. 2010;111(6):1548-1551.
[18] SOMSUNDER RG, ARCHANA NB, SHIVKUMAR G, et al, Comparing efficacy of perineural dexmedetomidine with intravenous dexmedetomidine as adjuvant to levobupivacaine in supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Anesth Essays Res. 2019;13(3):441-445.
[19] SHASHIKALA TK, AND K. MADHYASTHA. A prospective randomized double blinded study to evaluate the efficacy of dexmedetomidine 50 μg intravenously and perineurally as an adjunct to 0.5% ropivacaine for supraclavicular brachial plexus block. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 2017;21(4):413-419.
[20] 曾祥芳,肖合元.盐酸右美托咪定应用于超声引导下臂丛神经阻滞的镇痛效果分析[J]. 系统医学,2019,4(12):30-32.
[21] 李岩,王辉,邓莹,等.静脉输注右美托咪定对臂丛阻滞效果的随机对照研究[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2018,50(5):845-849.
[22] 杨爱明,王祥.右美托咪定复合罗哌卡因治疗锁骨上臂丛神经阻滞的效果观察[J]. 医药前沿, 2019,9(22):151-153.
[23] 刘玉,刘绍正,王先锋.右美托咪定或舒芬太尼复合左旋布比卡因用于臂丛神经阻滞的效果观察[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2018,40(1):59-61.
[24] 林福森,廖锡强,卢贵明,等.罗哌卡因复合右美托咪定应用于臂丛神经阻滞的效果分析[J].内蒙古医学杂志,2017,49(6):645-648.
[25] 张宁,孙保民,程燕,等.地塞米松复合右美托咪定对臂丛神经阻滞效果的影响[J].河北医科大学学报,2016,37(8):935-939.
[26] 李凯,赵国庆,李旭阳,等.右美托咪定与肾上腺素作为局部麻醉药佐剂对臂丛神经阻滞效果的对比[J].国际麻醉学与复苏杂志,2016,37(8):692-695.
[27] 金耀君,赵璇.罗哌卡因复合右美托咪定对超声引导下腋路臂丛神经阻滞麻醉的影响[J].上海医学,2015,38(2):110-114.
[28] 张鹏,刘婷,陈俊,等.Narcotrend监测下右美托咪定复合罗哌卡因用于臂丛阻滞麻醉的观察[J].安徽医学,2014,35(4):446-449.
[29] 李金玉,葛东建,祁宾,等.不同剂量右美托咪定混合罗哌卡因用于臂丛神经阻滞的效果[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2013,33(6):711-713.
[30] 占乐云,周密.右美托咪定对左布比卡因腋路臂丛神经阻滞效果的影响[J]. 中国医师进修杂志,2012,35(24):57-59.
[31] 方国平,王华,张兆平,等,右美托咪定增强甲磺酸罗哌卡因臂丛神经阻滞效果的临床观察[J].医学理论与实践,2015,28(12):1568-1570.
[32] ABDALLAH FW, DWYER T, CHAN VW, et al. IV and perineural dexmedetomidine similarly prolong the duration of analgesia after interscalene brachial plexus block. Anesthesiology. 2016;124(3):683-695.
[33] CHEN BS, PENG H, WU SN. Dexmedetomidine, an α 2 -adrenergic agonist, inhibits neuronal delayed-rectifier potassium current and sodium current. Br J Anaesth. 2009;103(2):244-254.
[34] TALKE P, LOBO E, BROWN R. Systemically administered alpha2-agonist-induced peripheral vasoconstriction in humans. Anesthesiology. 2003;99(1):65-70.
[35] 马波,刘志恒,王显春.右美托咪定镇痛的临床应用进展[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2018,34(11): 1136-1139.
[36] 张安生,曾宾,王剑鸣,等.锁骨上臂丛神经阻滞时不同进针方向对起效平面的影响[J] 医学临床研究,2007,24(1):67-68,71.
[37] GUPTA K, TIWARI V, GUPTA PK, et al. Prolongation of subarachnoid block by intravenous dexmedetomidine for sub umbilical surgical procedures: a prospective control study. Anesth Essays Res. 2014;8(2):175-178.
[38] EBERT TJ, HALL JE, BARNEY JA, et al. The effects of increasing plasma concentrations of dexmedetomidine in humans. Anesthesiology. 2000;93(2):382-394.
[39] GERLACH AT, DASTA JF. Dexmedetomidine: An Updated Review. Ann Pharmacother. 2007;41(2):530-531.
[40] GERTLER R, BROWN HC, MITCHELL DH, et al. Dexmedetomidine: a novel sedative-analgesic agent. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2001;14(1):13-21. |
 文题释义:
文题释义: