| [1] Khademi R, Mohebbi-Kalhori D, Hadjizadeh A.Computational study of culture conditions and nutrient supply in a hollow membrane sheet bioreactor for large-scale bone tissue engineering. J Artif Organs. 2014; 17(1):69-80.
[2] Alevc,liM,Asahara T.Endothelial progenitor cells: A novel tool for the therapy of ischemic diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011; 15:949-965
[3] 庞浩.血管内皮祖细胞促进骨缺损修复重建的作用机制研究[D]. 重庆: 第三军医大学, 2013.
[4] Christian N, Charlotte S,Theresia P, et al.The cell surface proteome of human mesenchymal stromal cells PLoS One. 2011;6(5):1546-1651.
[5] Luang S,Leung V,Peng S, et al. Developmental definition of MSCs: new insights into pending questions. Cell Reprogram. 2011;13(6):465-472.
[6] Li JH, Liu DY, Zhang FM,et al. Human dental pulp stem cell is a promising autologous seed cell forbone tissue engineering. Chin Med J.2011;124(23): 4022-4028.
[7] 姚超,卜令学,王科,等.应用细胞片层技术构建组织工程骨修复犬下颌骨缺损的实验研究.华西口腔医学杂志,2012,30(3):229-233.
[8] Menicanin D, Mrozik KM, Wada N, et al. Periodontalligament- derived stem cells exhibit the capacity for long-term survival, self-renewal, and regeneration of multiple tissue types in vivo. Stem Cells Dev.2014;23(9):1001-1011
[9] Zeng HL, Zhong Q, Qin YL, et al.Hypoxia-mimetic agents inhibit oliferation and alter the morphology of human umbilical cord-derived mesenehymal stem cells.BMC Cell Biol.2011; 12(1): 32-42.
[10] 谷子芽,李颖,张文元,等.几种胚胎干细胞标志在牙周膜细胞中的表达及意义[J],口腔医学,2013,33(12):796-880.
[11] 张凤秋,孟焕新,韩劫,等.人牙周膜间充质干细胞的分离培养及超微结构观察[J],北京大学学报(医学版),2014,46(2):274-277.
[12] 罗傲翔,吴补领,侯晋,等. 3D培养牙周膜干细胞生物学特性的初步研究[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2014,24(5):264-268.
[13] 柬丽红,曹灵,闫明,等.不同发育阶段的人牙周膜干细胞增殖能力和成牙/成骨能力的比较研究[J].口腔生物医学,2013,4(2):65-69.
[14] 叶菁,张戎,褚云娟,等.正常和炎症来源的人牙周膜干细胞内皮向分化能力的比较[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2014,24(1):7-12.
[15] 贺慧霞,刘洪臣,马军利,等.牙周膜干细胞用于犬牙槽嵴组织工程化增高的实验研究[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2013,11(4):199-204.
[16] 段学静.釉基质蛋白在体外对诱导性多能干细胞的作用及其共同在牙周再生中的应用[D].济南:山东大学口腔医学院,2010.
[17] Hynes K, Menicanin D, Han J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from ips cells facilitate periodontal regeneration.J Dent Res. 2013,92(9):833-839.
[18] Szpalski C, Barbaro M, Sagebin F,et al.Bone tissue engineering: current strategies and techniques-part II:Cell types.Tissue Eng Part B Rev,2012,18(4):258-269.
[19] 付维力, 项舟.血管化组织工程骨构建中细胞共培养体系的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(2):179-185.
[20] Xu N, Liu H,Qu F, et al.Hypoxia inhibits the differentiation of me senchymal stem cells into osteoblasts by activation of Notch signaling. Exp Mol Pathol.2013;19:748-758
[21] 赵娴.自体外周血EPCs与BMSCs联合PDPBB构建微血管化生物骨[D].昆明: 昆明医科大学, 2013
[22] Estrela C,Alencar A,Kitten GT,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells in the dental tissues:perspectives for tissue regeneration. BrazDent J.2011;22(2):91-98.
[23] Xie H, Ⅱu H.A novel mixed•type stem cell pelet for cementum periodontal ligament-like complex.J Periodontol. 2012; 83(6): 805-815.
[24] Yang ZH, Jin F, Zhang XJ, et al.A novel possible strategy based on self-assembly approach to achieve complete periodontal regenera-tion.Artif Organs.2010;34(7):603-609.
[25] Lei G, Yu Y, Jiang Y, et al.Diferentiation ofBMMSCsinto odon-toblast-like cells induced by natural dentine matrix.Arch OralBiol.Pii:S0003-9969(13)00007-1.
