| [1]Abolqhsaemian M, Samiezadeh S, Jafari D, et al. Displacement of the hip center of rotation after arthroplasty of Crowe III and IV dysplasia: a radiological and biomechanical study. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(6): 1031-1035.
[2]Grunert R, Kretzschmar C, Rotsch C, et al. 2014. Development of an optical measurement system for hip implant surgery to evaluate the leg length and the hip rotation center. Middle East Conference on Biomedical Engineering (MECBME), Hilton Hotel, Doha, Qatar.17-20.
[3]Ha YC, Yoo JJ, Lee YK, et al. Acetabular component positioning using anatomic landmarks of the acetabulum. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2012;470: 3515-3523.
[4]Charissoux JL, Asloum Y, Marcheix PS. Surgical management of recurrent dislocation after total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(1 Suppl):S25-34.
[5]Goel A, Lau EC, Ong KL. Dislocation Rates Following Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Have Plateaued in the Medicare Population. J Arthroplasty. 2014.
[6]Robbins GM, Masri BA, Garbuz DS, et al. Treatment of hip instability. Orthop Clin North Am. 2001;32:593.
[7]Khalifa AR, Marzouk AR, Alam M, et al. Short-term results of primary total hip arthroplasty for Protrusio Acetabuli. Int J. 2014;2(4): 538-542.
[8]Bicanic G, Barbaric K, Bohacek I, et al. Current concept in dysplastic hip arthroplasty: Techniques for acetabular and femoral reconstruction. World J Orthop. 2014;5(4):412-424.
[9]Wu X, Lou LM, Li SH, et al. Soft tissue balancing in total hip arthroplasty for patients with adult dysplasia of the hip. Orthop Surg. 2009;1(3):212-215.
[10]Holzapfel BM, Greimel F, Prodinger PM,et al. Total hip replacement in developmental dysplasia using an oval-shaped cementless press-fit cup. Int Orthop. 2012;36(7): 1355-1361.
[11]Delp SL, Komattu AV, Wixson RL. Superior displacement of the hip in total joint replacement: effects of prosthetic neck length, neck-stem angle, and anteversion angle on the moment-generating capacity of the muscles. J Orthop Res. 1994;12:860-870.
[12]Ranawat CS, Dorr LD, Inglis AE. Total hip arthroplasty in protrusio acetabuli of rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 1980;62(7):1059-1065.
[13]Bell AL, Pedersen DR, Brand RA. A comparison of the accuracy of several hip center location prediction methods. J Biomech,1990;23(6):617-621.
[14]Bouffard V, Beqon M, Farhadnia P, et al. Hip joint center localisation: A biomechanical application to hip arthroplasty population.World J Orthop. 2012;3(8):131-136.
[15]Krishnan SP, Carrington RW, Mohiyaddin S, et al. Common misconceptions of normal hip joint relations on pelvic radiographs. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(3);409-412.
[16]Wu X, Li SH, Lou LM, et al. The techniques of soft tissue release and true socket reconstruction in total hip arthroplasty for patients with severe developmental dysplasia of the hip. Int Orthop. 2012;36(9):1795-1801.
[17]Boudriot U, Hilgert J, Hinrichs F. Determination of the rotational center of the hip. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006; 126(6):417-420.
[18]Bicanic G, Delimar D, Delimar M, et al. Influence of the acetabular cup position on hip load during arthroplasty in hip dysplasia. Int Orthop. 2009;33(2): 397-402.
[19]Fousek J, Indrakova P. Total hip arthroplasty in post-dysplastic hip arthritis. Can type and position of the acetabular component influence longevity of the prosthesis? Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2007;74(1): 47-54.
[20]Kim DH, Cho SH, Jeong ST, et al. Restoration of the center of rotation in revision total hip arthroplasty. Arthroplasty. 2010; 25(7):1041-1046.
[21]Edurado GR, Ricardo FF, David D, et al. Reconstruction of the rotation center of the hip after oblong cups in revision total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Traumatol. 2013;14(1):39-49.
[22]Bouffard V, Begon M, Champagne A, et al. Hip joint center location: a biomechanical application to hip arthroplasty population. World J Orthop. 2012;3(8): 131-136.
[23]Lazarinis S, Milbrink J, Mattsson P, et al. Bone loss around a stable, partly threaded hydroxyapatite-coated cup: prospective cohort study using RSA and DXA. Hip Int. 2014; 24(2):155-166.
[24]王坤正.初次全髋关节置换术选择骨水泥或生物型固定方式的比较[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2012,6(4):492-495.
