中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (17): 2655-2658.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.17.006
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
个体化设计钛网植骨融合内固定恢复颈椎曲度
文 睿,叶 飞,蒲海波,魏书一
- 泸州医学院附属医院脊柱外科,四川省泸州市 646000
Individual designed titanium mesh used in bone graft fusion and internal fixation to restore cervical curvature
Wen Rui, Ye Fei, Pu Hai-bo, Wei Shu-yi
- Department of Spine Surgery, the Affiliated Hospital of Luzhou Medical College, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
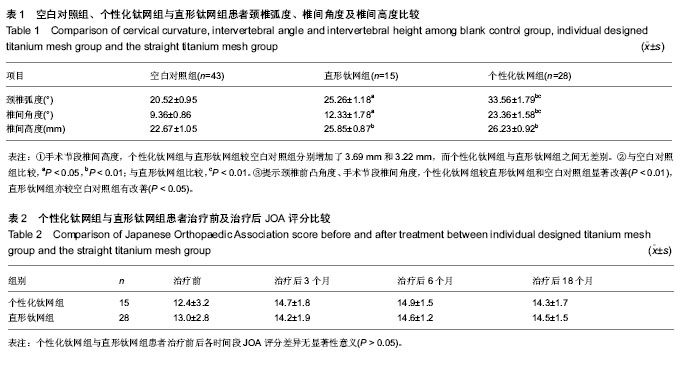
背景:钛网是近年来国内外应用于脊柱尤其是颈椎疾患的一种常用新型植骨支撑物,目前脊髓型颈椎病患者的前路手术中如何更好地改善颈椎前凸弧度仍是治疗的难点。 目的:观察脊髓型颈椎病患者经颈前路椎体次全切过程中,直形钛网与个体化设计钛网植骨融合内固定对颈椎曲度恢复及治疗后JOA评分的影响。 方法:纳入43例有椎体次全切、减压植骨内固定手术指征的脊髓型颈椎病患者,根据治疗内固定方案分为2组,个体化设计梯形钛网组15例,直形钛网组28例。所有患者于治疗前均拍摄颈椎正侧位X射线片作为空白对照。回顾2组患者的临床资料,比较治疗后JOA评分、颈椎弧度、椎间角度及椎间高度的差异。 结果与结论:颈椎前凸角度、手术节段椎间角度方面,个性化钛网组较直形钛网组和空白对照组显著改善(P < 0.01),直形钛网组亦较空白对照组有改善(P < 0.05)。手术节段椎间高度方面,个性化钛网组与直形钛网组较空白对照组分别增加了3.69 mm和3.22 mm,而个性化钛网组与直形钛网组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。JOA评分方面,个性化钛网组与直形钛网组患者各时间段差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。提示在脊髓型颈椎病患者行椎体次全切时,修剪钛网以模拟正常椎间盘前高后低的形状,可以更有效地恢复颈椎生理弧度和手术节段椎间角度。
中图分类号: