中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (17): 2667-2672.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.17.008
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
治疗股骨转子间骨折时头颈拉力螺钉不同置入位置的有限元计算
王冬冬1,高 峰2,程杰平2,苗巍巍2,徐春华2,朱伟民1
- 1吉林大学机械科学与工程学院,吉林省长春市 130022
2吉林大学第二医院骨科医院,吉林省长春市 130041
Finite element calculation of head and neck lag screws in different placement positions for intertrochanteric fracture
Wang Dong-dong1, Gao Feng2, Cheng Jie-ping2, Miao Wei-wei2, Xu Chun-hua2, Zhu Wei-min1
- 1College of Mechanical Science & Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, Jilin Province, China
2Hospital of Orthopedics, Second Hospital, Jilin University, Changchun 130041, Jilin Province, China
摘要:
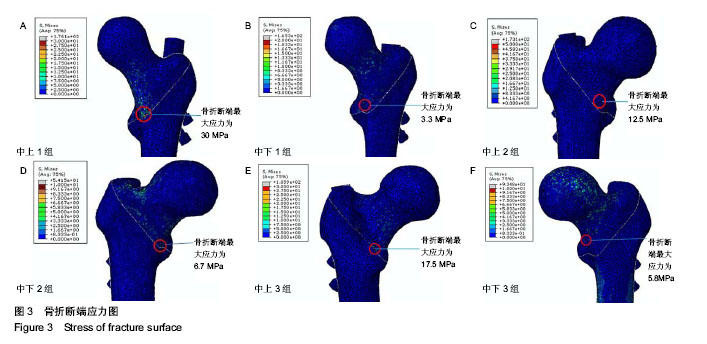
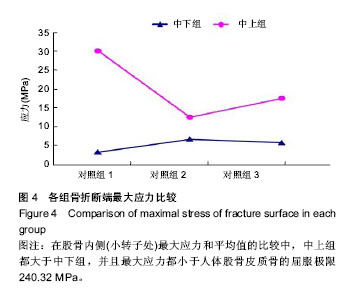
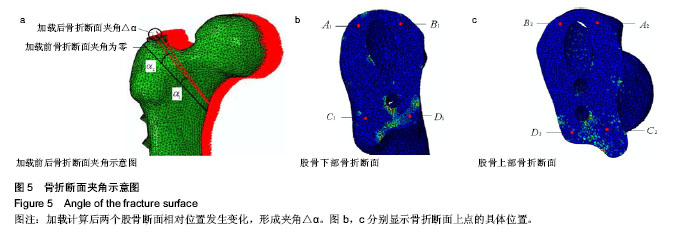
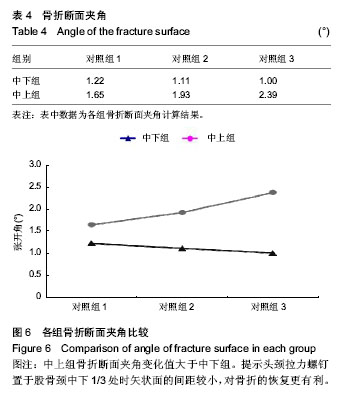
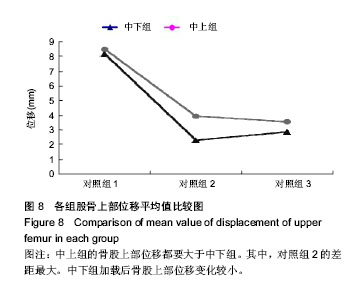
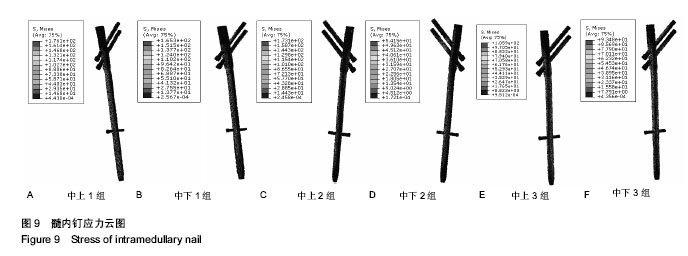
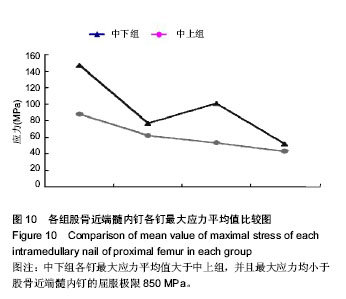
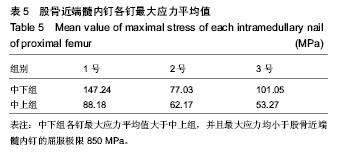
背景:课题组总结发现,股骨转子间骨折股骨近端髓内钉置入内固定治疗后出现髋内翻的病例中,除小部分由于股骨转子部粉碎性骨折和个别存在复位问题之外,绝大多数出现并发症的患者术后复查X射线片可见,2枚头颈拉力螺钉位置均位于股骨颈中上部。 目的:通过有限元计算,验证股骨近端髓内钉头颈拉力螺钉不同置入位置的生物力学性能,从而指导股骨近端髓内钉置入以减少置入后并发症的发生。 方法:利用MIMICS中的布尔运算将股骨近端髓内钉置入骨折模型,建立三维模型。实验分为2组:中下组股骨近端髓内钉头颈拉力螺钉置于股骨颈中下1/3处;中上组股骨近端髓内钉头颈拉力螺钉置于股骨颈中上1/3处。利用有限元软件计算头颈拉力螺钉于不同方向置入时股骨及股骨近端髓内钉的应力分布情况。 结果与结论:骨折断端应力分布结果显示,中下组小转子处所受压应力小于中上组,并且中下组股骨近端髓内钉各钉所受最大应力平均值大于中上组。骨折断面张开角测量结果显示,加载后中下组骨折断面张开角小于中上组。载荷与位移关系分析结果显示,加载后中下组股骨上部合位移小于中上组。说明2枚头颈拉力螺钉置入股骨颈中下1/3处时,生物力学性能更好,结构相对更稳定,受力更合理,在临床中具有重要的参考价值。
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)