| [1] Fonseca H,Moreira-Goncalves D,Coriolano HJ,et al.Bone quality: the determinants of bone strength and fragility. Sports Med.2014;44(1):37-53.[2] Raisz LG. Pathogenesis of osteoporosis: concepts, conflicts, and prospects.J Clin Invest.2005;115(12):3318-3325.[3] Coipeau P,Rosset P,Langonne A,et al.Impaired differentiation potential of human trabecular bone mesenchymal stromal cells from elderly patients.Cytotherapy.2009;11(5): 584-594.[4] Lill CA,Hesseln J,Schlege lU,etal.Biomechanical evaluation of healing in a non-critical defect in a large animal model of osteoporosis.JOrthop Res.2003;21(5):836-842.[5] Nikolaou VS, Efstathopoulos N, Kontakis G, et al.The influence of osteoporosis in femoral fracture healing time. Injury.2009;40(6):663-668.[6] Rachner TD, Khosla S, Hofbauer LC.et al.Osteoporosis: now and the future. Lancet. 2011;377(9773):1276-1287.[7] Eldesoqi K,Henrich D, El-Kady AM,e tal.Safety Evaluation of a Bioglass–Polylactic Acid Ctrlmposite Scaffold Seeded with Progenitor Cells in a Rat Skull Critical-Size Bone Defect. PLoS One.2014;9(2):1-13.[8] 毕志伟,黄东,欧阳海洋,等.同种异体骨移植治疗骨缺损的应用研究进展[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2014,32(5):623-625.[9] Kwan MD,Sellmyer MA,Quarto N, et al.Chemical control of FGF-2 release forpromotingcalvarial healing with adipose stem cells. J Biol Chem.2011;286(13): 11307-11313.[10] Pigossi SC,de Oliveira GJ,Finoti LS,et al.Bacterial cellulose- hydroxyapatite composites with osteogenic growth peptide (OGP) or pentapeptide OGP on bone regeneration in critical-size calvarial defect model. J Biomed Mater Res A.2015;103(10): 3397-3406.[11] Liu YS, Ou ME, Liu H, et al. The effect of simvastatin on chemotactic capability of SDF-1alpha and the promotion of bone regeneration. Biomaterials.2014;35(15): 4489-4498.[12] 徐伟,谢杨丽,翁土军,等.Wnt信号参与小鼠颅骨缺损后骨形成过程的初步研究[J].第三军医大学学报, 2014,36(8): 785-788.[13] Li S, Huang KJ, Wu JC,et al. Peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells: candidate cells responsible for healing critical-sizedcalvarial bone defects. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(4):359-368.[14] Yi Liu, Ruili Yang, Songtao Shi, et al. Systemic Infusion of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves Cell-Based Bone Regeneration via Upregulation of Regulatory T Cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(3-4): 498-509.[15] Zheng RC, Park YK, Kim SK,et al. Bone Regeneration of Blood-derived Stem Cells within Dental Implants. J Dent Res. 2015;94(9):1318-1325.[16] Gupta DM, Kwan M D, Slater BJ, et al. Applications of an athymic nude mouse model of nonhealing critical-sized calvarial defects. J Craniofac Surg.2008;19(1):192-197.[17] SavillePD.Changes in skeletal mass and fragility with castration in the rat:a model of osteoporosis.J Am Geriatr Soc.1969;17(2):155-166.[18] 何柳,王然,王晓文,等.低强度脉冲超声对骨质疏松症小鼠模型的作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(6):657-660.