| [1]Wang X, Ren J, Zhu W, et al. Fibrin sealant prevents gastrointestinal anastomosis dehiscence in intra-abdominal sepsis. Int Surg. 2007;92(1):27-31.[2]Avalos-González J, Portilla-deBuen E, Leal-Cortés CA, et al. Reduction of the closure time of postoperative enterocutaneous fistulas with fibrin sealant. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(22):2793-2800.[3]Horowitz B, Busch M. Estimating the pathogen safety of manufactured human plasma products: application to fibrin sealants and to thrombin. Transfusion. 2008;48(8):1739-1753.[4]Chouhan VD, De La Cadena RA, Nagaswami C, et al. Simultaneous occurrence of human antibodies directed against fibrinogen, thrombin, and factor V following exposure to bovine thrombin: effects on blood coagulation, protein C activation and platelet function. Thromb Haemost. 1997;77(2):343-349.[5]Davoodi P, Ng WC, Yan WC, et al. Double-Walled Microparticles-Embedded Self-Cross-Linked, Injectable, and Antibacterial Hydrogel for Controlled and Sustained Release of Chemotherapeutic Agents.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(35):22785-22800.[6]Hong LTA, Kim YM, Park HH, et al. An injectable hydrogel enhances tissue repair after spinal cord injury by promoting extracellular matrix remodeling. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):533.[7]Zhuo F, Liu X, Gao Q, et al. Injectable hyaluronan- methylcellulose composite hydrogel crosslinked by polyethylene glycol for central nervous system tissue engineering.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;81:1-7.[8]Zhou T, Li X, Li G, et al. Injectable and thermosensitive TGF-β1-loaded PCEC hydrogel system for in vivo cartilage repair. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):10553.[9]Gullbrand SE, Schaer TP, Agarwal P, et al. Translation of an injectable triple-interpenetrating-network hydrogel for intervertebral disc regeneration in a goat model. Acta Biomater. 2017;60:201-209.[10]Chen CH, Chen SH, Mao SH,et al. Injectable thermosensitive hydrogel containing hyaluronic acid and chitosan as a barrier for prevention of postoperative peritoneal adhesion. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;173:721-731.[11]Nguyen MK, Lee DS. Injectable biodegradable hydrogels. Macromol Biosci. 2010;10(6):563-579.[12]Bhattarai N, Gunn J, Zhang M. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(1):83-99.[13]Tan H, Ramirez CM, Miljkovic N, et al. Thermosensitive injectable hyaluronic acid hydrogel for adipose tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2009;30(36):6844-6853.[14]Gumera C, Rauck B, Wang Y. Materials for central nervous system regeneration: bioactive cues. Journal of Materials Chemistry. 2011; 21(20):7033-7051.[15]Lee KY, Mooney DJ. Hydrogels for tissue engineering. Chem Rev. 2001;101(7):1869-1879.[16]Xiao B, Lü S, Zhen C, et al. Self-reinforcing injectable hydrogel with both high water content and mechanical strength for bone repair. Chem Eng J. 2015; 288:546-556.[17]Pike DB, Cai S, Pomraning KR, et al. Heparin-regulated release of growth factors in vitro and angiogenic response in vivo to implanted hyaluronan hydrogels containing VEGF and bFGF. Biomaterials. 2006;27(30):5242-5251.[18]Liao X, Chen G, Jiang M. Hydrogels locked by molecular recognition aiming at responsiveness and functionality. Polymer Chemistry. 2012; 4(6):1733-1745.[19]Ngoenkam J, Faikrua A, Yasothornsrikul S, et al. Potential of an injectable chitosan/starch/beta-glycerol phosphate hydrogel for sustaining normal chondrocyte function. Int J Pharm. 