| [1] Jones AO, Houang MT, Low RS,et al. Medial meniscus posterior root attachment injury and degeneration: MRI findings. Australas Radiol. 2006;50(4):306-313.
[2] Aagaard H, Verdonk R. Function of the normal meniscus and consequences of meniscal resection. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 1999;9(3):134-140.
[3] Lerer DB, Umans HR, Hu MX,et al. The role of meniscal root pathology and radial meniscal tear in medial meniscal extrusion. Skeletal Radiol. 2004;33(10):569-574.
[4] Vedi V, Williams A, Tennant SJ,et al. Meniscal movement. An in-vivo study using dynamic MRI. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999; 81(1):37-41.
[5] Kenny C. Radial displacement of the medial meniscus and Fairbank's signs. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;(339):163-173.
[6] Park HJ, Kim SS, Lee SY,et al. Medial meniscal root tears and meniscal extrusion transverse length ratios on MRI. Br J Radiol. 2012;85(1019):e1032-1037.
[7] Miller TT, Staron RB, Feldman F,et al. Meniscal position on routine MR imaging of the knee. Skeletal Radiol. 1997;26(7): 424-427.
[8] Breitenseher MJ, Trattnig S, Dobrocky I,et al. MR imaging of meniscal subluxation in the knee. Acta Radiol. 1997;38(5): 876-879.
[9] Costa CR, Morrison WB, Carrino JA. Medial meniscus extrusion on knee MRI: is extent associated with severity of degeneration or type of tear. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 183(1):17-23.
[10] Bessette GC.The meniscus.Orthopedics. 1992;15(1):35-42.
[11] McBride ID, Reid JG. Biomechanical considerations of the menisci of the knee. Can J Sport Sci. 1988;13(4):175-187.
[12] Thompson WO, Thaete FL, Fu FH,et al. Tibial meniscal dynamics using three-dimensional reconstruction of magnetic resonance images. Am J Sports Med. 1991;19(3):210-215.
[13] Jones RS, Keene GC, Learmonth DJ,et al. Direct measurement of hoop strains in the intact and torn human medial meniscus. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1996;11(5): 295-300.
[14] Lee SY, Jee WH, Kim JM. Radial tear of the medial meniscal root: reliability and accuracy of MRI for diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191(1):81-85.
[15] Ahn JH, Lee YS, Yoo JC,et al. Results of arthroscopic all-inside repair for lateral meniscus root tear in patients undergoing concomitant anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2010 ;26(1):67-75.
[16] Allaire R, Muriuki M, Gilbertson L,et al. Biomechanical consequences of a tear of the posterior root of the medial meniscus. Similar to total meniscectomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008 ;90(9):1922-1931.
[17] Boxheimer L, Lutz AM, Treiber K,et al. MR imaging of the knee: position related changes of the menisci in asymptomatic volunteers. Invest Radiol. 2004 ;39(5):254-263.
[18] McDermott ID, Lie DT, Edwards A,et al.The effects of lateral meniscal allograft transplantation techniques on tibio-femoral contact pressures. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008; 16(6):553-560.
[19] Choi SH, Bae S, Ji SK,et al. The MRI findings of meniscal root tear of the medial meniscus: emphasis on coronal, sagittal and axial images. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012; 20(10):2098-2103.
[20] Bin SI, Kim JM, Shin SJ. Radial tears of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus. Arthroscopy. 2004 ;20(4):373-378.
[21] Lee YG, Shim JC, Choi YS,et al. Magnetic resonance imaging findings of surgically proven medial meniscus root tear: tear configuration and associated knee abnormalities. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2008;32(3):452-457.
[22] Ozkoc G, Circi E, Gonc U,et al. Radial tears in the root of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008;16(9):849-854. |
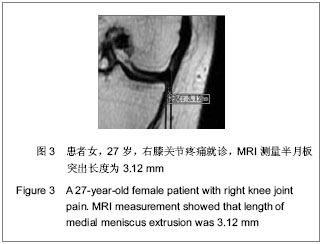
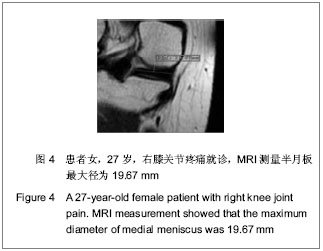
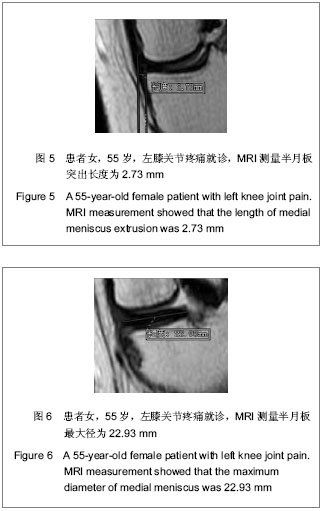

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)