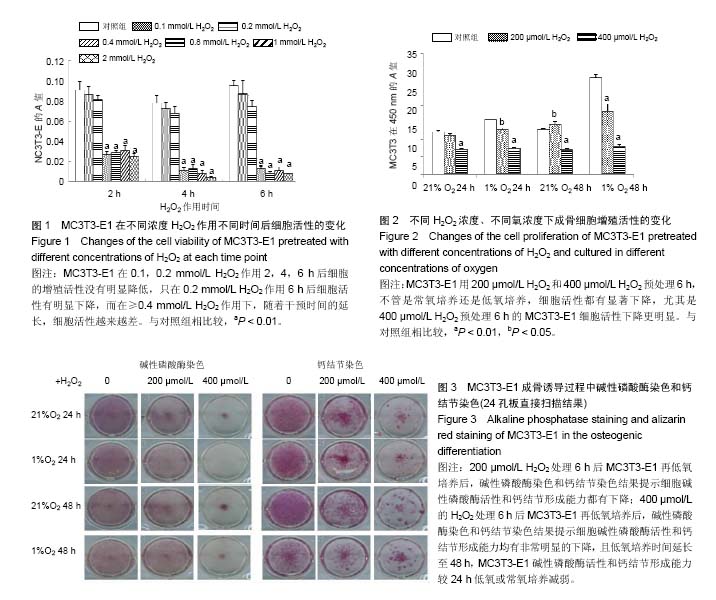
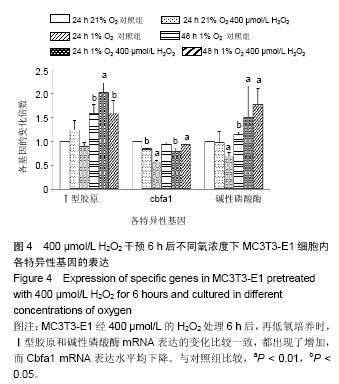
| [1] Harman D. The free radical theory of aging: the effect of age on serum mercaptan levels. J Gerontol. 1960;15:38-40.[2] Diana Hoogeboom D, Burgering BM. Should I stay or should I go: β-catenin decides under stress. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1796(2):63-74. [3] Sun L, Zhang J, Fang K,et al. Flavonoids from persimmon (Diospyros kaki) leaves (FPL) attenuate H2O2-induced apoptosis in MC3T3-E1 cells via the NF-kB pathway. Food Funct. 2014;5(3):471-479.[4] Pawaputanon Na Mahasarakham C, Izu Y, Nishimori Ket, al.Lgr4 expression in osteoblastic cells is suppressed by hydrogen peroxide treatment. J Cell Physiol. 2016. [Epub ahead of print][5] Wauquier F, Leotoing L, Coxam V, et al. Oxidative stress in bone remodeling and disease. Trends Mol Med.2009; 15(10): 468-477.[6] Holmquist-Mengelbier L, Fredlund E, Lofstedt T, et al. Recruitment of HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha to common target genes is differentially regulated in neuroblastoma: HIF-2alpha promotes an aggressive phenotype. Cancer Cell. 2006; 10(5): 413-423.[7] Guo S, Miyake M, Liu KJ, et al. Specific inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor 1 exaggerates cell injury induced by in vitro ischemia through deteriorating cellular redox environment.J Neurochem. 2009;108(5):1309-1321. [8] Stegen S, van Gastel N, Eelen G,et al. HIF-1α Promotes Glutamine-Mediated Redox Homeostasis and Glycogen-Dependent Bioenergetics to Support Postimplantation Bone Cell Survival. Cell Metab. 2016;23(2):265-279.[9] Chandel NS, Maltepe E, Goldwasser E, et al. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species trigger hypoxiainduced transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1998; 95(20):11715-11720.[10] Chavez A, Miranda LF, Pichiule P, et al. Mitochondria and Hypoxia-induced Gene Expression Mediated by Hypoxia-inducible Factors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1147: 312-320. [11] Nouri F, Salehinejad P, Nematollahi-Mahani SN,et al. Deferoxamine Preconditioning of Neural-Like Cells Derived from Human Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells as a Strategy to Promote Their Tolerance and Therapeutic Potential: An In Vitro Study. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016;36(5):689-700.[12] Hamada S, Sato A, Hara-Chikuma M, et al. Role of mitochondrial hydrogen peroxide induced by intermittent hypoxia in airway epithelial wound repair in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 2016;344(1):143-151.[13] Wang N, Wang F, Gao Y,et al. Curcumin protects human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells against oxidative stress-induced inhibition of osteogenesis. J Pharmacol Sci. 2016;132(3):192-200.[14] Fu C, Xu D, Wang CY, et al. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Promotes Osteoblastic Formation in H2O2 -Treated MC3T3-E1 Cells and Prevents Bone Loss in Ovariectomized Rats. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230(9):2184-2201.[15] Gómez-Puerto MC, Verhagen LP, Braat AK,et al. Activation of autophagy by FOXO3 regulates redox homeostasis during osteogenic differentiation. Autophagy. 2016;12(10):1804-1816.[16] Yang YH, Li B, Zheng XF,et al. Oxidative damage to osteoblasts can be alleviated by early autophagy through the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway--implications for the treatment of osteoporosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;77:10-20. [17] Wang L, Zhang YG, Wang XM,et al. Naringin protects human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced inhibition of osteogenic differentiation. Chem Biol Interact. 2015;242:255-261.[18] Lykov AP, Nikonorova YV, Bondarenko NA, et al. Proliferation, Migration, and Production of Nitric Oxide by Bone Marrow Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Wistar Rats in Hypoxia and Hyperglycemia. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2015;159(4): 443-445.[19] Cindrova-Davies T, van Patot MT, Gardner L,et al. Energy status and HIF signalling in chorionic villi show no evidence of hypoxic stress during human early placental development. Mol Hum Reprod. 2015;21(3):296-308.