[26] 王璇,刘奕杉,马艳,等.牙周膜干细胞诱导骨髓间充质干细胞的牙向分化[J],细胞与分子免疫学杂,2013,29(8):818-822.
[27] 童晓洁,兰泽栋,郑雅心,等.骨形成蛋白-2和牙胚细胞联合作用诱导人牙周膜干细胞表达成牙骨质细胞的表型研究[J],中国美容医学,2014,23(16):1343-1348 .
[28] Dapeng L, Xiaojie L, Ping G, et al.Erk1, 2 signalling is involved in the diferentiation of periodonml ligament stem cells to Schwann cells in dog.Arch Oral Biol.2014;59(5):487-491.
[29] 文军. 改良富血小板血浆对乳牙牙髓干细胞增殖和成骨分化的作用研究[D].广州: 南方医科大学,2014.
[30] 刘斌钰,刘斌焰,邢雁霞,等. PRP 在颅骨缺损修复中血管化的实验研究[J].山东大学学报(医学版),2015;53(2):27-33.
[31] 彭艳. 富血小板血浆激活PI3K/AKT/NFκB信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞再生及修复功能的相关研究[D],广州:南方医科大学,2013.
[32] 赵天源,孙红.骨组织工程支架材料及其血管化的研究进程[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(38):6832-6838.
[33] Sheu SY,Tsai CC, Sun JS, et al. Stimuatory effect of puerarin on bone for mation1 through coactivation of nitricoxide and bone morphogenetic protein-mitogen- activatedprotein kinases pathways in mice.Chin Med (eng1).2012;125(20):3646-3653
[34] Russell JA, Connor NP, Hartig GK. Iontophoretic delivery of nitric oxide donor improves local skin flap viability.J Rehabil Resdev.2010;47(1):61-66.
[35] Benjamin S, Sheyn D, Ben-David S,et al.Oxygenated environment enhances both stem cell survival and osteogenic differentiation.Tissue Eng Part A.2013;19:748-58.
[36] Zhang PJ, Liu BY, Zhang LH, et al. Effects of Shengtaiwang Potion on the Activity of Antistress and Antioxidase in Mice.Chi J Exp Tra Med For.2012;18(10):221-223.
[37] 李受益.双因子诱导骨组织工程支架快速血管化的动物实验研究[D].天津:天津医科大学,2013.
[38] Schwarz F,Ferrari D,Podolsky L,et al. Initial pattern of angiogenesis and bone formation following lateral ridge augmentation using rhPDGF and guided bone regeneration: an immunohistochemical study in dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(1):90-99.
[39] Liu N, Shi S, Deng M, et al. High levels of 13-catenin signaling reduce osteogenie differentiation of stem ce[1s in inflare-matory microenvironments through inhibition of the noncanonical Wnt pathway.J Bone Miner Res.2011;26(9):2082-2095.
[40] Zhou Y, Guan X, Wang H, et al. Hypoxia induces osteo-Genic/ angiogenic responses of bone marrow-derived mesenchyma1 8tromal ce11s seeded on bone-derived scaffolds via ERK1/2 and p38 pathways.Biotechnol Bioeng.2013;110(6):1794-1804.
[41] Li XD,Liu ZY,Chang B,et al.Panax notoginseng saponins promote osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells through the ERK and P38 MAPK signaling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem.2011;28(2):367-376.
[42] Aaigas N, Urefia C, Rodrigu ez-Carballo E, et al. Mitogen- activated protein kinase(MAPK)-regulated interactions between Osterix and Runx2 are critical for the Transcriptional Osteogenic Program.J Biol Cbem.2014; 289(39): 27105- 27117.
[43] 聂嘉,张博,顾斌,等. p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶在炎症微环境作用下对牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].中国医学科学院学报, 2015,37(1):1-7.
[44] Hughes FJ, Ghuman M, Talal A. Periodontal regeneration:a challenge for the tissue engineer?. Proc Inst Mech Eng H, 2010, 224(12):1345-1358.
[45] Lo KW , Ulery BD, Ashe KM, et al. Studies ofbone morphogenetic protein-based surgical repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2012;64(12):1277-1291.
[46] van Hout WM, Mink VDMA, Breugem CC, et al.Reconstruction of the alveolar cleft:can growth factor-aided tissue engineering replace autologous bone grafting?A literature review and systematic review of results obtained with bone morphogenetic protein-2. Clin Oral Investig.2011;15(3):297-303.
