中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (16): 2579-2584.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1185
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定与半髋关节置换治疗高龄不稳定型转子间骨折的Meta分析
欧阳剑锋,李柄权,玄文虎,王素伟
- 珠海市人民医院骨科,广东省珠海市 519000
Proximal femoral nail antirotation versus hemiarthroplasty in treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fracture in older adults: a meta-analysis
Ouyang Jianfeng, Li Bingquan, Xuan Wenhu, Wang Suwei
- Department of Orthopedics, Zhuhai People’s Hospital, Zhuhai 519000, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
股骨近端防旋髓内钉:作为最典型的髓内固定方式,具有以下特点:①其独有的螺旋刀片并挤压骨碎屑至周围部位,保留头颈部骨质;②增加了刀片与周围接触面积,提高固定锚合力;③独特的刀片设计,提示稳定,减少髋内翻畸形;④手术时间缩短,同时避免了取出内固定后股骨近端不稳定。
半髋关节置换:针对高龄不稳定型转子间骨折的治疗,半髋关节置换存在一定优势,主要表现在稳定性、下地负重时间及术后并发症上,但综合考虑到患者的基础疾病及病情复杂性时,半髋置换治疗对患者造成了更大的创伤,手术过程较长,也增加了患者的经济压力。同时,半髋置换治疗转子间骨折仍有争议,并未普及,况且人工关节假体寿命有限,也存在人工关节并发症的问题,增加了二次手术的风险。
摘要
背景:股骨转子间骨折目前手术治疗已达成共识。对于合并严重骨质疏松及内科病的高龄患者,不稳定型股骨转子间骨折采用何种手术方式及内固定选择,尚存不同的争议。
目的:通过Meta分析对股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定与半髋关节置换治疗高龄不稳定型转子间骨折的临床疗效及安全性进行评价。
