| [1] Sato Y,Kaji M,Higuchi F,et al.Changes in bone and calcium metabolism following hip fracture in elderly patients.Osteoporos Int. 2001;12:445-449.[2] Lotz J,Gaertner T,Hahn M,et al.Collagen type I metabolism after bone surgery.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1999;119:212-216 .[3] Court-Brown CM, McQueen MM. Nonunions of the proximal humerus: their prevalence and functional outcome. J Trauma. 2008; 64(6):1517-1521.[4] Gothlin G, Ericsson JL. Fine structural localization of alkaline phosphatase in the fracture callus of the rat. Histochemie. 1973;36(3):225-236. [5] Felix R, Herrmann W, Fleisch H. Stimulation of precipitation of calcium phosphate by matrix vesicles. J Biochem. 1978;170(3):681-691. [6] Anderson HC, Stechschulte DJ Jr, Collins DE, et al. Matrix vesicle biogenesis in vitro by rachitic and normal rat chondrocytes.Am J Pathol. 1990;136(2): 391-398. [7] Parker MJ, Raghavan R, Gurusamy K.Incidence of fracture-healing complications after femoral neck fractures.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;458:175-179.[8] Giannoudis PV, MacDonald DA, Matthews SJ,et al.Nonunion of the femoral diaphysis.The influence of reaming and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000;82(5):655-658.[9] Society COT.Nonunion following intramedullary nailing of the femur with and without reaming.Results of a multicenter randomized clinical trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(11):2093-2096. [10] Phieffer LS, Goulet JA.Delayed unions of the tibia.Instr Course Lect. 2006;55:389-401.[11] Oni OO, Mahabir JP, Iqbal SJ, et al. Serum osteocalcin and total alkaline phosphatase levels as prognostic indicators in tibial shaft fractures.Injury. 1989;20(1): 37-38.148.[12] Seibel MJ.Biochemical markers of bone turnover: part I: biochemistry and variability.Clin Biochem Rev. 2005; 26(4): 97-122.[13] Pedersen BJ,Schlemmer A, Hassager C,et al.Changes in the carboxyl-terminal propeptide of type I procollagen and other markers of bone formation upon five days of bed rest.Bone. 1995;17(1):91-95.[14] Lian J, Stewart C, Puchacz E,et al.Structure of the rat osteocalcin gene and regulation of vitamin D-dependent expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86(4):1143-1147.[15] Noite PA,Vander Krans A,Patka P,et al.Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound device for the noninvasive treatment of nonunions. J Trauma. 