[20] Hao Z, Ma Y, Wang J,et al. Hypoxia promotes AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and induces apoptosis in mouse osteoblasts. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(5):4892-4902. [21] Wang L, Wu B, Zhang Y,et al. Hypoxia promotes the proliferation of MC3T3-E1 cells via the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(4): 5267-5273.[22] Xu G, Xue M, Wang H,et al.Hypoxia inducible factor 1α antagonizes the hypoxia mediated osteoblast cell viability reduction by inhibiting apoptosis. Exp Ther Med. 2015;9(5): 1801-1806.[23] Lee D, Kook SH, Ji H,et al. N-acetyl cysteine inhibits H2O2-mediated reduction in the mineralization of MC3T3-E1 cells by down-regulating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.BMB Rep. 2015; 48(11): 636-641.[24] Liu AL, Zhang ZM, Zhu BF, et al. Metallothionein protects bone marrow stromal cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced inhibition of osteoblastic differentiation. Cell Biol Int. 2004; 28(12):905-911.[25] Bai XC, Lu D, Bai J, et al. Oxidative stress inhibits osteoblastic differentiation of bone cells by ERK and NF-kappaB. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 314 (1):197-207.[26] Arai M, Shibata Y, Pugdee K, et al. Effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS) on antioxidant system and osteoblastic differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells. IUBMB Life. 2007; 59 (1): 27-33.[27] Linares GR, Xing W, Govoni KE, et al. Glutaredoxin 5 regulates osteoblast apoptosis by protecting against oxidative stress. Bone. 2009; 44 (5): 795-804[28] Ralph SJ,Rodríguez-Enríquez S,Neuzil J, et al. The causes of cancer revisited: ‘‘Mitochondrial malignancy” and ROS-induced oncogenic transformation – Why mitochondria are targets for cancer therapy. Mol Aspects Med. 2010;31(2): 145-170.[29] Utting JC, Robins SP, Brandao-Burch A,et al. Hypoxia inhibits the growth, differentiation and bone-forming capacity of rat osteoblasts. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(10):1693-1702. [30] McCarthy TL, Yun Z, Madri JA, et al. Stratified control of IGF-I expression by hypoxia and stress hormones in osteoblasts。Gene. 2014;539(1):141-151.[31] Fan L,Zhang C,Yu Z, et al. Transplantation of hypoxia preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhances angiogenesis and osteogenesis in rabbit femoral head osteonecrosis. Bone.2015;81:544-553.[32] Salim A, Nacamuli RP, Morgan EF, et al. Transient changes in oxygen tension inhibit osteogenic differentiation and Runx2 expression in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279(38): 40007-40016. [33] Moon EJ, Sonveaux P, Porporato PE, et al. NADPH oxidase-mediated reactive oxygen species production activates hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) via the ERK pathway after hyperthermia treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107(47):20477-20482. [34] Chang S, Jiang X, Zhao C, et al. Exogenous low dose hydrogen peroxide increases hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha protein expression and induces preconditioning protection against ischemia in primary cortical neurons.Neurosci Lett. 2008; 441(1):134-138. [35] Wallace DC Colloquium paper: bioenergetics, the origins of complexity, and the ascent of man. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107 Suppl 2:8947-8953.[36] Horak P, Crawford AR, Vadysirisack DD, et al. Negative feedback control of HIF-1 through REDD1-regulated ROS suppresses tumorigenesis. Proc Nat1 Acad USA.2010; 107(10): 4675-4680. [37] Kaelin WG Jr, Ratcliffe PJ. Oxygen sensing by metazoans: the central role of the HIF hydroxylase pathway. Mol Cell. 2008;30(4):393-402. [38] Sasabe E, Yang Z, Ohno S, et al. Reactive oxygen species produced by the knockdown of manganese-superoxide dismutase up-regulatehypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;48(10):1321-1329.[39] Cao B, Chai C, Zhao S.Protective effect of Edaravone against hypoxia-induced cytotoxicity in osteoblasts MC3T3-E1 cells. IUBMB Life. 2015;67(12):928-933. [40] Movafagh S, Crook S, Vo K. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1a by reactive oxygen species: new developments in an old debate. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(5):696-703. |
.jpg)
.jpg)