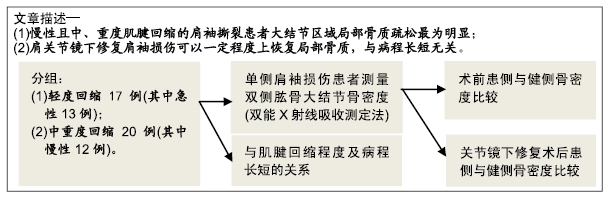
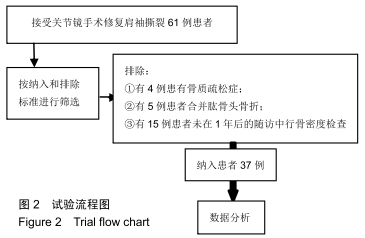
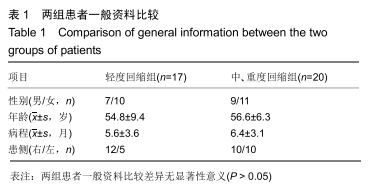
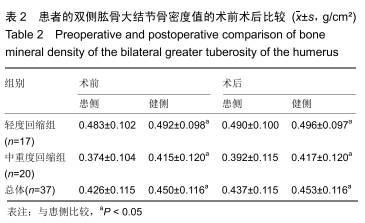
[1] VITALE MA, KLEWENO CP, JACIR AM, et al. Training resources in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2007;89(6):1393-1398.
[2] URWIN M, SYMMONS D, ALLISON T, et al. Estimating the burden of musculoskeletal disorders in the community: the comparative prevalence of symptoms at different anatomical sites, and the relation to social deprivation. Ann Rheum Dis. 1998;57(11):649-655.
[3] GALATZ LM, ROTHERMICH SY, ZAEGEL M, et al. Delayed repair of tendon to bone injuries leads to decreased biomechanical properties and bone loss. J Orthop Res.2005; 23(6):1441-1447.
[4] MEYER DC, FUCENTESE SF, KOLLER B, et al. Association of osteopenia of the humeral head with full-thickness rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2004;13(3):333-337.
[5] TINGART M J, APRELEVA M, ZURAKOWSKI D, et al. Pullout strength of suture anchors used in rotator cuff repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85(11):2190-2198.
[6] JIANG Y, ZHAO J, VAN HOLSBEECK MT, et al. Trabecular microstructure and surface changes in the greater tuberosity in rotator cuff tears. Skeletal Radiol.2002;31(9):522-528.
[7] TINGART MJ, APRELEVA M, LEHTINEN J, et al. Anchor design and bone mineral density affect the pull-out strength of suture anchors in rotator cuff repair: which anchors are best to use in patients with low bone quality?. Am J Sports Med.2004; 32(6):1466-1473.
[8] MEYER DC, MAYER J, WEBER U, et al. Ultrasonically implanted PLA suture anchors are stable in osteopenic bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2006;442:143-148.
[9] CHUNG SW, OH JH,GONG HS, et al. Factors affecting rotator cuff healing after arthroscopic repair: osteoporosis as one of the independent risk factors. Am J Sports Med.2011; 39(10):2099-2107.
[10] WILSON J, BONNER TJ, HEAD M, et al.Variation in bone mineral density by anatomical site in patients with proximal humeral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2009;91(6):772-775.
[11] DEORIO JK, COFIELD RH. Results of a second attempt at surgical repair of a failed initial rotator-cuff repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1984;66(4):563-567.
[12] PATTE D. Classification of rotator cuff lesions. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1990;(254):81-86.
[13] OH JH, SONG BW, KIM SH, et al. The measurement of bone mineral density of bilateral proximal humeri using DXA in patients with unilateral rotator cuff tear. Osteoporos Int.2014; 25(11):2639-2648.
[14] IDE J, KARASUGI T, OKAMOTO N, et al. Functional and structural comparisons of the arthroscopic knotless double-row suture bridge and single-row repair for anterosuperior rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015;24(10):1544-1554.
[15] BRAUNSTEIN V, OCKERT B, WINDOLF M, et al. Increasing pullout strength of suture anchors in osteoporotic bone using augmentation--a cadaver study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015;30(3):243-247.
[16] STRAUSS E, FRANK D, KUBIAK E, et al. The effect of the angle of suture anchor insertion on fixation failure at the tendon-suture interface after rotator cuff repair: deadman's angle revisited. Arthroscopy.2009;25(6):597-602.
[17] LIPORACE FA, BONO CM, CARUSO SA, et al. The mechanical effects of suture anchor insertion angle for rotator cuff repair. Orthopedics.2002;25(4):399-402.
[18] MALL NA, TANAKA MJ, CHOI LS, et al. Factors affecting rotator cuff healing.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(9): 778-788.
[19] MULLIGAN EP, DEVANNA RR, HUANG M, et al. Factors that impact rehabilitation strategies after rotator cuff repair. Phys Sportsmed.2012;40(4):102-114.
[20] TINGART MJ, APRELEVA M, VON STECHOW D, et al. The cortical thickness of the proximal humeral diaphysis predicts bone mineral density of the proximal humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2003;85(4):611-617.
[21] LEVY JC, ASHUKEM MT, FORMAINI NT. Factors predicting postoperative range of motion for anatomic total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2016;25(1):55-60.
[22] OH JH, SONG BW, LEE YS. Measurement of volumetric bone mineral density in proximal humerus using quantitative computed tomography in patients with unilateral rotator cuff tear.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(7):993-1002.
[23] WALDORFF EI, LINDNER J, KIJEK TG, et al. Bone density of the greater tuberosity is decreased in rotator cuff disease with and without full-thickness tears. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2011; 20(6):904-908.
[24] HELFEN T, SPRECHER CM, EBERLI U, et al. High-Resolution Tomography-Based Quantification of Cortical Porosity and Cortical Thickness at the Surgical Neck of the Humerus During Aging.Calcif Tissue Int. 2017;101(3): 271-279.
[25] SPROSS C, KAESTLE N, BENNINGER E, et al. Deltoid Tuberosity Index: A Simple Radiographic Tool to Assess Local Bone Quality in Proximal Humerus Fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(9):3038-3045.
[26] MATHER J, MACDERMID JC, FABER KJ, et al. Proximal humerus cortical bone thickness correlates with bone mineral density and can clinically rule out osteoporosis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2013;22(6):732-738.
[27] KIRCHHOFF C, KIRCHHOFF S, SPRECHER CM, et al. X-treme CT analysis of cancellous bone at the rotator cuff insertion in human individuals with osteoporosis: superficial versus deep quality. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(3): 381-387.
[28] Das Gesetz Der Transformation Der Knochen (The Law Of The Transformation Of Bones). British Medical Association. 1893: 1, 124.
[29] KIM YK, JUNG KH, KIM JW, et al. Factors affecting rotator cuff integrity after arthroscopic repair for medium-sized or larger cuff tears: a retrospective cohort study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2018;27(6):1012-1020.
[30] KWON J, KIM SH, LEE YH, et al.The Rotator Cuff Healing Index: A New Scoring System to Predict Rotator Cuff Healing After Surgical Repair. Am J Sports Med.2019;47(1):173-180.
[31] 刘宇,顾三军,徐耀增.巨大肩袖损伤的诊治现状与进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(9):823-828.
[32] YAMAGUCHI K, DITSIOS K, MIDDLETON WD, et al. The demographic and morphological features of rotator cuff disease. A comparison of asymptomatic and symptomatic shoulders.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(8):1699-1704.
|