2001;51(4): 693-702[16] Southwood LL, Frisbie DD, Kawcak CE,et al. Evaluation of serum biochemical markers of bone metabolism for early diagnosis of nonunion and infected nonunion fractures in rabbits. Am J Vet Res. 2003 ;64(6):727-735. [17] Ly TV,Swiontkowski MF.Treatment of femoral neck fractures in young adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90(10):2254-2266. [18] Yokoyama K,Itoman M, Uchino M, et al.Immediate versus delayed intramedullary nailing for open fractures of the tibial shaft: A multivariate analysis of factors affecting deep infection and fracture healing. Indian J Orthop. 2008;42(4):410-419.[19] Loder RT. The influence of diabetes mellitus on the healing of closed fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988;(232):210-216. [20] Foulk DA, Szabo RM. Diaphyseal humerus fractures: natural history and occurrence of nonunion. Orthopedics. 1995; 18(4):333-335.[21] Lindsey RW, Blair SR. Closed tibial-shaft fractures: which ones benefit from surgical treatment? J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 1996;4(1):35-43.[22] Herrmann M, Klitscher D,Georg T,et al.Different kinetics of bone markers in normal and delayed fracture healing of long bones.Clin Chem. 2002;48: 2263-2266 .[23] Webb LX, Winquist RA, Hansen ST. Intramedullary nailing and reaming for delayed union or nonunion of the femoral shaft. A report of 105 consecutive cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(212):133-141.[24] Wu CC. The effect of dynamization on slowing the healing of femur shaft fractures after interlocking nailing. J Trauma. 1997;43(2):263-267. [25] Weresh MJ, Hakanson R, Stover MD, et al. Failure of exchange reamed intramedullary nails for ununited femoral shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2000;14(5): 335-338. [26] Patil S, Montgomery R.Management of complex tibial and femoral nonunion using the Ilizarov technique, and its cost implications. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(7): 928-932. [27] Yu-yahiro JA,Michael RH,Dubin NH,et al.Serum and urine markers of bone metabolism during the year after hip fracture. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2001;49: 877-883.[28] Kyro A, Usenius JP, Aarnio M, et al. Are smokers a risk group for delayed healing of tibial shaft fractures? Ann Chir Gynaecol. 1993;82(4):254-262. [29] Adams CI, Keating JF, Court-Brown CM. Cigarette smoking and open tibial fractures. Injury. 2001;32(1): 61-65. [30] Eastell R,Yergey AL,Vieira NE,et al.Interrelationship among vitamin D metabolism,true calcium absorption,parathyroid function, and age in women: evidence of an age-related intestinal resistance to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D action.J Bone Miner Res. 1991;6(2):125-132.[31] Delmas PD.Biochemical markers of bone turnover for the clinical assessment of metabolic bone disease.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1990; 19(1):1-18.[32] Dahabreh Z,Calori GM, Kanakaris NK, et al.A cost analysis of treatment of tibial fracture nonunion by bone grafting or bone morphogenetic protein-7. Int Orthop. 2009;33(5):1407-1414. [33] Haining SA, Atkins RM, Guilland-Cumming DF,et al. Vitamin D metabolites in patients with established non-union of fracture. Bone Miner. 1986;1(3): 205-209.[34] Kaplan FS, Hayes WC, Keaveny TM,et al.Form and function of bone. In: Simon, SS. editor. Orthopaedic basic science. Rosemont (IL): Amercan Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons,1994:127-184.[35] Linkhart SG, Linkhart TA, Taylor AK,et al.Synthetic peptidebased immunoassay for amino-terminal propeptide of type I procollagen: application for evaluation of bone formation.Clin Chem. 1993;39(11 Pt 1):2254-2258.[36] Gineyts E,Cloos PA,Borel O,et al.Racemization and isomerization of type I collagen C-telopeptides in human bone and soft tissues: assessment of tissue turnover. Biochem J. 2000;345(Pt 3):481-485.[37] Blokhuis TJ,De Bruine JH, Bramer JA ,et al.The reliability of plain radiography in experim- ental fracture healing. Skeletal Radiol. 2001;30:151-156 .[38] Caruso G, Lagalla R,Derchi L,et al.Monitoring of fracture calluses with color Dopplers on ography. H Clin Ultrasound. 2000;28:20-27.[39] Seibel MJ.Molecular markers of bone turnover:Biochemical technical and analytical aspects. Osteoporos Int. 2000;11( suppl 6):18-29.[40] Szulc P.Delmas PD. Biochemical markers of bone turnover in men.Calcif Tissue Int. 2001;69: 229-234 .[41] Laurer HL,Hagenbourger O,Quast S,et al.Sequential changes and pattern of bone specific al kaline phosphtase after trauma. Eur J Trauma. 2000;1: 33-38.[42] Kurdy NM.Serology of abnormal fracture healing:The role of PINP, PICP, and BsALP. J Orthop Trauma. 2000;14:48-53.[43] Borys J,Grabowska SZ, Antonowicz B,et al.The concentuation of C-terminal propeptide of type I procollagen in blood serum in the course of mandibular fracture healing (preliminary report) .Tocz Akad Med Bial Ymst. 2001;46:251-262 .[44] Ingle BM,Hay SM,Bottjer HM,et al.Changes in bone mass and bone turnover following ankle fracture.Osteporos Int. 1999;10:408-415.[45] Moghaddam A,Müller U,Roth HJ,et al.TRACP 5b and CTX as osteological markers of delayed fracture healing. Injury. 