[19] Bliuc D, NguyenND, Nguyen TV, et al. Compound risk of high mortality following osteoporotic fracture and refracture in elderly women and men. J Bone Miner Res.2013;28(11): 2317-2324.[20] Rokn AR, Shakeri AS, Etemad-Moghadam S, et al. Regenerative Effects of Three Types of Allografts on Rabbit Calvarium: An Animal Study.J Dent (Tehran).2015;12(11): 823-834.[21] Felsenberg D,Boonen S.The bone quality framework:determinants of bone strength and their interrelationships and implications for osteoporosis management.Clin Ther.2005; 27(1):1-11.[22] 杨其芬,邵秉一,杨德琴,等. OP小鼠模型的建立及其骨髓贴壁基质细胞体外增殖活性的初步研究[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2015, 19(1),1966-1971.[23] Li Y, Fan L, Hu J,et.al. MiR-26a Rescues Bone Regeneration Deficiency of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived From Osteoporotic. Mol Ther.2015;23(8):1349-57.[24] Azuma K, Furuzawa M, Fujiwara S.et al.Effects of Active Mastication on Chronic Stress-Induced Bone Loss in Mice. Int J Med Sci. 2015; 12(12): 952-957.[25] Riggs BL, Khosla S, Melton LJ 3rd.Sex steroids andthe construction and conservation of the adult skeleton. Endocr Rev. 2002;23(3):279-302.[26] Wang L, Huang C, Li Q, et al.Osteogenic differentiation potential of adipose-derived stem cells from ovariectomized mice.Cell Prolif. 2017 Apr;50(2). doi: 10.1111/cpr.12328.[27] Zhang Y, Wang L, Deng F, et al. Determination of a critical size calvarial defect in senile osteoporotic mice model based on in vivo micro-computed tomography and histological evaluation. Arch Gerontol Geriatr.2015; 61(1): 44-55.[28] 胡宜成,刘鑫,沈际佳,等.犬骨髓间充质干细胞复合磷酸钙骨水泥修复骨缺损的实验研究 [J].上海口腔医学, 2014, 23(4): 402-408.[29] Wang X, Ackermann M, Wang S, et al. Amorphous polyphosphate/amorphous calcium carbonate implant material with enhanced bone healing efficacy in a critical-size defect in rats. Biomed Mater.2016;11(3): 035005.[30] Wang Z, Hu H, Li Z, et al. Sheet of osteoblastic cells combined with platelet-rich fibrin improves the formation of bone in critical-size calvarial defects in rabbits. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2016;54(3): 316-321.[31] 甘宁,郁雪松,陈军,等.杨梅素减轻去卵巢大鼠OP [J].第三军医大学学报,2016, 38(6): 614-618.[32] 唐宇星,赵庆,杨中萌,等.音猬因子修饰纳米晶胶原基骨复合骨髓间充质干细胞修复股骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017,21(14):2180-2185[33] Chen J, Yu J, He Q, et al. A novel injectable porous surface modified bioactive bone cement for vertebroplasty: an in vivo biomechanical and osteogenic study in a rabbit osteoporosis model. Am J Transl Res.2015;7(3): 548.[34] Costa L, Lopes B, Lanis A, et al. Bone demineralization in the lumbar spine of dogs submitted to prednisone therapy. J Vet PharmacolTher. 2010; 33(6): 583-586.[35] Schmitz JP, Hollinger JO. The critical size defect as an experimental model for craniomandibulofacialnonunions . ClinOrthopRelat Res.1986;2(05): 299-308.[36] Choi H,Jeong BC,Hur SW, et al.The Angiopoietin-1 Variant COMP-Ang1 Enhances BMP2-Induced Bone Regeneration with Recruiting Pericytes in Critical Sized Calvarial Defects. PLoS One. 2015; 10(10): e0140502.