| [1] 丁小衍,刘小林,刘育杰,等. 去细胞同种异体神经修复材料临床应用初步报告[J].中华显微外科杂志,2009,32(6):448-450.[2] Jiang B,Zhang B, Zhang D,et al. Study on small gap sleeve bridging peripheral nerve injury. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol.2006;34(2):55-74.[3] Zhang ZL,Xin L,Song JZ,et al. Bridging peripheral nerves using a deacetyl chitin conduit combined with short term electrical stimulation. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(10): 1075-1078.[4] Zhivolupov SA, Odinak MM,Rashidov NA, et al. Impulse magnetic stimulation facilitates synaptic regeneration in rats following sciatic nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2012; 7(17): 1299-1303.[5] Brodal A. Neurological anatomy in relation to clinical medicine. 3rd ed. USA: Oxford University Press, 1981: 1-32.[6] Chen MH, Ren QX, Yang WF, et al. Influences of HIF-lα on Bax/Bcl-2 and VEGF expressions in rats with spinal cord injury. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013; 6(11): 2312-2322.[7] Preyat N, Rossi M, Kors J, et al. Intracellular nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide promotes TNF-induced necroptosis in a sirtuin-dependent manner. Cell Death Different. 2015; 10(4): 367-374.[8] Lu XM,Shu YH,Qiu CH,et al. Protective effects and anti-apoptotic role of nerve growth factor on spinal cord neurons in sciatic nerve-injured rats. Neurol Res. 2014;36(9): 814-823. [9] 崔红岩,谢小波.脊髓硬膜外电刺激的数学模型[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2008,27(1):61-69.[10] Rattay F,Minassian K,Dimitrijevic MR. Epidural electrical stimulation of posterior structures of the human lumbosacral cord:2.quantitative analysis by computer modeling. Spinal Cord. 2000;38(8):473-489.[11] Chiba A, Nakanishi H, Hiruma S, et al. Magnetieally induced motor evoked potentials and H-reflex during nembutal and ketamine anesthesiaadministration in rats. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 1998;101:43-57. [12] 王熠钊,徐江,黄晓林,等.硬膜外脊髓电刺激电压及频率变化对正常大鼠脊髓反射的影响[J].中华物理医学及康复杂志, 2010, 32(1):17-21.[13] Zhang C, Zhang G, Rong W, et al. Early applied electric field stimulation attenuates secondary apoptotic responses and exerts neuroprotective effects in acute spinal cord injury of rats. Neuroscience. 2014;16(3):260-271.[14] Oakley JC, Weiner RL. Spinal cord stimulation for complex regional pain syndrome: Aprospective study of 19 patients at two centers. Neuromodulaton. 2012;11(2):47-51. [15] Lee SC, 徐贯杰,刘小立.脊髓电刺激在疼痛治疗中的应用[J]. 实用疼痛学杂志,2005,1(2):70-73.[16] 胡文,顾晓松.周围神经损伤动物模型神经再生效果的评价[J]. 中华显微外科杂志,2012,35(5):435-439.[17] 陈允震,王琛,王道清,等. 指数曲线电刺激促进周围神经损伤修复的实验研究[J].中华纤维外科杂志,2003,23(5): 299-303.[18] 李剑,姜保国,张殿英,等. 生物套管小间隙桥接修复周围神经的实验研究[J].中华手外科杂志,2003,19(2): 118-120.[19] Tong JX, Rich KM. Diphenylpiperazines enhance regeneration after facial nerve injury. J Neurobiology. 1997;26 (5):339-347.[20] Nakamura SI, Myers RR. Injury to dorsal root ganglia alters innervation of spinal cord dorsal horn lamina involved in nociception. Spine. 2000; 25(5): 537-542.[21] Bandtlow CE, Schmidt MF, Hassinger TD, et al. Role of intracellular calcium in NI-35-evoked collapse of neuronal growth cones. Science. 1993;259:80-83.[22] 黄飞,王怀经,李振平,等. 联合应用NGF和GM1对坐骨神经损伤大鼠脊髓神经元的保护作用[J]. 解剖学杂志, 2005, 28(3): 323-325.[23] 湛宏鸣,吴良芳,保天然,等.针刺对去部分背根和背根节NGF mRNA的影响[J].神经解剖学杂志,2000,16(4):319.[24] 赵华,陈允震,刘海春,等.自体骨髓基质干细胞移植联合电刺激治疗脊髓损伤的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010,18(12): 1019-1022.[25] Min Y, Beom J, Oh BM, et al. Possible effect of repetitive magnetic stimulation of the spinal cord on the limb angiogenesis in healthy rats and its clinical implication for the treatment of lymphedema. Clin Cancer Res.2010;16:47.[26] Gyawali S, Solis L,Chong SL, et al. Intermittent electrical stimulation redistributes pressure and promotes tissue oxygenation in loaded muscles of individuals with spinal cord injury. J Appl Physiol. 2012;110(1):246-255.[27] Zhang ZL, Li X, Zuo SJ, et al.Bridging peripheral nerves using a deacetyl chitin conduit combined with short-term electrical stimulation. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9 (10): 1075-1078 [28] 李少华,侯铁胜.电刺激对大鼠坐骨神经切断后脊髓运动神经元凋亡调控基因表达的影响[J].中华创伤杂志,2001,17(7): 398-401.[29] Liang H, Yu F, Tong Z, et al. Effect of ischemia post- conditioning on skeletal muscle oxidative injury, mTOR, Bax, Bcl-2 proteins expression in ischemia-reperfusion rabbits. Molecul Biol Report. 2013;40(1): 507-514.[30] Singh B,Xu QG,Franz CK,et al. Accelerated axon outgrowth,guidance,and target reinnervation across nerve transection gaps following a brief electrical stimulation paradigm. J Neurosurg. 2012;116:498-512. |
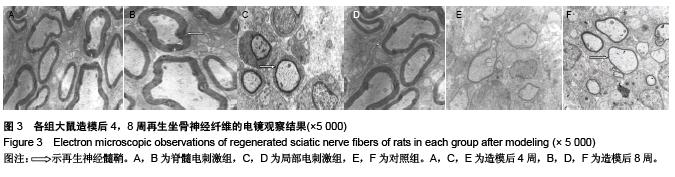
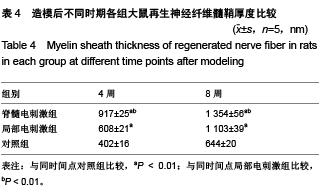
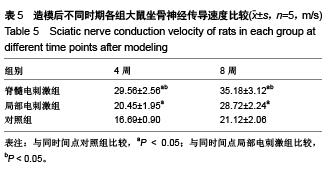
.jpg)
.jpg)