2010;391(1-2):115-124.[20]Chiu YL, Chen SC, Su CJ, et al. pH-triggered injectable hydrogels prepared from aqueous N-palmitoyl chitosan: in vitro characteristics and in vivo biocompatibility. Biomaterials. 2009;30(28):4877-4888.[21]Zhang H, Qadeer A, Mynarcik D, et al. Delivery of rosiglitazone from an injectable triple interpenetrating network hydrogel composed of naturally derived materials. Biomaterials. 2011;32(3):890-898.[22]Marsich E, Borgogna M, Donati I, et al. Alginate/lactose-modified chitosan hydrogels: a bioactive biomaterial for chondrocyte encapsulation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;84(2):364-376.[23]Leor J, Tuvia S, Guetta V, et al. Intracoronary injection of in situ forming alginate hydrogel reverses left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in Swine. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009;54(11):1014-1023.[24]Sakai S, Hirose K, Moriyama K, et al. Control of cellular adhesiveness in an alginate-based hydrogel by varying peroxidase and H(2)O(2) concentrations during gelation. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(4):1446-1452.[25]Thomas R, Soumya KR, Mathew J, et al. Inhibitory effect of silver nanoparticle fabricated urinary catheter on colonization efficiency of Coagulase Negative Staphylococci. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2015;149:68-77.[26]刘蕊,沈蕾,栗茜,等. 新型表面镀银手术器械抗菌性能研究[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2011,21(12):713-715.[27]Suliman Y AO, Ali D, Alarifi S, et al. Evaluation of cytotoxic, oxidative stress, proinflammatory and genotoxic effect of silver nanoparticles in human lung epithelial cells. Environ Toxicol. 2015;30(2):149-160.[28]邓红梅. 坤泰胶囊联合纳米银抗菌水凝胶治疗老年性阴道炎的研究[J]. 中国医学创新, 2015,12(19):94-96.[29]郑允权,郭养浩,饶强,等. 纳米氯化银/壳聚糖抗菌敷料的制备及功能评价[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2016, 34 (2) :188-191.[30]Yu H, Xu X, Chen X, et al. Preparation and antibacterial effects of PVA‐PVP hydrogels containing silver nanoparticles. Journal of Applied Polymer Science. 2007; 103(1): 125-133.[31]Thomas V, Yallapu MM, Sreedhar B, et al. A versatile strategy to fabricate hydrogel-silver nanocomposites and investigation of their antimicrobial activity. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2007; 315(1):389-395.[32]Sun S, Wang L, Wang A. Adsorption properties of crosslinked carboxymethyl-chitosan resin with Pb(II) as template ions. J Hazard Mater. 2006;136(3):930-937.[33]Ito T, Yeo Y, Highley CB, et al. The prevention of peritoneal adhesions by in situ cross-linking hydrogels of hyaluronic acid and cellulose derivatives. Biomaterials. 2007;28(6):975-983.[34]Ruhela D, Riviere K, Szoka FC Jr. Efficient synthesis of an aldehyde functionalized hyaluronic acid and its application in the preparation of hyaluronan-lipid conjugates. Bioconjug Chem. 2006;17(5):1360-1363.[35]Jin Y, Dong S. One-pot synthesis and characterization of novel silver-gold bimetallic nanostructures with hollow interiors and bearing nanospikes. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 2003; 107(47): 12902-12905.[36]Yin B, Ma H, Wang S, et al. Electrochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles under protection of poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone). The Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 2003;107(34): 8898-8904. |
.jpg)
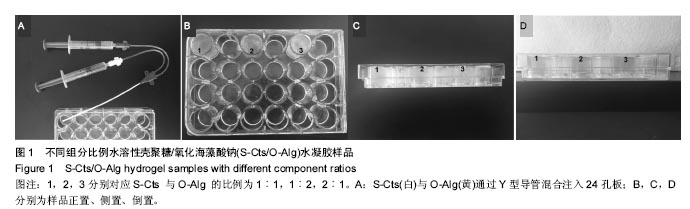
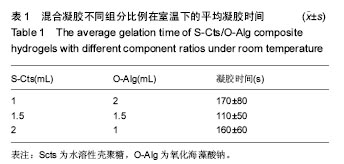
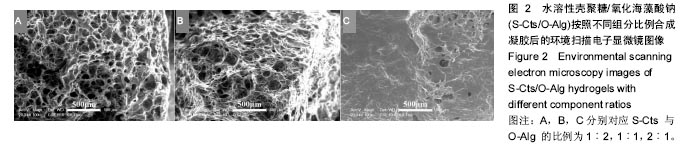
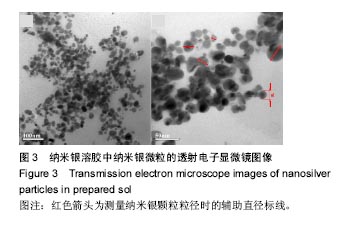

.jpg)