| [1]Ishikawa F, Shimazu H, Shultz LD, et al. Purified human hematopoietic stem cells contribute to the generation of cardiomyocytes through cell fusion. FASEB J. 2006;20(7): 950-952.
[2]Lee OK, Kuo TK, Chen WM, et al. Isolation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood. Blood. 2004;103(5):1669-1675.
[3]Rao J, Shen J, Quan D, et al. Property studies on three-dimensional porous blended silk scaffolds. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2009;23(10):1264-1270.
[4]Huang Y, Dai ZQ, Ling SK, et al. Gravity, a regulation factor in the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Sci. 2009;16:87.
[5]Schulze-Tanzil G, Mobasheri A, de Souza P, et al. Loss of chondrogenic potential in dedifferentiated chondrocytes correlates with deficient Shc-Erk interaction and apoptosis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2004;12(6):448-458.
[6]Secco M, Zucconi E, Viera NM, et al. Multipotent stem cells from umbilical cord: cord is richer than blood! Stem Cells. 2008;26:146-150.
[7]Secco M, Zucconi E, Viera NM, et al. Multipotent stem cells from umbilical cord: cord is richer than blood! Stem Cells. 2008;26:146-150.
[8]蓝孝同,王英振.骨髓间充质干细胞治疗骨性关节炎的研究进展[J].齐鲁医学杂志,2010,25(2):186-188.
[9]Szpalski C,Barbaro M,Saqebin F,et al. Bone tissue engineering:current strategies and techniques--part II:Cell types. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2012;18(4):258-269.
[10]于艳秋,任海琴,云伟,等.人类脐血来源的间充质干细胞向软骨和成骨细胞分化的实验研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2008, 25(6):1385-1389.
[11]解继胜,黄海玲,唐毓金,等.人脐带血间充质干细胞分离培养及向软骨细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(16): 3065-3068.
[12]Au A, Boehm CA, Mayes AM, et al. Formation of osteogenic colonies on well-defined adhesion peptides by freshly isolated human marrow cells. Biomaterials,2007,28(10):1847-1861.
[13]Broxmeyer HE. Insights into the biology of cord stem/progenitor cells. Cells Prolif. 2011;44:55-59.
[14]Fonseka M, Ramasamy R, Yip WK, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hUCB-MSC) Inhibits the Proliferation of K562 (Human Erythromyeloblastoid Leukemic Cell Line).Cell Biol Int. 2012. [Epub ahead of print]
[15]Kim JS, Lee HK, Kim MR, et al. Differentially expressed proteins of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human cord blood (hUCB) during osteogenic differentiation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008;72(9):2309-2317.
[16]Gennery AR,Cant AJ. Cord blood stem cell transplantation in primary immune deficiencies. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;7(6):528-534.
[17]Erices A, Conget P, Mingudl JJ, et al. Meaenchymaal progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood. Br J Heamatol. 2000;109:235-242.
[18]Malgieri A,Kantzari E,Patrizi MP,et al. Bone marrow and umbilical cord blood human mesenchymal stem cells:state of the art. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2010;3:248-269.
[19]Mohyeddin Bonab MA, Alimoghaddam KA,Goliaei ZA, et al. Which factors cm affect cord blood variables?Transfusion. 2004:44(5);690-693.
[20]Sibov TT, Severino P, Marti LC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood: parameters for isolation, characterization and adipogenic differentiation. Cytotechnology. 2012;64(5):511-521.
[21]Ma LL, Meng FB, Shi P, et al. Quantity and proliferation rate of mesenchymal stem cells in human cord blood during gestation. Cell Biol Int. 2012;36(4):415-418.
[22]Liu QH, Ge J, Liu KY. Are CD133 and CD271 useful in positive selection to enrich umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells? Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2010; 18(5): 1286-1291.
[23]Zhang H, Li A, Rao GZ, et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood and its bone inducing activity in vitro. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2010;19(3): 290-295.
[24]Zhang Y, Wang L, Yang M, et al. Experimental study on culture of human mesenchymal stem cells from cord blood using autologous serum Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2008;25(5):1155-1160.