2011;42(8):758-764. [46] Hanson DA, Weis MA, Bollen AM,et al.A specific immunoassay for monitoring human bone resorption:quantitation of type I collagen cross-linked N-telopeptides in urine. J Bone Miner Res. 1992; 7(11):1251-1258. [47] Rosen HN,Moses AC,Garber J,et al.Utility of biochemical markers of bone turnover in the follow-up of patients treatment with biphosphonates. Calcif Tissue Int. 1998;63:363-368. [48] Garcia-Perez MA, Moreno-Mercer J, Tarin JJ, et al. Similar efficacy of low and standard doses of transdermal estradiol in controlling bone turnover in postmenopausal women.Gynecol Endocrinol. 2006; 22(4):179-184.[49] Kon T,Cho TJ, Aizawa T,et al. Expression of osteoprotegerin, receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (osteoprotegerin ligand) and related proinflammatory cytokines during fracture healing. J Bone Miner Res. 2001;16(6):1004-1014. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨不连:正常骨骼的代谢处于动态平衡之中,成骨过程和破骨过程紧密耦联,而骨不连患者的这一动态平衡被破坏,骨吸收大于骨形成,最终形成骨不连,如果能够通过测量骨代谢生化标志物浓度从而有效地对骨代谢过程进行监测,就有可能为早期诊断骨不连提供依据。
骨特异性碱性磷酸酶:是骨生长过程中持续释放时间最长的细胞因子,并且还具有组织特异性强、时间变异性小的特点。其由成骨细胞产生,是碱性磷酸酶的亚型,存在于成骨细胞膜结合物。骨特异性碱性磷酸酶是反映骨形成和成骨细胞活性的敏感和特异指标,能排除肝、肾、肠等疾病影响,是成骨细胞的胞外酶,成骨细胞活性增强,则骨特异性碱性磷酸酶分泌增加。
文题释义:
骨不连:正常骨骼的代谢处于动态平衡之中,成骨过程和破骨过程紧密耦联,而骨不连患者的这一动态平衡被破坏,骨吸收大于骨形成,最终形成骨不连,如果能够通过测量骨代谢生化标志物浓度从而有效地对骨代谢过程进行监测,就有可能为早期诊断骨不连提供依据。
骨特异性碱性磷酸酶:是骨生长过程中持续释放时间最长的细胞因子,并且还具有组织特异性强、时间变异性小的特点。其由成骨细胞产生,是碱性磷酸酶的亚型,存在于成骨细胞膜结合物。骨特异性碱性磷酸酶是反映骨形成和成骨细胞活性的敏感和特异指标,能排除肝、肾、肠等疾病影响,是成骨细胞的胞外酶,成骨细胞活性增强,则骨特异性碱性磷酸酶分泌增加。.jpg) 文题释义:
骨不连:正常骨骼的代谢处于动态平衡之中,成骨过程和破骨过程紧密耦联,而骨不连患者的这一动态平衡被破坏,骨吸收大于骨形成,最终形成骨不连,如果能够通过测量骨代谢生化标志物浓度从而有效地对骨代谢过程进行监测,就有可能为早期诊断骨不连提供依据。
骨特异性碱性磷酸酶:是骨生长过程中持续释放时间最长的细胞因子,并且还具有组织特异性强、时间变异性小的特点。其由成骨细胞产生,是碱性磷酸酶的亚型,存在于成骨细胞膜结合物。骨特异性碱性磷酸酶是反映骨形成和成骨细胞活性的敏感和特异指标,能排除肝、肾、肠等疾病影响,是成骨细胞的胞外酶,成骨细胞活性增强,则骨特异性碱性磷酸酶分泌增加。
文题释义:
骨不连:正常骨骼的代谢处于动态平衡之中,成骨过程和破骨过程紧密耦联,而骨不连患者的这一动态平衡被破坏,骨吸收大于骨形成,最终形成骨不连,如果能够通过测量骨代谢生化标志物浓度从而有效地对骨代谢过程进行监测,就有可能为早期诊断骨不连提供依据。
骨特异性碱性磷酸酶:是骨生长过程中持续释放时间最长的细胞因子,并且还具有组织特异性强、时间变异性小的特点。其由成骨细胞产生,是碱性磷酸酶的亚型,存在于成骨细胞膜结合物。骨特异性碱性磷酸酶是反映骨形成和成骨细胞活性的敏感和特异指标,能排除肝、肾、肠等疾病影响,是成骨细胞的胞外酶,成骨细胞活性增强,则骨特异性碱性磷酸酶分泌增加。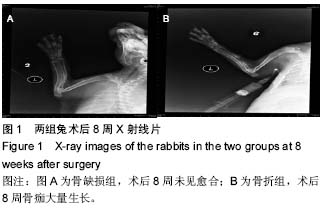
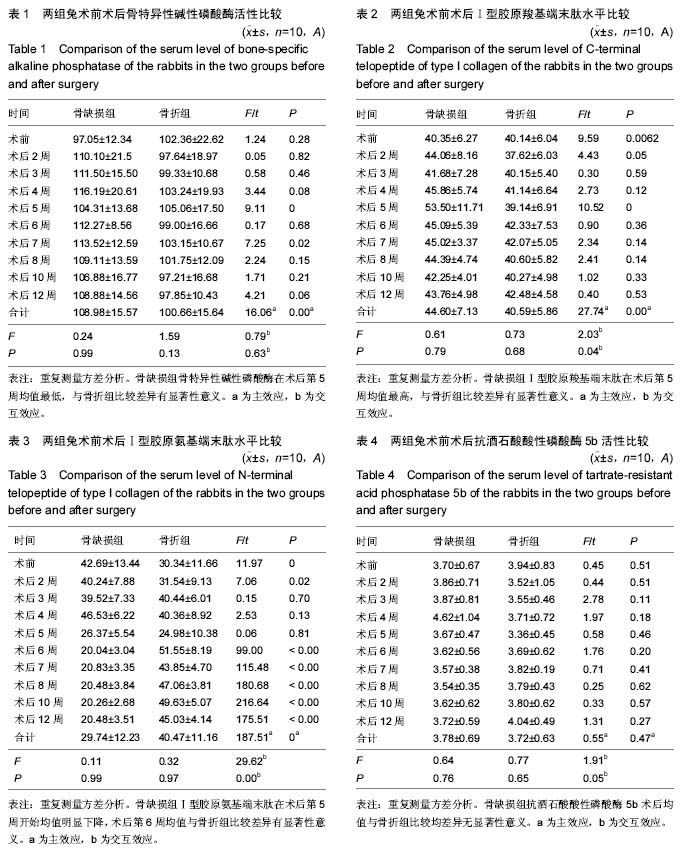
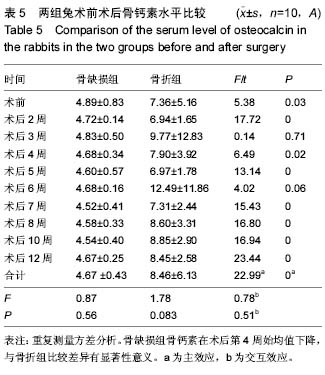
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨不连:正常骨骼的代谢处于动态平衡之中,成骨过程和破骨过程紧密耦联,而骨不连患者的这一动态平衡被破坏,骨吸收大于骨形成,最终形成骨不连,如果能够通过测量骨代谢生化标志物浓度从而有效地对骨代谢过程进行监测,就有可能为早期诊断骨不连提供依据。
骨特异性碱性磷酸酶:是骨生长过程中持续释放时间最长的细胞因子,并且还具有组织特异性强、时间变异性小的特点。其由成骨细胞产生,是碱性磷酸酶的亚型,存在于成骨细胞膜结合物。骨特异性碱性磷酸酶是反映骨形成和成骨细胞活性的敏感和特异指标,能排除肝、肾、肠等疾病影响,是成骨细胞的胞外酶,成骨细胞活性增强,则骨特异性碱性磷酸酶分泌增加。
文题释义:
骨不连:正常骨骼的代谢处于动态平衡之中,成骨过程和破骨过程紧密耦联,而骨不连患者的这一动态平衡被破坏,骨吸收大于骨形成,最终形成骨不连,如果能够通过测量骨代谢生化标志物浓度从而有效地对骨代谢过程进行监测,就有可能为早期诊断骨不连提供依据。
骨特异性碱性磷酸酶:是骨生长过程中持续释放时间最长的细胞因子,并且还具有组织特异性强、时间变异性小的特点。其由成骨细胞产生,是碱性磷酸酶的亚型,存在于成骨细胞膜结合物。骨特异性碱性磷酸酶是反映骨形成和成骨细胞活性的敏感和特异指标,能排除肝、肾、肠等疾病影响,是成骨细胞的胞外酶,成骨细胞活性增强,则骨特异性碱性磷酸酶分泌增加。