| [1] Helwig P, Hindenlang U, Hirschmüller, et al. A femoral model with all relevant muscles and hip capsule ligaments. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2013;16(6): 669-677.
[2] 方国芳, 林荔军, 于博, 等.不同状态下股骨的应力分布及临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(17):3045-3047.
[3] 钟务学, 张银网, 朱海波, 等.采用体绘制方法建立人股骨三维有限元模型及其应力分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(17): 3048-3051.
[4] 成海平, 柳松杨, 王兴伟, 等.人股骨上段三维有限元模型的建立[J]. 生物医学工程研究, 2010, 19(2):106-108.
[5] 马信龙, 付鑫, 马剑雄, 等.人股骨近端空间结构重建新方法及有限元模型的建立[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2011, 28(1):71-75.
[6] 谭勇, 樊继波, 李莎, 等.股骨上段有限元几何模型的建立与分析[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2012,18(4):305-308,374.
[7] 万磊, 李义凯, 原林, 等.基于中国数字人CT 数据重建膝关节有限元模型[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2006,21(4):271-273.
[8] Latifi MH, Ganthel K, Rukmanikanthan S, et al. Prospects of implant with locking plate in fixation of subtrochanteric fracture: experimental demonstration of its potential benefits on synthetic femur model with supportive hierarchical nonlinear hyperelastic finite element analysis. Biomed Eng Online. 2012;11: 23.
[9] Orwoll ES, Marshall LM, Nielson CM, et al. Finite element analysis of the proximalfemur and hip fracture risk in older men. J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(3):475-483.
[10] Amin S, Kopperdhal DL, Melton LJ 3rd, et al. Association of hip strength estimates by finite-element analysis with fractures in women and men. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(7): 1593-1600.
[11] Cooper C, Cole ZA, Holroyd CR, et al. Secular trends in the incidence of hip and other osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2011;22(5):1277-1288.
[12] Alexander GE 3rd, Gutierrez S, Navak A, et al. Biomechanical model of a high risk impending pathologic fracture of the femur: lesion creation based on clinically implemented scoring systems. Clin Biomech. 2013;28(4): 408-414.
[13] 樊向利, 郭征, 宫赫, 等.正常人股骨近端生物力学性能的区域性分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2011,26(7):601-603.
[14] 王沫楠, 王红晶, 杜志江, 等.股骨假体热应力有限元分析[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2012, 44(7):38-42.
[15] 邹冬华, 李正东, 黄平, 等.股骨有限元模型的建立及损伤生物力学验证[J].法医学杂志, 2011, 27(4), 241-245.
[16] Koivumäki JE, Thevenot J, Pulkkinen P, et al. Cortical bone finite element models in the estimation of experimentally measured failure loads in the proximal femur. Bone. 2012;51(4):737-740.
[17] Rawal BR, Bhatnagar N. An investigation on the effect of groove geometry on cementless femoral stem component in hip arthroplasty. Pak J Biol Sci. 2013;16(24):2073-2075.
[18] 李峰, 吴华.基于DICOM数据构建股骨三维有限元模型的精确力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(30):5483-5489.
[19] Grassi L, Väänänen SP, Amin Yavari S,et al.Experimental validation of finite element model for proximal composite femur using optical measurements.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2013;21:86-94.
[20] Hambli R, Bettamer A, Allaoui S. Finite element prediction of proximal femur fracture pattern based on orthotropic behaviour law coupled to quasi-brittle damage. Med Eng Phys. 2012;34(2): 202-210.
[21] Dickinson AS, Taylor AC, Ozturk H, et al. Experimental validation of a finite element model of the proximal femur using digital image correlation and a composite bone model. J Biomech Eng. 2011;133(1): 014504.
[22] Grassi L, Väänänen SP, Amin Yavari S, et al. Experimental validation of finite element model for proximal composite femur using optical measurements. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2013;21: 86-94.
[23] Lewis CL, Sahrmann SA, Moran DW. Effect of position and alteration in synergist muscle force contribution on hip forces when performing hip strengthening exercises. Clin Biomech. 2009;24(1): 35-42.
[24] Rybicki EF, Simomen FA, Weis EB Jr. On the mathematical analysis of stress in the human femur. J Biomech. 1972;5(2): 203-215.
[25] Lenaerts L, van Lenthe GH. Multi-level-specific modeling of the proximal femur: a promising tool to quantify the effect of osteoporosis treatment. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2009;367(1895): 2079-2093.
[26] Poggie RA, Turgeon TR, Coutts RD. Failure analysis of aceramic bearing acetabular component. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(2): 367-375.
[27] Cheung G, Zalzal P, Bhandari M, et al. Finite element analysis of a femoral retrograde intramedullary nail subject to gait loading. Med Eng Phys. 2004;26(2): 93-108.
[28] Poggie RA, Turgeon TR, Coutts RD. Failure analysis of aceramic bearing acetabular component. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(2):367-375. |
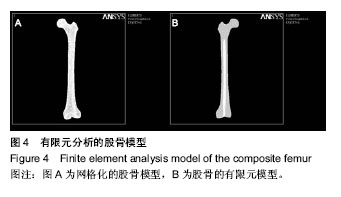
.jpg)
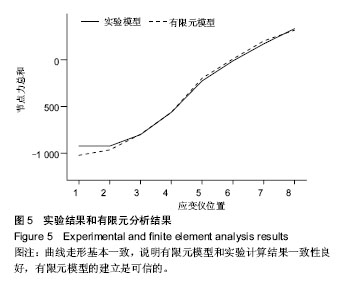
.jpg)