| [1] Hiwatari N, Shimura S, Sasaki T, et al. Prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in patients with mucous hypersecretion. Am Rev Respir Dis.1991;143(1):182-185.[2] Mannino DM, Etzel RA,Parrish RG.Pulmonary fibrosis deaths in the United States, 1979-1991. An analysis of multiple-cause mortality data. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;153(5):1548-1552.[3] Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.2011;183(6):788-824.[4] Thickett DR, Kendall C, Spencer LG, et al. Improving care for patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) in the UK: a round table discussion. Thorax. 2014;69(12):1136-1140.[5] Meltzer EB, Noble PW. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2008;3:8.[6] Coward WR, Saini G, Jenkins G. The pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Ther Adv Respir Dis.2010;4(6): 367-388.[7] Harari S, Caminati A. IPF: new insight on pathogenesis and treatment. Allergy. 2010;65(5):537-553.[8] Hardie WD, Glasser SW, Hagood JS. Emerging concepts in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis. Am J Pathol.2009;175(1):3-16.[9] B BM, Lawson WE, Oury TD, et al. Animal models of fibrotic lung disease. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013;49(2):167-179.[10] Muggia FM, Louie AC, Sikic BI. Pulmonary toxicity of antitumor agents. Cancer Treat Rev.1983;10(4):221-243.[11] Moore BB, Hogaboam CM. Murine models of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008;294(2): L152-160.[12] Chung MP, Monick MM, Hamzeh NY, et al. Role of repeated lung injury and genetic background in bleomycin-induced fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003;29(3 Pt 1):375-380.[13] Degryse AL, Tanjore H, Xu XC, et al. Repetitive intratracheal bleomycin models several features of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010;299(4): L442-452.[14] Adamson IY, Bowden DH. The pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am J Pathol. 1974;77(2):185-197.[15] Ekimoto H, Takahashi K, Matsuda A, et al. Experimentally induced bleomycin pulmonary toxicity--comparison of the systemic (intraperitoneal) and local (intratracheal) administration. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 1983;10(12): 2550-2557.[16] Harrison JH Jr, Lazo JS. Plasma and pulmonary pharmacokinetics of bleomycin in murine strains that are sensitive and resistant to bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988;247(3):1052-1058.[17] 肖强,郑晓滨,刘香,等. 静脉注射不同剂量博莱霉素诱导小鼠肺纤维化的比较研究[J]. 临床肺科杂志,2015,20(2):251-255,256.[18] Szapiel SV, Elson NA, Fulmer JD, et al. Bleomycin-induced interstitial pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis.1979;120(4):893-899.[19] Hubner RH, Gitter W, El Mokhtari NE, et al. Standardized quantification of pulmonary fibrosis in histological samples. Biotechniques. 2008;44(4):507-511, 514-507.[20] Chen YL, Lv J, Ye XL, et al. Sorafenib inhibits transforming growth factor beta1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and apoptosis in mouse hepatocytes. Hepatology. 2011;53(5):1708-1718.[21] 郑家概,王飞,农云军,等.柱前衍生高效液相色谱法对动物组织中胶原蛋白的测定[J]. 分析测试学报. 2008;27(12):1383-1385.[22] Degryse AL, Lawson WE. Progress toward improving animal models for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Med Sci. 2011;341(6):444-449.[23] Davis GS, Leslie KO, Hemenway DR. Silicosis in mice: effects of dose, time, and genetic strain. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 1998;17(2):81-97.[24] Piguet PF, Collart MA, Grau GE, et al.Requirement of tumour necrosis factor for development of silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Nature. 1990;344(6263):245-247.