[37] Qureshi AT,Doyle A,Chen C,et al.Photoactivated miR-148b-nanoparticle conjugates improve closure of critical size mouse calvarial defects.Acta Biomater. 2015;12: 166-173.[38] Das A, Segar CE, Hughley BB, et al. The promotion of mandibular defect healing by the targeting of S1P receptors and the recruitment of alternatively activated macrophages. Biomaterials.2013;34(38): 9853-9862.[39] 靳慧勇,侯天勇,罗飞,等.小鼠股骨临界骨缺损模型的构建及评估 [J].第三军医大学学报, 2011, 33(22): 2331-2334. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨极量缺损:又称之为临界骨缺损(Critical size defect,CSD),是指动物依靠自身修复能力不能恢复的最小骨缺损。其目的是减少因动物的年龄、种系、骨缺损所在部位不同等因素对骨缺损愈合的影响,排除自身混杂因素的干扰,从而使建立的骨缺损模型更加地可靠。Gupta等研究确定小鼠颅骨极量缺损为4 mm。
微计算机断层扫描技术(micro computed tomography,Micro-CT):又称微型CT、显微CT,是一种非破坏性的3D成像技术,可以在不破坏样本的情况下清楚了解样本的内部显微结构。它与普通临床的CT最大的差别在于分辨率极高,可以达到微米(μm)级别,目前国内一家自主研发Micro-CT的公司已经将分辨率提高到0.5 μm,具有良好的“显微”作用。Micro-CT可用于医学、药学、生物、考古、材料、电子、地质学等领域的研究。
文题释义:
骨极量缺损:又称之为临界骨缺损(Critical size defect,CSD),是指动物依靠自身修复能力不能恢复的最小骨缺损。其目的是减少因动物的年龄、种系、骨缺损所在部位不同等因素对骨缺损愈合的影响,排除自身混杂因素的干扰,从而使建立的骨缺损模型更加地可靠。Gupta等研究确定小鼠颅骨极量缺损为4 mm。
微计算机断层扫描技术(micro computed tomography,Micro-CT):又称微型CT、显微CT,是一种非破坏性的3D成像技术,可以在不破坏样本的情况下清楚了解样本的内部显微结构。它与普通临床的CT最大的差别在于分辨率极高,可以达到微米(μm)级别,目前国内一家自主研发Micro-CT的公司已经将分辨率提高到0.5 μm,具有良好的“显微”作用。Micro-CT可用于医学、药学、生物、考古、材料、电子、地质学等领域的研究。.jpg) 文题释义:
骨极量缺损:又称之为临界骨缺损(Critical size defect,CSD),是指动物依靠自身修复能力不能恢复的最小骨缺损。其目的是减少因动物的年龄、种系、骨缺损所在部位不同等因素对骨缺损愈合的影响,排除自身混杂因素的干扰,从而使建立的骨缺损模型更加地可靠。Gupta等研究确定小鼠颅骨极量缺损为4 mm。
微计算机断层扫描技术(micro computed tomography,Micro-CT):又称微型CT、显微CT,是一种非破坏性的3D成像技术,可以在不破坏样本的情况下清楚了解样本的内部显微结构。它与普通临床的CT最大的差别在于分辨率极高,可以达到微米(μm)级别,目前国内一家自主研发Micro-CT的公司已经将分辨率提高到0.5 μm,具有良好的“显微”作用。Micro-CT可用于医学、药学、生物、考古、材料、电子、地质学等领域的研究。
文题释义:
骨极量缺损:又称之为临界骨缺损(Critical size defect,CSD),是指动物依靠自身修复能力不能恢复的最小骨缺损。其目的是减少因动物的年龄、种系、骨缺损所在部位不同等因素对骨缺损愈合的影响,排除自身混杂因素的干扰,从而使建立的骨缺损模型更加地可靠。Gupta等研究确定小鼠颅骨极量缺损为4 mm。
微计算机断层扫描技术(micro computed tomography,Micro-CT):又称微型CT、显微CT,是一种非破坏性的3D成像技术,可以在不破坏样本的情况下清楚了解样本的内部显微结构。它与普通临床的CT最大的差别在于分辨率极高,可以达到微米(μm)级别,目前国内一家自主研发Micro-CT的公司已经将分辨率提高到0.5 μm,具有良好的“显微”作用。Micro-CT可用于医学、药学、生物、考古、材料、电子、地质学等领域的研究。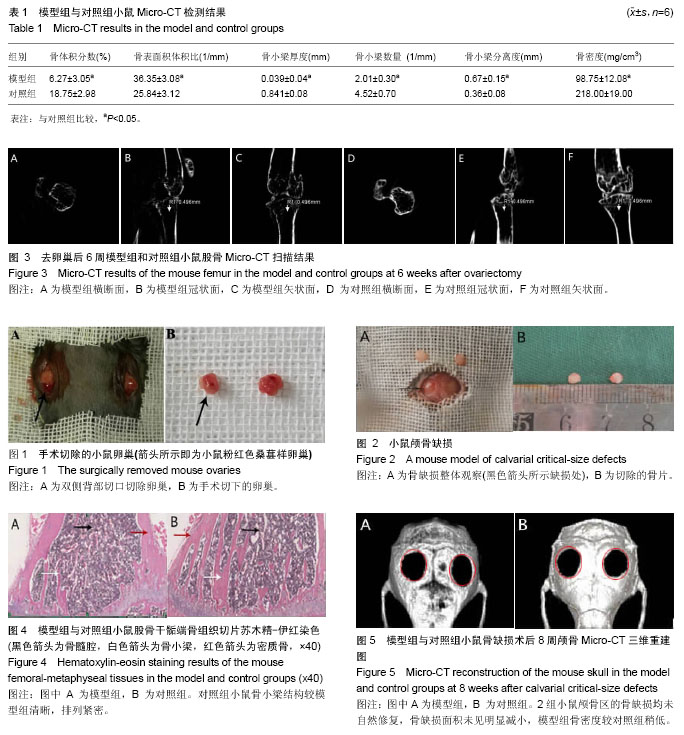
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨极量缺损:又称之为临界骨缺损(Critical size defect,CSD),是指动物依靠自身修复能力不能恢复的最小骨缺损。其目的是减少因动物的年龄、种系、骨缺损所在部位不同等因素对骨缺损愈合的影响,排除自身混杂因素的干扰,从而使建立的骨缺损模型更加地可靠。Gupta等研究确定小鼠颅骨极量缺损为4 mm。
微计算机断层扫描技术(micro computed tomography,Micro-CT):又称微型CT、显微CT,是一种非破坏性的3D成像技术,可以在不破坏样本的情况下清楚了解样本的内部显微结构。它与普通临床的CT最大的差别在于分辨率极高,可以达到微米(μm)级别,目前国内一家自主研发Micro-CT的公司已经将分辨率提高到0.5 μm,具有良好的“显微”作用。Micro-CT可用于医学、药学、生物、考古、材料、电子、地质学等领域的研究。
文题释义:
骨极量缺损:又称之为临界骨缺损(Critical size defect,CSD),是指动物依靠自身修复能力不能恢复的最小骨缺损。其目的是减少因动物的年龄、种系、骨缺损所在部位不同等因素对骨缺损愈合的影响,排除自身混杂因素的干扰,从而使建立的骨缺损模型更加地可靠。Gupta等研究确定小鼠颅骨极量缺损为4 mm。
微计算机断层扫描技术(micro computed tomography,Micro-CT):又称微型CT、显微CT,是一种非破坏性的3D成像技术,可以在不破坏样本的情况下清楚了解样本的内部显微结构。它与普通临床的CT最大的差别在于分辨率极高,可以达到微米(μm)级别,目前国内一家自主研发Micro-CT的公司已经将分辨率提高到0.5 μm,具有良好的“显微”作用。Micro-CT可用于医学、药学、生物、考古、材料、电子、地质学等领域的研究。