| [1] 郑启新,邹枕玮,郭晓东,等.腰椎间盘退变性疾病的研究进展及展望[J].中华实验外科杂志,2010,27(11):1573-1576.
[2] 黄菊英,李海云,菅凤增.腰椎间盘突出症有限元模型的建立与分析[J].计算机生物力学研究,2012,12(4):394-398.
[3] Strange DG, Fisher ST, Boughton PC, et al. Restoration of compressive loading properties of lumbar discs with a nucleus implant: a finite element analysis study. Spine J. 2010;10:602-609.
[4] Natarajan RN,Williams JR, Andersson GB. Modeling changes in intervertebral disc mechanics with degeneration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88( Suppl 2):36-40.
[5] Fessler RG, O' Toole JE, Eichholz KM, et al. The development of minimally invasive spine surgery. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2006; 17(4):401-409.
[6] Bresnahan L, Ogden AT, Natarajan RN, et al. A biomechanical evaluation of graded posterior element removal for treatment of lumbar stenosis: comparison of a minimally invasive approach with two standard laminectomy techniques. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(1):17-23.
[7] Hyun SJ, Kim YB, Kim YS, et al. Postoperative changes in paraspinal muscle volume: comparison between paramedian interfascial and midline approaches for lumbar fusion.Korean Med Sci. 2007;4: 646-651.
[8] 王本杰,赵德伟,芦健民,等.显微外科微创技术与传统手术治疗腰椎间盘突出症的比较观察[J].中华显微外科杂志,2011, 34(9): 182-184.
[9] Rohlmann A, Zander T, Rao M,et al. Applying a follower load delivers realistic results for simulating standing.J Biomech. 2009;42(10):1520-1526.
[10] Nakamura T, Iribe T, Asou Y,et al. Effects of compressive loading on biomechanical properties of disc and peripheral tissue in a rat tailmodel. Eur Spine J.2009,18(11):1595- 1603.
[11] Kim H, Lim DH, Oh HJ, et al. Effects of nonlinearity in the materials used for the semi-rigid pedicle screw systems on biomechanical behaviors of the lumbar spine after surgery. Biomed Mater. 2011;6(5): 055005.
[12] Fagan MJ, Julian S, Mohsen AM. Finite element analysis in spine research. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2002;216(5):281- 298.
[13] Boger A, Heini P, Windolf M, et al. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty: a biomechanical study of low-modulus PMMA cement. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(12):2118-2125.
[14] Bowden AE1, Guerin HL, Villarraga ML, et al. Quality of motion considerations in numerical analysis of motion restoring implants of the spine. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2008;23(5):536-544.
[15] Pitzen T, Geisler F, Matthis D, et al. A finite element model for predicting the biomechanical behaviour of the human lumbar spine. Control Eng Pract. 2002;10:83-90.
[16] 黄菊英,李海云,吴浩.腰椎间盘突出症力学特征的仿真计算方法[J].医用生物力学,2012,27(1):96-101.
[17] 苏晋,赵文志,陈秉智,等.椎板不同切除范围对腰椎生物力学影响的有限元分析[J].生物医学工程杂志,2012,29(3):466-469.
[18] Gu WY, Mao XG, Foster RJ, et al. The anisotropic hydraulic permeability of human lumbar annulus fibrosus. Influence of age, degeneration, direction, and water content. Spine. 1999; 24(23): 2449-2455.
[19] Yamamoto I, Panjabi MM, Crisco T, et al. Three-dimensiona, lmovements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine (Phila Pa 1976), 1989;14:1256-1260.
[20] Danjabi MM,Abumi K,Duranceau J,et al. Biomechanical evaluation of spinal fixation devices. Spine. 1988;13(10): 11-35.
[21] Li G, Wang S, Passias P, et al. Segmental in vivo vertebral motion during functional human lumbar spine activities. Eur Spine. 2009;18:1013-1021.
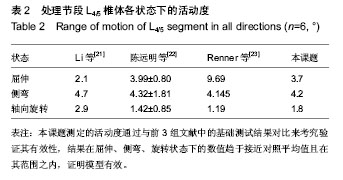
[22] 陈远明,靳安民,陈锋,等.单节段腰椎活动度对邻近节段运动的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(17):13177-3182.
[23] Renner SM,Natarajan RN,Patwardhan AG,et al. Novel model to analyze the effect of a large compressive follower pre-load on range of motions in a lumbar spine. Biomechanics. 2007; 40:1326-1332.
[24] 成思源,谢韶旺.Geomagic Studio逆向工程技术及应用[M].北京:清华大学出版社, 2010:63-78.