[47] Grgurevic L, Macek B, Mercep M, et al. Bone morphogenetie protein(BMP)1-3 enhances bone repair. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2011;408(1):25-31.
[48] Su J, Xu H, Sun J, et al. Dual delivery of BMP-2 and bFGF from a new nano-composite scaffold, loaded with vascular stents for large-size mandibular defect regeneration. J Mol Sci. 2013;14(6): 12714-12728.
[49] Park SY, Kim KH, Shin SY, et al. Dual delivery of rhPDGF-BB and bone nlalTow mesenchymal stromal cells expressing the BMP-2 gene enhance bone formation in a critical-sized defect model.TsueEngPartA.2013;19(21-22):2495-2505.
[50] Guo Y,Zeng Q,Yan Y,et al.Proliferative effect and osteoin-ductive potential of extracellular matrix coated on cell culture plates. Springerplus.2013;2(1):303.
[51] Hakki SS, Bozkurt B, Hakki EE, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2, -6, and-7 differently regulate osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem ceHs. J Biomed Mater Res BAppl Biomater.2014;102(1):119-130.
[52] Khanna-Jain R, Agata H, Vuorinen A, et al.Addition of BMP-2 or BMP-6 to dexamethasone, ascorbic acid, and betaglycerophosphate may not enhance osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells.Growth Factors. 2010;28(6):437-446.
[53] 曹钰,杜娟,范志朋.表皮生长因子Epiregulin促进牙周膜干细胞成骨分化[J].北京口腔医学,2013,21(3):125-128.
[54] 张鹏涛,钟良军,张远, 等.维甲酸诱导小型猪牙周膜干细胞的体外成骨[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(49):9218-9222.
[55] 谷子芽,翟强,吕秋峰, 等.地塞米松诱导牙周膜干细胞的定向成骨分化及凋亡 [J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(40):7090-7095.
[56] Saleh FA,Whyte M,Genever PG,et al.Effects of endothelial cells on human mesenchymal stem cell activity in a three- dimensional in vitro model.Eur Cell Mater. 2011;22:242-257.
[57] 钟志华,施斌,周先略.牙周膜干细胞在磷酸三钙/壳聚糖支架上生长的体外实验[J].口腔医学研究,2015,1(2):113-116.
[58] 姜力铭.PLGA纳米纤维支架缓释辛伐他汀促进骨再生的研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2011.
[59] 吴欢欢.组织工程骨构建策略及自体浓缩骨髓血复合支架修复齿槽裂的临床研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2014.
[60] 余遵雄.铌酸钾钠压电陶瓷的制备及其生物学性能研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2014.
[61] 申德山,刘亚蕊,张清彬等.牙周膜干细胞移植促进兔牙槽突裂成骨修复研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2013,2:96-99.
[62] 赵丙姣,李远远,刘月华.聚己内酯静电纺丝支架与人牙周膜干细胞的生物相容性[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2014,30(5):269-272.
[63] Traini T, Novaes AB,Piattelli A et al.The relationship between interimplant distances and vascularization of the interimplant bone. Clin Oral Implants Res.2010;21(8):822-829.
[64] 宋晓彬.VEGF及BMP2基因修饰对血管化组织工程骨的影响及机制研究[D].济南:山东大学,2012.
[65] 陈广栋, 陈建常. 低强度脉冲超声波促进组织工程骨血管化重建的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010;18(17):1450-1452.
[66] 王居勇,沈惠良,刘利民, 等.经低强度超声波照射后组织工程骨成骨的组织学观察[A]. 第8届北京国际康复论坛文集(上册)[C], 2013:112-117.
[67] 申琳,刘文佳,杨振华, 等.静态压力对人牙周膜干细胞凋亡相关蛋白表达的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2015,15(12):2213-2218.
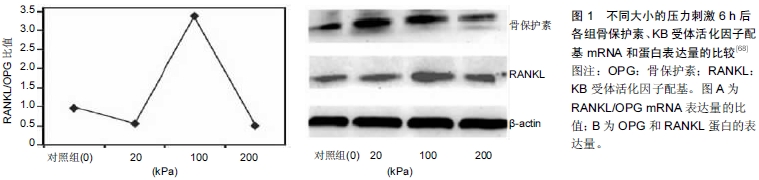
[68] 马小杰,刘文佳,杨振华, 等.静压力对人牙周膜干细胞骨向分化能力的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2015,25(3):137-141. |