中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (5): 688-693.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.05.014
• 心脏及血管损伤动物模型 Animal models of heart and vascular damage • 上一篇 下一篇
升麻苷H-1利用鼻腔嗅觉区鼻-脑通道进行鼻脑靶向给药的可行性
武密山1,赵素芝2,高维娟3,王 茹1,韩红伟1,师旭亮1
- 1河北中医学院基础医学院方剂学教研室,河北省石家庄市 050200;2石家庄市长安区胜北社区卫生服务中心,河北省石家庄市 050041;3河北省心脑血管病中医药防治重点实验室,河北省石家庄市 050091
Feasibility of nasal brain targeted drug delivery through the nose-brain channel in the nasal olfactory region using cimicifugoside H-1
Wu Mi-shan1, Zhao Su-zhi2, Gao Wei-juan3, Wang Ru1, Han Hong-wei1, Shi Xu-liang1
- 1Department of Formulaology, Basic Medicine College, Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, Hebei Province, China; 2Changan District Shengbei Community Health Center of Shijiazhuang, Shijiazhuang 050041, Hebei Province, China; 3Hebei Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Research on Cardio-Cerebrovascular Disease, Shijiazhuang 050091, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
脑靶向药物递送:根据生物体的生理学、病理学和分子生物学特性,借助受体、载体与配体、抗体的作用,将药物选择性地递送至脑靶细胞的一种递药系统。理想的脑靶向给药系统应该有3个要素:即定位蓄积、控释、无毒且可生物降解。根据脑靶向机制,将药物脑靶向系统分为两大类型:生物学脑靶向给药系统和化学脑靶向给药系统。生物学脑靶向给药系统主要是以抗体为基础,包括单克隆抗体识别,寻找新的潜在靶向体以及基因治疗;化学脑靶向给药系统即通过化学合成反应、化学修饰合成药物的非活性衍生物,使药物与特殊设计的“载体”以共价键的方式相连,到达脑靶向组织、细胞,利用酶断开共价键,释放出活性药物。
鼻腔给药入脑途径:①经鼻腔呼吸区黏膜毛细血管吸收,经血液循环透过血脑屏障。②药物通过嗅黏膜上皮或嗅神经进入嗅球或脑脊液,此通路依赖嗅黏膜下层与蛛网膜下隙相通的解剖结构,转运到脑组织中。
背景:近些年研究表明,鼻腔给药作为脑靶向给药的途径之一,可有效使通过其他给药途径不易透过血脑屏障的药物绕过血脑屏障,靶向递送到脑部,为治疗中枢神经系统疾病提供一种极有发展前景的给药途径。
目的:研究大鼠鼻腔给药及静脉注射升麻苷H-1的药代动力学和脑靶向性归经的组织分布特性,探索升麻苷H-1利用鼻腔嗅觉区的鼻-脑通道进行鼻脑靶向给药的可行性。
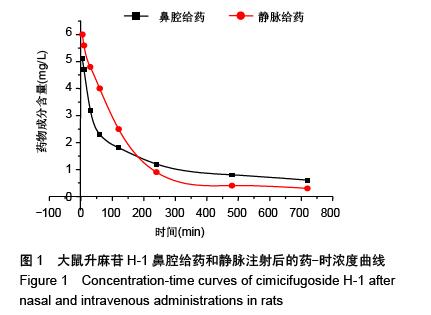
方法:鼻腔给药及静脉注射给予升麻苷H-1后,检测各时间点血浆和主要的归经组织器官(肺、脾、胃、大肠、肝、肾、脑、大脑、小脑、脑脊液、嗅球、嗅区等)药物浓度,绘制药-时曲线,用DAS程序拟合房室模型并计算药代动力学参数。
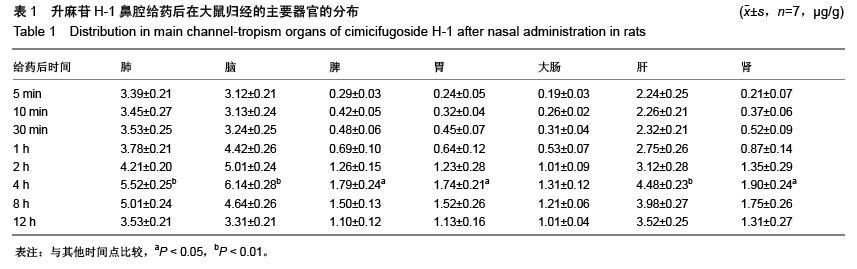
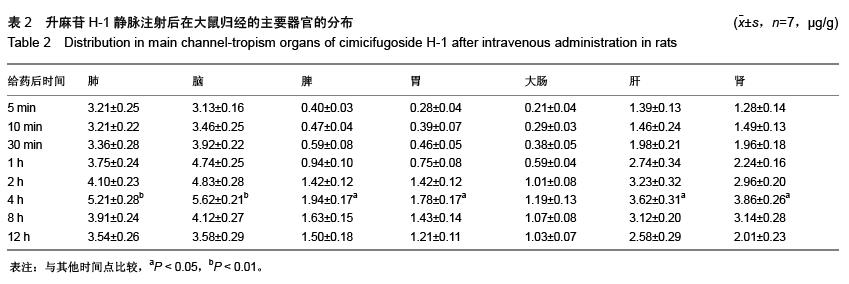
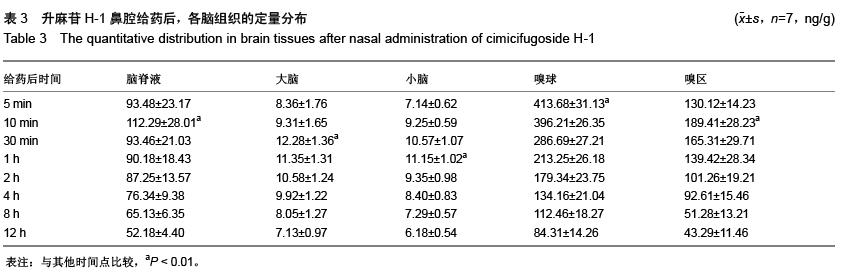
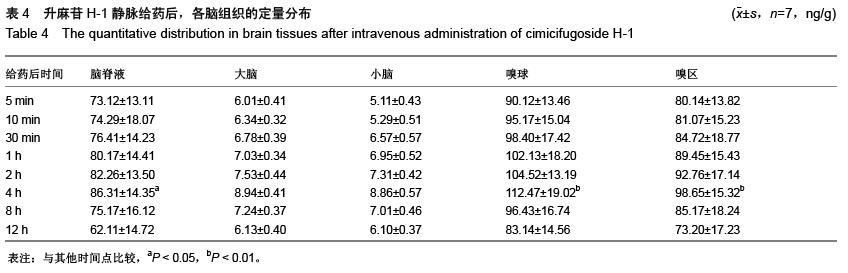
结果与结论:①升麻苷H-1 吸收迅速,分布广泛。在主要的归经器官中,肺、脑药物浓度分布均远高于其他脏器组织。②升麻苷H-1鼻腔给药后经以下吸收通路直接转运入脑:鼻腔嗅黏膜吸收进入蛛网膜下腔的嗅球,然后相继进入嗅区、脑脊液大脑、小脑等部位,嗅球是药物分子经鼻腔入脑的必经之路。③与静脉注射给药相比,升麻苷H-1鼻腔给药具有明显的肺、脑靶向性。
ORCID: 0000-0003-3959-9906(武密山)

.jpg)