| [1] Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69-90.[2] Perz JF, Armstrong GL, Farrington LA, et al. The contributions of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer worldwide. J Hepatol. 2006;45(4): 529-538.[3] Ott JJ, Stevens GA, Groeger J, et al. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: new estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity. Vaccine. 2012; 30(12):2212-2219.[4] Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2095-2128.[5] Goldstein ST, Zhou F, Hadler SC, et al. A mathematical model to estimate global hepatitis B disease burden and vaccination impact. Int J Epidemiol. 2005;34(6):1329-1339.[6] Wang FS, Fan JG, Zhang Z, et al. The global burden of liver disease: the major impact of China. Hepatology. 2014;60(6): 2099-2108.[7] Fong CY, Chak LL, Biswas A, et al. Human Wharton's jelly stem cells have unique transcriptome profiles compared to human embryonic stem cells and other mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(1):1-16.[8] Banas A, Yamamoto Y, Teratani T, et al. Stem cell plasticity: learning from hepatogenic differentiation strategies. Dev Dyn. 2007;236(12):3228-3241.[9] Groth A, Ottinger S, Kleist C, et al. Evaluation of porcine mesenchymal stem cells for therapeutic use in human liver cancer. Int J Oncol. 2012;40(2):391-401.[10] 庞一琳,张斌,陈虎. 间充质干细胞与肿瘤细胞相互作用:促进还是抑制[J]. 中华细胞与干细胞杂志:电子版,2013, 3(1): 30-37.[11] 中华医学会肝病学分会. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2015更新版)[J]. 中华传染病杂志,2015,21(11):219-240.[12] Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology.2001;33(2):464-470.[13] 杨秉辉. 原发性肝癌的临床诊断与分期标准[J]. 中华肝脏病杂志,2001,9(6):324-324.[14] 中国抗癌协会肝癌专业委员会中国抗癌协会临床肿瘤学协作委员会中华医学会肝病学分会肝癌学组. 原发性肝癌规范化诊治专家共识[J]. 临床肿瘤学杂志, 2009, 14(3):259-269.[15] 刘波,董静,张骏飞,等.人脐带间充质干细胞治疗慢加急性肝衰竭患者近期疗效与安全性分析[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2013, 16(1):29-31.[16] Xue HL, Zeng WZ, Wu XL, et al. Clinical therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in the treatment of end-stage liver disease. Transplant Proc. 2015;47(2):412-418.[17] Qiao L, Xu Z, Zhao T, et al. Suppression of tumorigenesis by human mesenchymal stem cells in a hepatoma model. Cell Res. 2008;18(4):500-507.[18] Yan XL, Jia YL, Chen L, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma-associated mesenchymal stem cells promote hepatocarcinoma progression: role of the S100A4-miR155-SOCS1-MMP9 axis. Hepatology. 2013; 57(6):2274-2286.[19] 张杭杰. 间充质干细胞在原发性肝癌形成前和形成后的不同作用及机制研究[D]. 