[25] Barbarin V, Nihoul A, Misson P, et al.The role of pro- and anti-inflammatory responses in silica-induced lung fibrosis. Respir Res. 2005;6112.[26] Walkin L, Herrick SE, Summers A, et al.The role of mouse strain differences in the susceptibility to fibrosis: a systematic review. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2013;6(1):18.[27] Huaux F, Liu T, McGarry B, et al. Dual roles of IL-4 in lung injury and fibrosis. J Immunol. 2003;170(4):2083-2092.[28] Reid LM. Needs for animal models of human diseases of the respiratory system. Am J Pathol. 1980;101(3 Suppl):S89-101.[29] Hashimoto N, Jin H, Liu T, et al. Bone marrow-derived progenitor cells in pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2004; 113(2):243-252.[30] Park SH, Saleh D, Giaid A, et al. Increased endothelin-1 in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis and the effect of an endothelin receptor antagonist. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1997;156(2 Pt 1):600-608.[31] 孟婕,彭张哲,陶立坚.小剂量多次尾静脉注射与气管内滴注博来霉素致小鼠肺纤维化模型的比较研究[J].中南大学学报:医学版,2013(12):1228-1232.[32] 涂常力,刘香,郑晓滨,等.静脉注射博来霉素诱导肺纤维化模型小鼠的稳定性评价[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(40): 6436-6443.[33] Hashimoto S, Gon Y, Takeshita I, et al. Transforming growth Factor-beta1 induces phenotypic modulation of human lung fibroblasts to myofibroblast through a c-Jun-NH2-terminal kinase-dependent pathway. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163(1):152-157.[34] Denney L, Byrne AJ, Shea TJ, et al. Pulmonary Epithelial Cell-Derived Cytokine TGF-beta1 Is a Critical Cofactor for Enhanced Innate Lymphoid Cell Function. Immunity. 2015; 43(5):945-958.[35] Sheppard D. Transforming growth factor beta: a central modulator of pulmonary and airway inflammation and fibrosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2006;3(5):413-417.[36] Woods LT, Camden JM, El-Sayed FG, et al. Increased Expression of TGF-beta Signaling Components in a Mouse Model of Fibrosis Induced by Submandibular Gland Duct Ligation. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0123641.[37] Milara J, Navarro R, Juan G, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate is increased in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and mediates epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Thorax. 2012; 67(2):147-156.[38] Border WA, Noble NA. Transforming growth factor beta in tissue fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 1994;331(19):1286-1292.[39] Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, et al. The myofibroblast: one function, multiple origins. Am J Pathol. 2007;170(6): 1807-1816.[40] Barkauskas CE, Noble PW. Cellular mechanisms of tissue fibrosis. 7. New insights into the cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014;306(11): C987-996. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
肺纤维化:是以成纤维细胞增殖及大量细胞外基质聚集并伴炎症损伤、组织结构破坏为特征的一类肺疾病的终末期改变。肺纤维化严重影响呼吸功能,临床表现为干咳、进行性呼吸困难。
博来霉素:别名争光霉素,是一种广谱抗肿瘤药。注射给药后,在血中消失较快,广泛分布到各组织器官中,尤以肺和皮肤较多,因这两种器官细胞的酰胺酶活性低,博来霉素水解失活少,常蓄积导致毒副作用,例如肺纤维化,故博来霉素成为诱导动物肺纤维化模型的常用药物之一。
文题释义:
肺纤维化:是以成纤维细胞增殖及大量细胞外基质聚集并伴炎症损伤、组织结构破坏为特征的一类肺疾病的终末期改变。肺纤维化严重影响呼吸功能,临床表现为干咳、进行性呼吸困难。
博来霉素:别名争光霉素,是一种广谱抗肿瘤药。注射给药后,在血中消失较快,广泛分布到各组织器官中,尤以肺和皮肤较多,因这两种器官细胞的酰胺酶活性低,博来霉素水解失活少,常蓄积导致毒副作用,例如肺纤维化,故博来霉素成为诱导动物肺纤维化模型的常用药物之一。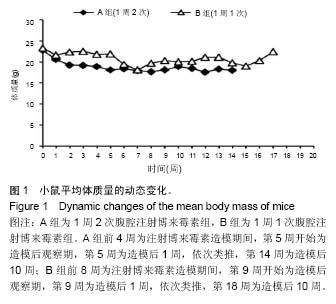
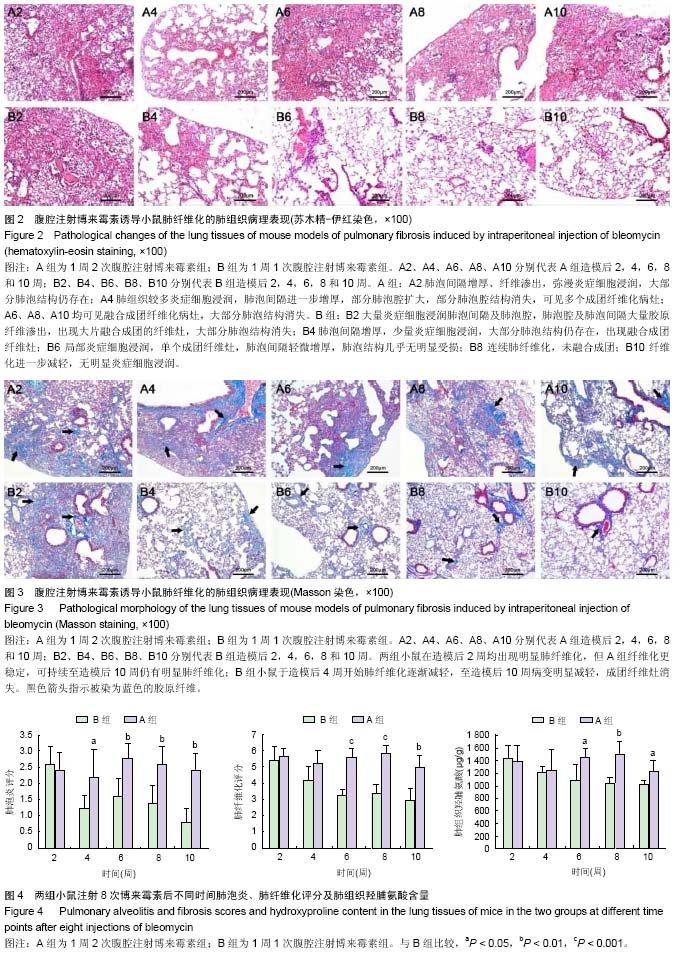

.jpg) 文题释义:
肺纤维化:是以成纤维细胞增殖及大量细胞外基质聚集并伴炎症损伤、组织结构破坏为特征的一类肺疾病的终末期改变。肺纤维化严重影响呼吸功能,临床表现为干咳、进行性呼吸困难。
博来霉素:别名争光霉素,是一种广谱抗肿瘤药。注射给药后,在血中消失较快,广泛分布到各组织器官中,尤以肺和皮肤较多,因这两种器官细胞的酰胺酶活性低,博来霉素水解失活少,常蓄积导致毒副作用,例如肺纤维化,故博来霉素成为诱导动物肺纤维化模型的常用药物之一。
文题释义:
肺纤维化:是以成纤维细胞增殖及大量细胞外基质聚集并伴炎症损伤、组织结构破坏为特征的一类肺疾病的终末期改变。肺纤维化严重影响呼吸功能,临床表现为干咳、进行性呼吸困难。
博来霉素:别名争光霉素,是一种广谱抗肿瘤药。注射给药后,在血中消失较快,广泛分布到各组织器官中,尤以肺和皮肤较多,因这两种器官细胞的酰胺酶活性低,博来霉素水解失活少,常蓄积导致毒副作用,例如肺纤维化,故博来霉素成为诱导动物肺纤维化模型的常用药物之一。