[25]刘明,王岩,陈继营,等.1436髋Ribbed假体单中心应用分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(14):1051-1053.
[26]史庆轩,李佩佳,孙磊,等.662髋Ribbed假体中远期临床疗效观察[J].中国矫形外科志,2012,20(15):1370-1373.
[27]Dalury DF, Kelley TC, Adams MJ. Modern proximally tapered uncemented sems can be safely used in Dorr Type C femoral bone. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(6):1014-1018.
[28]Dandachli W, Nakhla A, Iranpour F, et al. Can the acetabular position be derived from a pelvic frame of reference? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(4):886-893.
[29]Abolqhsaemian M, Samiezadeh S, Jafari D, et al. Displacement of the hip center of rotation after arthroplasty of Crowe III and IV dysplasia: a radiological and biomechanical study. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(6):1031-1035.
[30]Dib Z, Dardenne G, Poirier N, et al. Detection of the hip center in computer-assisted surgery: An in vitro assessment study. IRBM. 2013;34(4):319-321.
[31]García-Rey E, Fernández-Fernández R, Durán D, et al. Reconstruction of the rotation center of the hip after oblong cups in revision total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Traumatol. 2013;14(1): 39-49.
[32]Lenaerts G, Groote DF, Demeulenaere B, et al. Subject-specific hip geometry affects predicted hip joint contace forces during gait. J Biomech. 2008;41: 1243-1252.
[33]Heller MO, Schröder JH, Matziolis G, et al. Musculoskeletal load analysis. A biomechanical explanation for clinical results-and more? (in German). Orthopade. 2007;36(3):188, 190-194.
[34]Nawabi DH, Meftal M, Nam D, et al. Durable fixation achieved with medialized, high hip center cementless THAs for Crowe II and III dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(2): 630-636.
[35]Kaneuji A , Suqimori T, Ichiseki T, et al. Minimum ten-year results of a porous acetabular component for Crowe I to III hip dysplasia using an elevated hip center. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24(2): 187-194.
[36]Baqhdadi YM, Larson AN, Sierra RJ. Restoration of the hip center during THA performed for protrusio acetabuli is associated with better implant survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(10):3251-3259.
[37]Kaneuji A, Sugimori T, Ichiseki T, et al. Minimum ten-year results of a porous acetabular component for Crowe I to III hip dysplasia using an elevated hip center. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24:187- 194 .
[38]Bicanic G, Delimar D, Delimar M, et al. Influence of the acetabular cup position on hip load during arthroplasty in hip dysplasia. Int Orthop. 2009;33:397-402.
[39]Hartofilakidis G, Karachalios T. Total hip arthroplasty for congenital hip disease. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A: 242-250.
[40]Sknk EL, Zaltz I, Heare T, et al. Acetabular cartilage and labral damage observed during surgical hip dislocation for stable slipped capital femoral epiphysis. J Pediatr Orthop. 2010; 30(1): 26-30.
[41]Shi HF, Xiong J, Chen YX, et al. Radiographic analysis of the restoration of hip joint center following open reduction and internal fixation of acetabular fractures: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:277.
[42]The B, Kootstra JW, Hosman AH, et al. Comparison of the techniques for correction of magnification of pelvic X-ray for hip surgery planning. J Digit Imaging. 2007; 20(4): 329-335. |

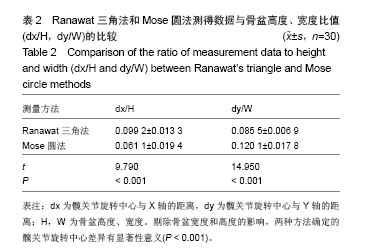
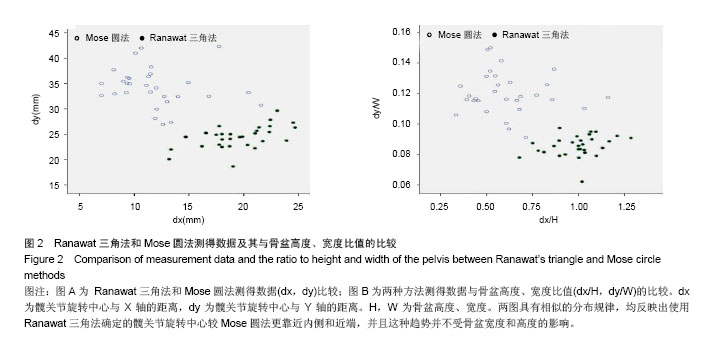
.jpg)