| [1]Mandapalli PK, Labala S, Jose A, et al. Layer-by-Layer Thin Films for Co-Delivery of TGF-β siRNA and Epidermal Growth Factor to Improve Excisional Wound Healing. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech. 2017;18(3):809-820. [2]Nakamichi M, Akishima-Fukasawa Y, Fujisawa C, et al. Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Induces Angiogenic Properties of Fibrocytes to Stimulate Vascular Formation during Wound Healing. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(12): 3203-3216.[3]Lord MS, Ellis AL, Farrugia BL, et al. Perlecan and vascular endothelial growth factor-encoding DNA-loaded chitosan scaffolds promote angiogenesis and wound healing. J Control Release. 2017;250:48-61.[4]丁韧,汤学明.创伤愈合的细胞生物学进展[J].创伤外科杂志, 2000,2(1):59.[5]王红梅,郭光华,曾小平,等.骨髓间充质干细胞靶向治疗大鼠烫伤创面愈合[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2010,32(1):69-72.[6]Lopez-Santalla M, Menta R, Mancheño-Corvo P, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells modulate experimental autoimmune arthritis by inducing an early regulatory innate cell signature. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2016;4(2):213-224.[7]De Jesus MM, Santiago JS, Trinidad CV, et al. Autologous Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for the Treatment of Psoriasis Vulgaris and Psoriatic Arthritis: A Case Report. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(11):2063-2069.[8]Riester SM, Denbeigh JM, Lin Y, et al. Safety Studies for Use of Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells in a Rabbit Model for Osteoarthritis to Support a Phase I Clinical Trial. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(3):910-922.[9]Panés J, García-Olmo D, Van Assche G, et al. Expanded allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (Cx601) for complex perianal fistulas in Crohn's disease: a phase 3 randomised, double-blind controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10051):1281-1290.[10]Staff NP, Madigan NN, Morris J, et al. Safety of intrathecal autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with ALS. Neurology. 2016;87(21):2230-2234.[11]Chen YW, Scutaru TT, Ghetu N, et al. The Effects of Adipose-Derived Stem Cell-Differentiated Adipocytes on Skin Burn Wound Healing in Rats. J Burn Care Res. 2017; 38(1):1-10.[12]闫飞,王曌华,刘艳玲,等.脐带间充质干细胞促进烫伤创面愈合的作用机制[J].中国生物制品学杂志,2016,29(10): 1047-1051.[13]Fang F, Huang RL, Zheng Y, et al. Bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the proliferative and profibrotic phenotype of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts and keloid fibroblasts through paracrine signaling. J Dermatol Sci. 2016;83(2):95-105.[14]Qu Y, Zhang Q, Cai X, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-181-5p-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells prevent liver fibrosis via autophagy activation. J Cell Mol Med. 2017 Apr 6. [Epub ahead of print][15]Hu L, Wang J, Zhou X, et al. Exosomes derived from human adipose mensenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 2016;6:32993.[16]Zhang J, La X, Fan L, et al. Immunosuppressive effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in rat burn models. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(5):5129-5136.[17]吴在德,吴肇汉. 外科学[M]. 7版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2008.[18]褚锋,刘建国,唐帆,等.小鼠Ⅲ度烧伤模型的复制及皮肤病理形态改变的动态观察[J].中国实验动物学报, 2009,17(3): 213-215.[19]Zhang K, Pei Y, Gan Z, et al. Local Administration of Thiamine Ameliorates Ongoing Pain in a Rat Model of Second-Degree Burn. J Burn Care Res. 2017 Feb 7. [Epub ahead of print][20]Lavertu M, Filion D, Buschmann MD. Heat-induced transfer of protons from chitosan to glycerol phosphate produces chitosan precipitation and gelation. Biomacromolecules. 2008;9(2):640-650.[21]Niranjan R, Koushik C, Saravanan S, et al. A novel injectable temperature-sensitive zinc doped chitosan/β-glycerophosphate hydrogel for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013;54:24-29.[22]Dhivya S, Saravanan S, Sastry TP, et al. Nanohydroxyapatite-reinforced chitosan composite hydrogel for bone tissue repair in vitro and in vivo. J Nanobiotechnology. 2015;13:40.