方法:按照Cochrane系统评价的方法,计算机检索下列数据库(2008至2018年):Medline、PubMed、SPINGER、John Wiley、Science Direct、EBSCO、CNKI、万方、维普数数据库。英文检索词:proximal femoral nail ant-irotation or PFNA,hemiarthroplasty,unstable intertrochanteric fractures;中文检索词包括:股骨近端防旋髓内钉,半髋关节置换,不稳定型股骨转子间骨折。按照纳入及排除标准筛选文献并行质量评价,运用RevMan 5.1统计软件进行分析。
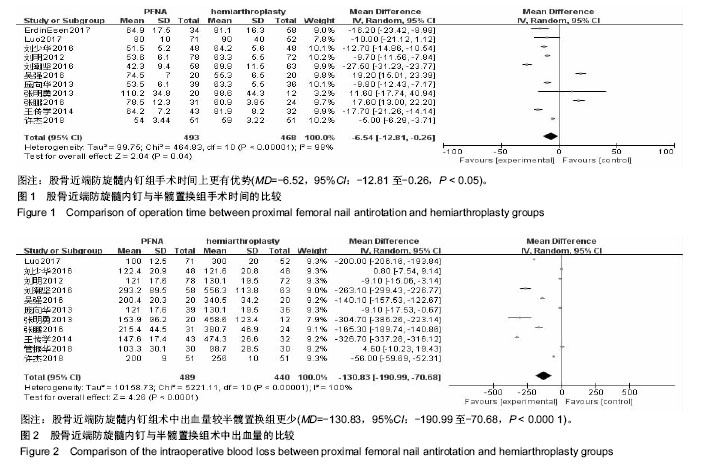
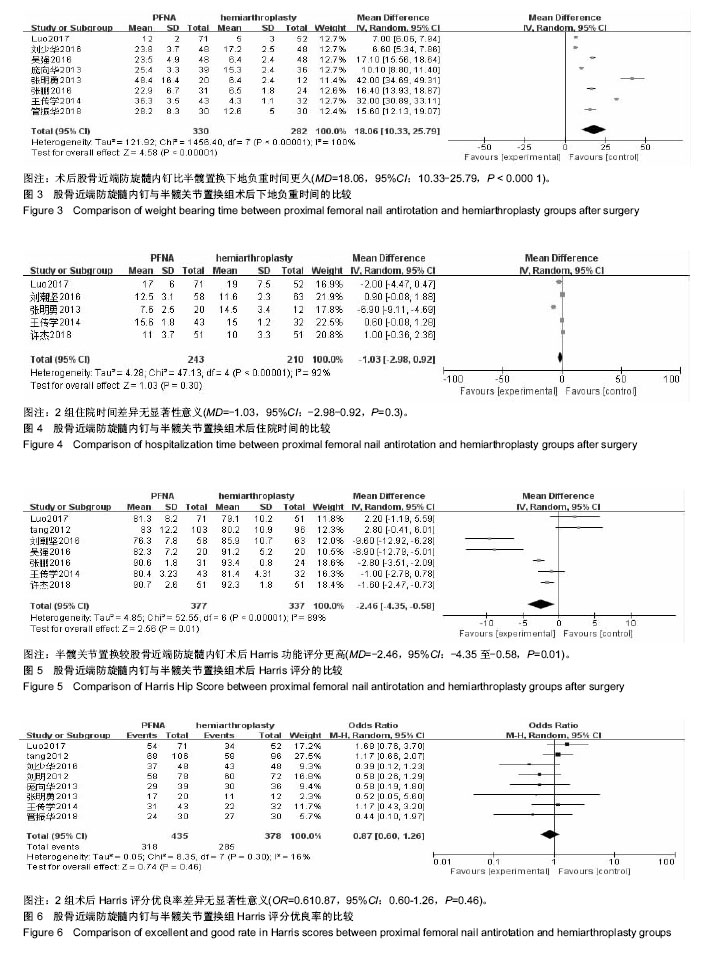
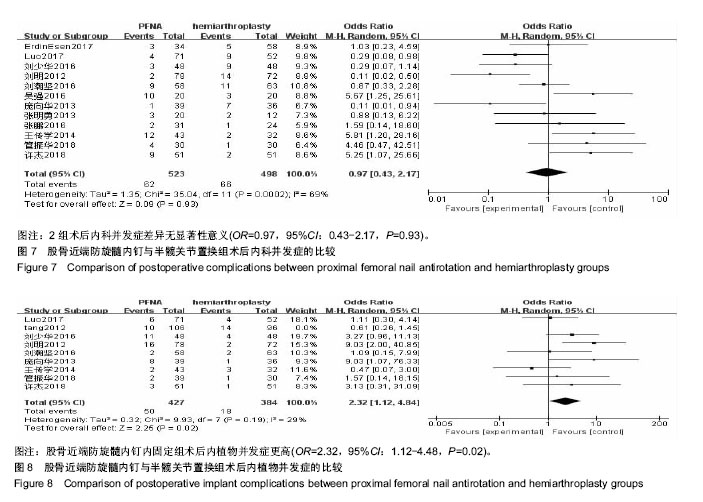
结果与结论:①共纳入13个临床试验,共1 223例患者,其中提及随机分组方法的文献有6篇;②Meta分析结果显示,股骨近端防旋髓内钉组手术时间更短[MD=-6.54,95%Cl(-12.81,-0.21),P < 0.01],术中出血量更少[MD=-130.83,95%CI(-190.99,-70.68),P < 0.01],但内植物并发症发生率更高[RR=2.32,95%Cl(1.12,4.84),P < 0.01];③半髋置换组术后下地负重时间更早[MD=18.06,95%CI(10.3,25.79),P < 0.000 1],术后Harris评分增高较股骨近端防旋髓内钉组更明显[MD=-8.19,95%CI(-9.45,-6.93), P < 0.01];④术后内科并发症、住院时间、Harris评分优良率对比,2组患者差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);⑤结果表明,股骨近端防旋髓内钉组较半髋关节置换组手术时间更短,出血量更少,但其术后内植物并发症较半髋关节组发生率也更高。而半髋关节置换组在术后Harris评分、术后下地负重时间方面更有优势。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-2708-8500(欧阳剑锋)
中图分类号:
.jpg)