| [1]Yudianti R, Indrarti L. Effect of Water Soluble Polymer on Structure and Mechanical Properties of Bacterial Cellulose Composites. J Applied Sci. 2008; 8(1):177-180.[2]Tercjak A, Gutierrez J, Barud HS, et al. Nano- and macroscale structural and mechanical properties of in situ synthesized bacterial cellulose/PEO-b-PPO-b-PEO biocomposites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(7): 4142-4150.[3]Hutchens S. Synthesis and initial characterization of a calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite-bacterial cellulose composite. Knoxville: University of Tennessee, 2004.[4]Ul-Islam M, Khan T, Park JK. Water holding and release properties of bacterial cellulose obtained by in situ and ex situ modification. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2012;88(2):596-603.[5]Ul-Islam M, Khan T, Park JK. Nanoreinforced bacterial cellulose-montmorillonite composites for biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2012;89(4):1189-1197.[6]Xiao L, Mai Y, He F, et al. Bio-based green composites with high performance from poly(lactic acid) and surface-modified microcrystalline cellulose. J Materials Chemistry. 2012; 22(31):15732-15739. [7]Fu L, Zhang J, Yang G. Present status and applications of bacterial cellulose-based materials for skin tissue repair. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;92(2):1432-1442.[8]Kowalska-Ludwicka K, Cala J, Grobelski B, et al. Modified bacterial cellulose tubes for regeneration of damaged peripheral nerves. Arch Med Sci. 2013;9(3):527-534.[9]Leitao AF, Silva JP, Dourado F, et al. Production and Characterization of a New Bacterial Cellulose/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) .Nanocomposite.Materials. 2013; 6(5):1956-1966.[10]Martins NCT, Freire CSR, Neto CP, et al. Antibacterial paper based on composite coatings of nanofibrillated cellulose and ZnO. Colloids & Surfaces A Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects. 2013;417(417):111-119.[11]Oshima T, Taguchi S, Ohe K, et al. Phosphorylated bacterial cellulose for adsorption of proteins. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2011; 83(2):953-958.[12]Chen S, Teng Q. Quantitative Immobilization of Phthalocyanine onto Bacterial Cellulose for Construction of a High-Performance Catalytic Membrane Reactor. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(7): E846. [13]Khamrai M, Banerjee SL, Kundu PP. Modified bacterial cellulose based self-healable polyeloctrolyte film for wound dressing application. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;174:580-590.[14]Lee YJ, An SJ, Bae EB, et al. The Effect of Thickness of Resorbable Bacterial Cellulose Membrane on Guided Bone Regeneration. Materials (Basel). 2017;10(3): E320.[15]Lin WC, Lien CC, Yeh HJ, et al. Bacterial cellulose and bacterial cellulose-chitosan membranes for wound dressing applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;94(1):603-611.[16]Cao Z, Luo X, Zhang H, et al. A facile and green strategy for the preparation of porous chitosan-coated cellulose composite membranes for potential applications as wound dressing. Cellulose. 2016; 23(2):1349-1361.[17]Zhang J, Rong J, Li W, et al. Preparation and characterization of bacterial cellulose/polyacrylamide hydrogel. Acta Polymerica Sinica. 2011;11(6):602-607.[18]Chang ST, Chen LC, Lin SB, et al. Nano-biomaterials application: Morphology and physical properties of bacterial cellulose/gelatin composites via crosslinking. Food Hydrocolloids. 2012;27(1):137-144.[19]Wan WK, Campbell G, Zhang ZF, et al. Optimizing the tensile properties of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel for the construction of a bioprosthetic heart valve stent. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002; 63(6):854-861.[20]Liu X, Wang X, Liu D. Recent development of the research on the structure effects and responsive mechanism of intelligent hydrogels. Chemistry. 2000;63(10):1-6.[21]Hassan CM, Peppas NA. Structure and applications of PVA hydrogels produced by conventional crosslinking or by freezing/thawing methods. Advance in Polymer Science. 2000;153:37-65.[22]Stauffer SR, Peppast NA. Poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels prepared by freezing-thawing cyclic processing.Polymer. 1992;33(18):3932-3936.[23]Stammen JA, Williams S, Ku DN, et al. Mechanical properties of a novel PVA hydrogel in shear and unconfined compression. Biomaterials. 2001;22(8):799-806.[24]Paradossi G, Cavalieri F, Chiessi E, et al. Poly(vinyl alcohol) as versatile biomaterial for potential biomedical applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2003;14(8):687-691.[25]杨巍威. 聚丙烯酰胺及衍生物/三钛酸纳米片层复合水凝胶的光催化制备及其性能[D]. 泉州:华侨大学, 2015.[26]孙黛楠. 水凝胶纳米复合材料的增强机理研究[D]. 南京:南京师范大学, 2015.[27]Gonzalez JS, Maiolo AS, Hoppe CE, et al. Composite Gels Based on Poly (Vinyl alcohol) for Biomedical Uses. Procedia Materials Science. 2012; 1(1):483-490.[28]Li WD, Rong JH, Lin ZD, et al. Preparation and characterization of bacterial cellulose reinforced pva/pvp hydrogels. Acta Polymerica Sinica. 2012; 12(4):357-364.[29]孙东平, 陈啸, 杨加志,等. 纳米细菌纤维素\聚乙烯醇\聚乙二醇多孔复合水凝胶:中国, CN105237925A[P]. 2016-01-13. [30]周玉惠. 细菌纤维素/聚乙烯醇复合材料的制备研究进展[J]. 胶体与聚合物, 2013,31(3):135-137.[31]Tang W, Jia S, Jia Y, et al. The influence of fermentation conditions and post-treatment methods on porosity of bacterial cellulose membrane. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 2010; 26(1):125-131. [32]Tang WH, Ma X, Jia YY, et al. Bacterial cellulose production by Acetobacter xylinum in static fed-batch culture. Food and Fermentation Industries. 2008; 34(2):21-23. [33]王彩霞, 洪枫. 细菌纤维素基复合水凝胶的制备及其评价[D]. 上海:东华大学,2013.[34]杜倩雯,陈琳,钟春燕,等. BC/PVA/PEG增强型复合水凝胶的制备及其表征[J]. 广东化工, 2014, 41(16):17-18.[35]Li WD, Rong JH, Lin ZD, et al. Preparation and characterization of bacterial cellulose reinforced PVA/PVP hydrogels. Acta Polymerica Sinica. 2012; 12(4):357-364.[36]Shah N, Ha JH, Park JK. Effect of reactor surface on production of bacterial cellulose and water soluble oligosaccharides by Glu-conacetobacter hansenii PJK. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering. 2010; 15(1): 110-118.[37]Ha JH, Park JK. Improvement of bacterial cellulose production in Acetobacter xylinum, using byproduct produced by Gluconacetobacter hansenii. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering. 2012; 29(5):563-566.[38]翁诗甫.傅里叶变换红外光谱分析[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2010.[39]胥杰龙. 改性明胶/聚丙稀酰胺复合水凝胶及其用于软骨缺损修复的研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学, 2016.[40]Kloxin AM, Kasko AM, Salinas CN, et al. Photodegradable hydrogels for dynamic tuning of physical and chemical properties. Science. 2009;324(5923):59-63.[41]林建明, 唐群委, 吴季怀, 等.高强度PAM/PVA互穿网络水凝胶的合成[J].华侨大学学报,2010,31(1):41-48.[42]Ma RY, Xiong DS, Miao F, et al. Novel PVP/PVA hydrogelsfor articular cartilage replacement. Materials Science & Engineering C. 2009; 29(6):1979-1983.Shi Y, Xiong D. Microstructure and friction properties of PVA/PVP hydrogels for articular cartilage repair as function of polymerization degree and polymer concentration. Wear. 2013; 305(1-2):280-285. |
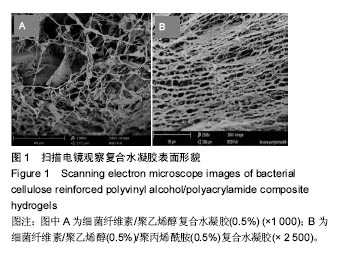
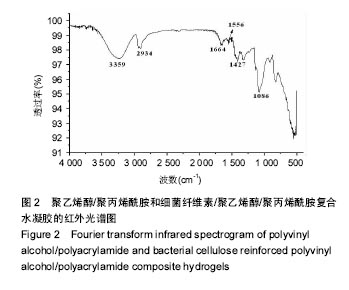
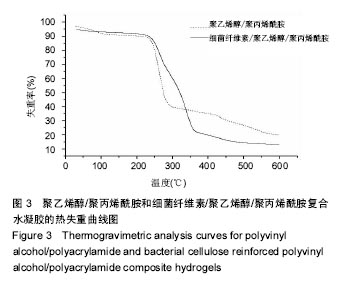
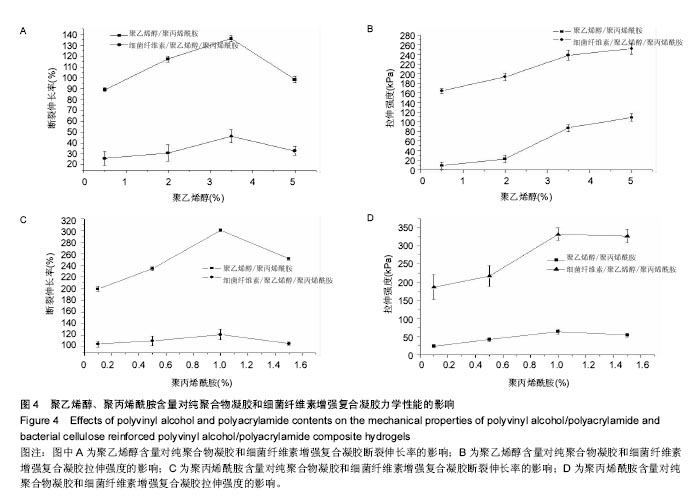
.jpg)
.jpg)