[25]Fan X, Liu T, Liu Y, et al. Optimization of primary culture condition for mesenchymal stem cells derived from umbilical cord blood with factorial design. Biotechnol Prog. 2009; 25(2):499-507.
[26]Rong LJ, Chi Y, Yang SG, et al. Effects of interferon-γ on biological characteristics and immunomodulatory property of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2012;20(2):421-426.
[27]Jang MW, Yun SP, Park JH, et al. Cooperation of Epac1/Rap1/Akt and PKA in prostaglandin E(2) -induced proliferation of human umbilical cord blood derived mesenchymal stem cells: involvement of c-Myc and VEGF expression.J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(12):3756-3767.
[28]Ko E, Lee KY, Hwang DS. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells undergo cellular senescence in response to oxidative stress. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(11):1877-1886.
[29]Laitinen A, Nystedt J, Laitinen S. The isolation and culture of human cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells under low oxygen conditions. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;698:63-73.
[30]Kern S, Eichler H, Stoeve J, et al. Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue, Stem Cells. 2006;24(5):1294-1301.
[31]Gong W, Han Z, Zhao H, et al. Banking human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for clinical use.Cell Transplant. 2012;21(1):207-216.
[32]邹叶青,贺文凤,石庆之,等.骨髓与脐带血间充质干细胞的生物学特性比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床研究,2008,12(21): 4141-4143.
[33]高杨,李立,冉江华,等. 两种分离脐血间充质干细胞的方法比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(19):3472-3475.
[34]Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[35]Hirvonen T, Suila H, Kotovuori A, et al. The i blood group antigen as a marker for umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(3): 455-464.
[36]Yu Y,Ren H,Yun W,et al. Differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into chondroblast and osteoblasts. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2008;25(6):1385-1389.
[37]农丕地,解继胜,黄海玲.体外诱导人脐带血间充质干细胞为软骨细胞的初步研究[J].右江民族医学院学报,2007,29(5):689-691.
[38]Yan H,Yu C.Repair of full-thickness cartilage defects with cells of different origin in a rabbit model. Arthroscopy. 2007; 23(2): 178-187.
[39]Fenq X,Tian S,Sun K,et al. Effect of platelet lysate on chondrogenic differentiation of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;25(10):1250-1255.
[40]Jin HJ,Park SK,Oh W,et al. Down-regulation of CD105 is associated with multi-lineage differentiation in human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;381(4):676-681.
[41]Blain EJ. Mechanical regulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Front Biosci. 2007;12:507-527.
[42]李丽艳,杜江,黄金中.兔软骨细胞诱导人脐血间充质干细胞成软骨的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(49): 9713-9714. |
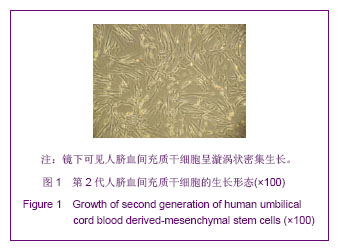
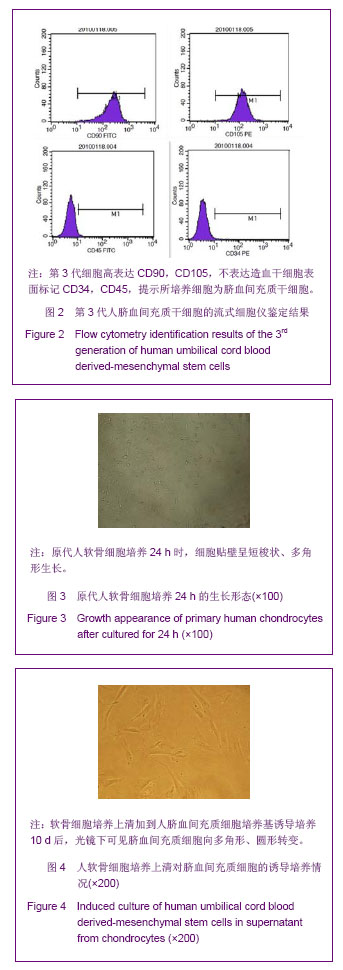

.jpg)