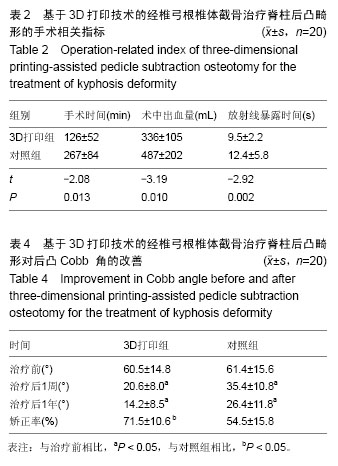
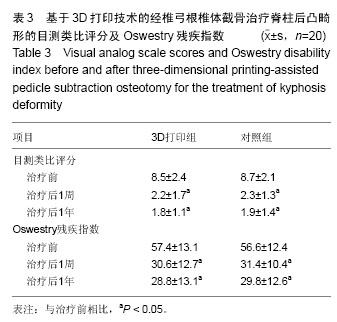
| [1] Suk SI, Kim JH, Lee SM, et al. Anterior-posterior surgery versus posterior closing wedge osteotomy in posttraumatic kyphosis with neurologic compromised osteoporotic fracture. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28(18):2170-2175.[2] Qian BP, Qiu Y, Wang B, et al. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy through pseudarthrosis to correct thoracolumbar kyphotic deformity in advanced ankylosing spondylitis. Eur Spine J. 2012;21(4): 711-718. [3] Arun R, Dabke HV, Mehdian H. Comparison of three types of lumbar osteotomy for ankylosing spondylitis: a case series and evolution of a safe technique for instrumented reduction. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(12): 2252-2260. [4] 钱邦平,邱勇,季明亮,等.跳跃式双节段经椎弓根椎体截骨治疗重度强直性脊柱炎胸腰椎后凸畸形[J].中华医学杂志, 2013,93(7):491-495.[5] Ji ML, Qian BP, Qiu Y, et al. Change of aortic length after closing-opening wedge osteotomy for patients with ankylosing spondylitis with thoracolumbar kyphosis: a computed tomographic study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(22):E1361-1367. [6] Qian BP, Jiang J, Qiu Y, et al. Radiographical predictors for postoperative sagittal imbalance in patients with thoracolumbar kyphosis secondary to ankylosing spondylitis after lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(26): E1669-1675. [7] Enercan M, Ozturk C, Kahraman S, et al. Osteotomies/spinal column resections in adult deformity. Eur Spine J. 2013;22 Suppl 2:S254-264. [8] 王岩,张雪松,张永刚,等.后路扩大“蛋壳”技术行畸形脊椎切除矫治重度成人先天性脊柱侧后凸[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2006,16(9):655-658.[9] 邱勇,朱泽章,吕锦瑜,等.强直性脊柱炎胸腰椎后凸畸形两种截骨矫形术式的疗效比较[J].中华骨科杂志,2002, 22(12):719-722.[10] 李景欣,瞿东滨,金大地.腰椎单节段经椎弓根椎体截骨术矫治强直性脊柱炎后凸畸形[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008, 16(3):182-184.[11] Kawahara N, Tomita K, Baba H, et al. Closing-opening wedge osteotomy to correct angular kyphotic deformity by a single posterior approach. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(4):391-402.[12] Murrey DB, Brigham CD, Kiebzak GM, et al. Transpedicular decompression and pedicle subtraction osteotomy (eggshell procedure): a retrospective review of 59 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27(21):2338-2345.[13] Kanno H, Aizawa T, Ozawa H, et al. Spine-shortening vertebral osteotomy in a patient with tethered cord syndrome and a vertebral fracture. Case report. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;9(1):62-66.[14] 齐强,陈仲强,郭昭庆,等.脊柱前方垫高后方闭合截骨矫形术治疗胸腰段脊柱后凸畸形的初步报告[J].中华外科杂志, 2006,44(8):551-555.[15] Chen IH, Chien JT, Yu TC. Transpedicular wedge osteotomy for correction of thoracolumbar kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis: experience with 78 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(16):E354-360.[16] 陈仲强,李危石,郭昭庆,等.胸腰段陈旧骨折继发后凸畸形的外科治疗[J].中华外科杂志,2010,43(4):201-204.[17] Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Rinella A, et al. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance. Surgical technique. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A Suppl 1:44-50.[18] Popa I, Oprea M, Andrei D, et al. Utility of the pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the correction of sagittal spine imbalance. Int Orthop. 2016;40(6):1219-1225.[19] Zhuang Q, Zhang J, Wang S, et al. Multiple cervical hemivertebra resection and staged thoracic pedicle subtraction osteotomy in the treatment of complicated congenital scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25 Suppl 1: 188-193.[20] Gao R, Wu J, Yuan W, et al. Modified partial pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the correction of post-traumatic thoracolumbar kyphosis. Spine J. 2015; 15(9):2009-2015.[21] 曾岩,陈仲强,郭昭庆,等.中-重度脊柱后凸成角畸形后路矫形手术的并发症及其对策[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011, 21(6):468-473.[22] Blondel B, Schwab F, Bess S, et al. Posterior global malalignment after osteotomy for sagittal plane deformity: it happens and here is why. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(7):E394-401.[23] 师继红,陆声,张元智,等.数字化脊柱椎弓根导航模板在胸腰椎骨折中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(2): 138-141.[24] 高方友,王曲,刘窗溪,等.个体化3D打印模型辅助后路螺钉内固定治疗颅颈交界区畸形[J].中华神经外科杂志, 2013,29(9):896-901.[25] 陈宣煌,许卫红,黄文华,等.基于3D打印的腰椎椎弓根螺钉数字化置入及临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(17): 2752-2757.[26] 马立敏,张余,周烨,等.3D打印技术在股骨远端骨肿瘤的应用[J].中国数字医学,2013, 8(8):70-72.[27] Wasinpongwanich K, Paholpak P, Tuamsuk P, et al. Morphological study of subaxial cervical pedicles by using three-dimensional computed tomography reconstruction image. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014;54(9):736-745.[28] Lee JY, Lee JW, Pang KM, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of magnesium-based resorbable metallic screw system in a bilateral sagittal split ramus osteotomy model using three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;72(2): 402.e1-13.[29] Yang M, Zeng C, Guo S, et al. Digitalized design of extraforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a computer-based simulation and cadaveric study. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e105646.[30] Dankowski R, Baszko A, Sutherland M, et al. 3D heart model printing for preparation of percutaneous structural interventions: description of the technology and case report. Kardiol Pol. 2014;72(6):546-551.[31] 严斌,张国栋,吴章林,等. 3D打印导航模块辅助腰椎椎弓根螺钉精确植入的实验研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2014,32(3):252-255.[32] Illés T, Somoskeöy S. Comparison of scoliosis measurements based on three-dimensional vertebra vectors and conventional two-dimensional measurements: advantages in evaluation of prognosis and surgical results. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(6): 1255-1263.[33] Smith-Petersen MN, Larson CB, Aufranc OE. Osteotomy of the spine for correction of flexion deformity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1969;66:6-9.[34] Lenke LG, O'Leary PT, Bridwell KH, et al. Posterior vertebral column resection for severe pediatric deformity: minimum two-year follow-up of thirty-five consecutive patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34(20):2213-2221.[35] Thomasen E. Vertebral osteotomy for correction of kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;(194):142-152.[36] Qian BP, Jiang J, Qiu Y, et al. The presence of a negative sacral slope in patients with ankylosing spondylitis with severe thoracolumbar kyphosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(22):e188. |
.jpg)

.jpg)