[23]Cheng YH, Yang SH, Su WY, et al. Thermosensitive chitosan-gelatin-glycerol phosphate hydrogels as a cell carrier for nucleus pulposus regeneration: an in vitro study. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(2):695-703.[24]Kiyozumi T, Kanatani Y, Ishihara M, et al. Medium (DMEM/F12)-containing chitosan hydrogel as adhesive and dressing in autologous skin grafts and accelerator in the healing process. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2006;79(1):129-136.[25]Kiyozumi T, Kanatani Y, Ishihara M, et al. The effect of chitosan hydrogel containing DMEM/F12 medium on full-thickness skin defects after deep dermal burn. Burns. 2007;33(5):642-648.[26]Hu MS, Maan ZN, Wu JC, et al. Tissue engineering and regenerative repair in wound healing. Ann Biomed Eng. 2014;42(7):1494-1507.[27]Ud-Din S, Volk SW, Bayat A. Regenerative healing, scar-free healing and scar formation across the species: current concepts and future perspectives. Exp Dermatol. 2014;23(9):615-619.[28]Dahiya P. Burns as a model of SIRS. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009;14:4962-4967.[29]Silva L, Garcia L, Oliveira B, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome in burn patients: incidence and risk factor analysis. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2016;29(3): 178-182.[30]Kim A, Lang T, Xue M, et al. The Role of Th-17 Cells and γδ T-Cells in Modulating the Systemic Inflammatory Response to Severe Burn Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4): E758.[31]Cao F, Liu T, Xu Y, et al. Culture and properties of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells: characteristics in vitro and immunosuppression in vivo. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(7):7694-7709.[32]Xishan Z, Baoxin H, Xinna Z, et al. Comparison of the effects of human adipose and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on T lymphocytes. Cell Biol Int. 2013;37(1): 11-18.[33]Maria AT, Maumus M, Le Quellec A, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Autoimmune Disorders: State of the Art and Perspectives for Systemic Sclerosis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017;52(2):234-259.[34]Shalaby SM, Sabbah NA, Saber T, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells modulate the immune response in chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis model. IUBMB Life. 2016;68(2):106-115. [35]Manferdini C, Maumus M, Gabusi E, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells exert antiinflammatory effects on chondrocytes and synoviocytes from osteoarthritis patients through prostaglandin E2. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(5): 1271-1281.[36]Liu S, Yuan M, Hou K, et al. Immune characterization of mesenchymal stem cells in human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly and derived cartilage cells. Cell Immunol. 2012;278(1-2): 35-44.[37]Soleymaninejadian E, Pramanik K, Samadian E. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells: cytokines and factors. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2012;67(1): 1-8.[38]Masson F. Skin hydration and hyaluronic acid. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2010;137 Suppl 1:S23-25.[39]Deitch EA, Gelder F, McDonald JC. Prognostic significance of abnormal neutrophil chemotaxis after thermal injury. J Trauma. 1982;22(3):199-204.[40]Hacker S, Mittermayr R, Nickl S, et al. Paracrine Factors from Irradiated Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Improve Skin Regeneration and Angiogenesis in a Porcine Burn Model. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25168.[41]Ong HT, Redmond SL, Marano RJ, et al. Paracrine Activity from Adipose-Derived Stem Cells on In Vitro Wound Healing in Human Tympanic Membrane Keratinocytes. Stem Cells Dev. 2017;26(6):405-418.[42]Zhong Z, Gu H, Peng J, et al. GDNF secreted from adipose-derived stem cells stimulates VEGF-independent angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 2016;7(24):36829-36841. |
.jpg)

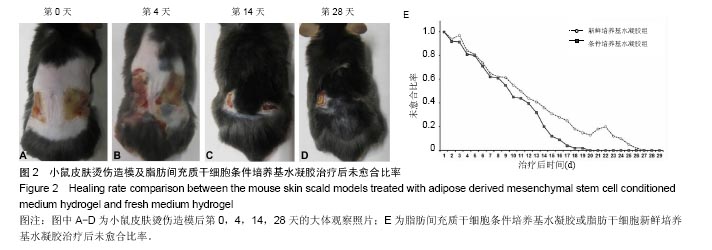
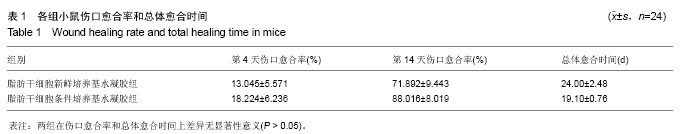
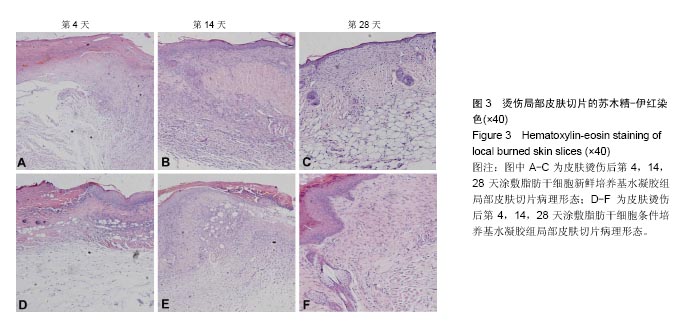

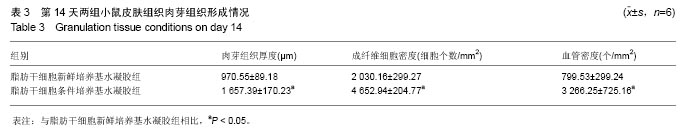
.jpg)
.jpg)