上海:第二军医大学, 2016.[20] Huang JF, Takayasu K, Okada S, et al. Primary hepatocellular carcinoma detected long after tumor markers and lymph node metastases--beyond our vision. Dig Dis Sci. 2006;51(3):610-615.[21] Li D, Mallory T, Satomura S. AFP-L3: a new generation of tumor marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Chim Acta. 2001;313(1-2):15-19.[22] Bae JS, Park SJ, Park KB, et al. Acute exacerbation of hepatitis in liver cirrhosis with very high levels of alpha-fetoprotein but no occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Intern Med. 2005;20(1):80-85.[23] Block TM, Comunale MA, Lowman M, et al. Use of targeted glycoproteomics to identify serum glycoproteins that correlate with liver cancer in woodchucks and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(3):779-784.[24] 周鸿,刘晔,陈炜,等. MELD评分在肝硬化患者预后评估中作用的临床研究[J]. 肝胆外科杂志, 2010,18(4):251-256.[25] 董怀平,王力,赵岐刚,等. AFU、AFP-L3、HCY联合检测对原发性肝癌早期诊断临床价值的研究[J].中国实验诊断学,2007, 11(4):485-487.[26] Taketa K, Sekiya C, Namiki M, et al. Lectin-reactive profiles of alpha-fetoprotein characterizing hepatocellular carcinoma and related conditions. Gastroenterology. 1990; 99(2):508-518.[27] Yamashita F, Tanaka M, Satomura S, et al. Prognostic significance of Lens culinaris agglutinin A-reactive alpha-fetoprotein in small hepatocellular carcinomas. Gastroenterology. 1996;111(4):996-1001.[28] Taketa K, Endo Y, Sekiya C, et al. A collaborative study for the evaluation of lectin-reactive alpha-fetoproteins in early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1993; 53(22):5419-5423.[29] 李鲁平,谷海峰,陈霖,等. 甲胎蛋白异质体L3对低浓度甲胎蛋白肝癌诊断的临床意义[J].中华实验和临床病毒学杂志,2013, 27(6):452-454.[30] Toyoda H, Kumada T, Tada T, et al. Changes in highly sensitive alpha-fetoprotein for the prediction of the outcome in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. Cancer Med. 2014;3(3):643-651.[31] Liaw YF, Sung JJ, Chow WC, et al. Lamivudine for patients with chronic hepatitis B and advanced liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(15):1521-1531.[32] Wong GL, Chan HL, Mak CW, et al. Entecavir treatment reduces hepatic events and deaths in chronic hepatitis B patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2013;58(5): 1537-1547.[33] Yu PF, Huang Y, Han YY, et al. TNFα-activated mesenchymal stromal cells promote breast cancer metastasis by recruiting CXCR2+ neutrophils. Oncogene. 2017;36(4):482-490. |
.jpg)
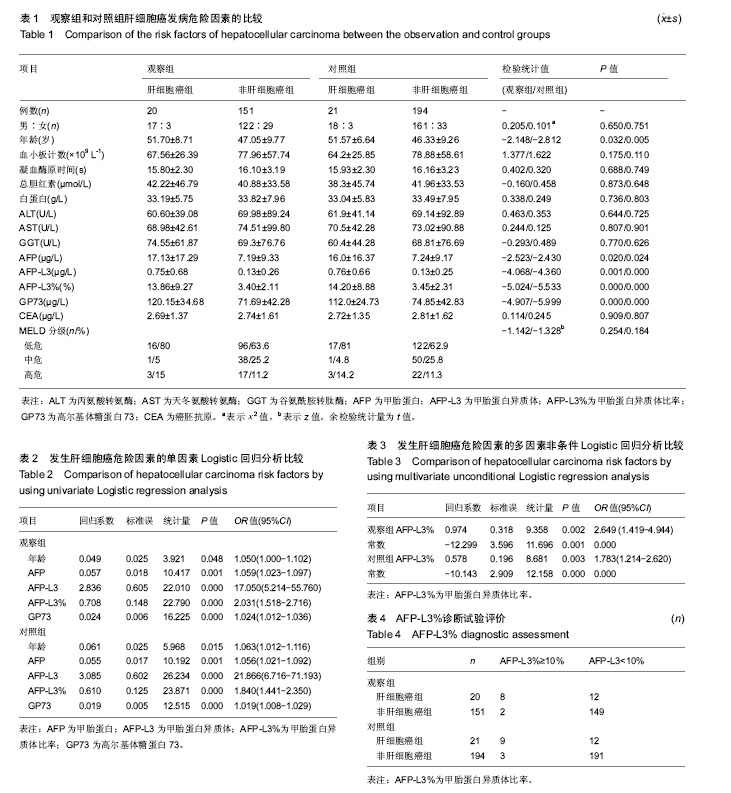
.jpg)
.jpg)