[25] 李海波,方杰,陈其昕,等.髓核摘除术对腰椎生物力学特性影响的有限元研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2011,29(1): 89-93.
[26] 宋升,芮永军,孙振,等.模拟腰椎间盘髓核摘除后疲劳载荷对腰椎稳定性的影响[J]中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(48): 9040-9043.
[27] Michalek AJ, Funabashi KL, Iatridis JC. Needle puncture injury of the rat intervertebral disc affects torsional and compressive biomechanics differently. Eur Spine J. 2010, 19(12): 2110-2116.
[28] Adams MA,Freeman BJ,Morrison HP, et al. Mechanical initiation of intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 2000; 5(13):1625-1636.
[29] 迟增德,刘尚礼,李春海,等.腰椎髓核摘除后小关节应力分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(5):377-380.
[30] Kuroki H, Goel VK, Holekamp SA, et al. Contributions of flexion-extension cyclic loads to the lumbar spinal segment stability following different discectomy procedures. Spine. 2004;29(3):E39-46.
[31] Otoshi K, Kikuchi S, Konno S, et al. The reactions of glial cells and endoneurial macrophages in the dorsal root ganglion and their contribution to pain-related behavior after application of nucleus pulposus onto the nerve root in rats. Spine. 2010;35 (3):264-271.
[32] Hayashi S, Taira A, Inoue G, et al. TNF-alpha in nucleus pulposus induces sensory nerve growth : a study of the mechanism of discogenic low back pain using TNF-alpha-deficient mice. Spine. 2008;33(14): 1542-1546.
[33] Schulte TL, Leistra F, Bullmann V, et al. Disc height reduction in adjacent segments and clinical outcome 10 years after lumbar 360 degrees fusion. Eur Spine J. 2007;16:2152-2158.
[34] Carragee EJ,Spinnickie AO,Alamin TF,et al. A prospective controlled study of limited versus subtotal posterior discectomy short -term outcomes in patients with herniated lumbar intervertebral discs and large posterior annular defect. Spine. 2006;31(6):653-657.
[35] Yorimitsu E, Chiba K, Toyama Y, et al. Long-term outcomes of standard discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: a follow-up study of more than 10 years. Spine. 2001;26:652-657.
[36] Cinotti G, Roysam GS, Eisenstein SM, et al. Ipsilateral recurrent lumbar disc herniation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998; 80(5):825-832.
[37] 侯树勋,李明全,白巍,等.腰椎髓核摘除术远期疗效评价[J].中华骨科杂志,2003,23(9):513-516.
[38] 陈学明,刘亚东,许崧杰,等.单节段腰椎间盘突出症单纯髓核摘除术后10年以上随诊观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(8): 644-649.
[39] 李玉成,邢星,孙文才,等.人工椎间盘及髓核假体的生物力学[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(22):4169-4172.
[40] 宋超,李新锋,刘祖德,等.腰椎棘突间撑开融合器治疗早期腰椎退变的三维有限元分析[J].中华临床医师杂志, 2013,7(3): 1039-1045.
[41] 张加芳,郑召民,张奎渤,等.经皮置入式腰椎棘突间撑开器的生物力学测试[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2011, 21(2):129-132. |
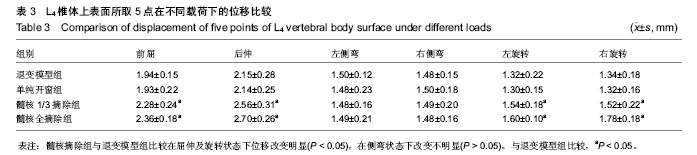
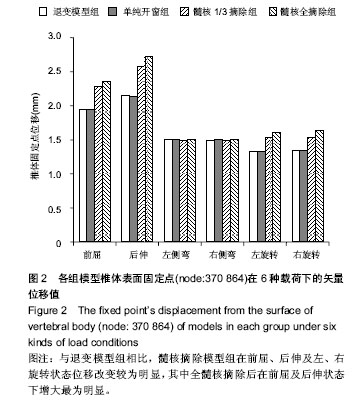
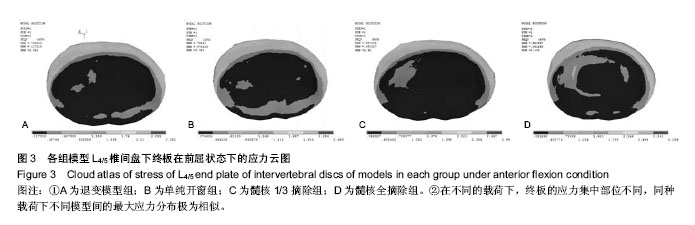
.jpg)
.jpg)