中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (33): 5318-5321.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.33.014
• 组织构建与生物活性因子 tissue construction and bioactive factors • 上一篇 下一篇
腰椎间盘退变与局部转化生长因子β1及炎性细胞因子的关系
胡家美1,徐新华1,乐敏莉2
- 湖北民族学院附属民大医院,1骨外科,2放射科,湖北省恩施州 445000
Lumbar disc degeneration is associated with local transforming growth factor beta1 and inflammatory cytokines
Hu Jia-mei1, Xu Xin-hua1, Le Min-li2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, 2Department of Radiology, Minda Hospital of Hubei University for Nationalities, Enshi 445000, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
背景:近年来随着椎间盘退变分子水平研究的不断进展,转化生长因子β1基因在椎间盘细胞的增殖分化过程中具有一定作用,且参与了椎间盘的损伤修复过程,但转化生长因子β1是否也参与了椎间盘退变的病理生理过程目前尚无定论。
目的:探讨腰椎间盘退变程度与转化生长因子β1及炎性细胞因子之间的关系。
方法:选择72例椎间盘退变患者作为观察组(轻度22例,中度26例,重度24例),30例非椎间盘退变患者作为对照组,检测两组患者椎间盘局部转化生长因子β1及白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8、肿瘤坏死因子α等炎性细胞因子水平,在两组之间及不同椎间盘退变程度患者之间进行对比分析。同时采用直线相关分析法分析转化生长因子β1与炎性细胞因子及腰椎间盘退变的相关性。
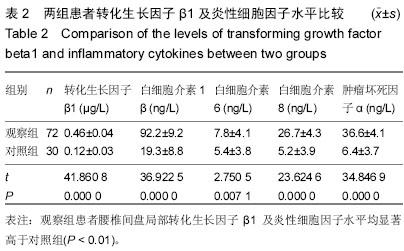
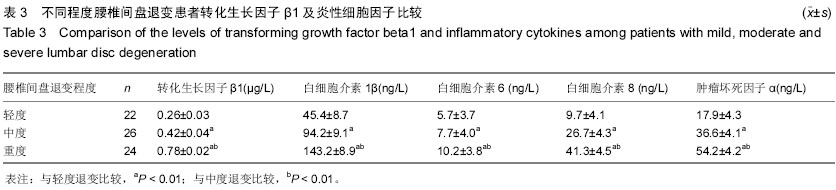
结果与结论:观察组患者腰椎间盘局部转化生长因子β1及白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8、肿瘤坏死因子α等炎性细胞因子水平均显著高于对照组(P < 0.01)。重度退变患者腰椎间盘局部转化生长因子β1及白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8、肿瘤坏死因子α等炎性细胞因子水平显著高于轻度及中度患者(P < 0.01),同时中度患者显著高于轻度患者(P < 0.01)。转化生长因子β1与白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8、肿瘤坏死因子α等炎性细胞因子以及椎间盘退变程度均呈显著正相关(r=0.198,0.312,0.356,0.275,0.724,P < 0.01)。提示转化生长因子β1及白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8、肿瘤坏死因子α等炎性细胞因子在退变椎间盘局部水平增高,且增高程度随着退变严重程度的增加而增加。
中图分类号: