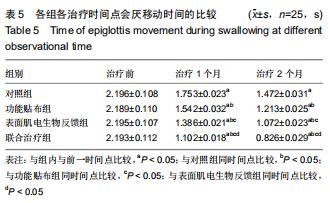
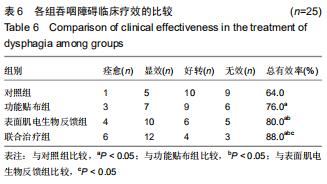
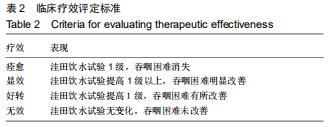
|
[1] OSUAFOR C, DONEGAN C.Prolonged dysphagia following stroke.Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 2017;38(1): 641-641.
[2] JONES O, CARTWRIGHT J, WHITWORTH A, et al. Dysphagia therapy post stroke: An exploration of the practices and clinical decision-making of speech-language pathologists in Australia.Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2018; 20(2):226-237.
[3] LI WJ,LIW,NIU XF, et al.A novel endoscopic surgery for dysphagia after stroke.Surg Endosc. 2018;32(1):127-133.
[4] ENAS EAE, FATHY K.Effect of swallowing training program on dysphagia following cerebrovascular stroke.Egyptian Nursing Journal.2018;15(2):125-134.
[5] HOLLY G,LAUREN H,ROSEANN C,et al.Use of Oral Hydration Protocols for Dysphagic Patients Following Stroke. ehabil Nurs. 2018;43(5):290-296.
[6] SONJA SK,CORINNA R,PAUL M,et al.Randomized trial of transcranial direct current stimulation for poststroke dysphagia. Ann Neurol. 2018;83(2):328-340.
[7] MOFTAH M, JADAVJI NM.Role of behavioral training in reducing functional impairments after stroke.Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(9):1507-1508.
[8] 励建安,贺小桦,陈方灿,等.功能性贴扎技术[M].北京:电子工业出版社,2019:4.
[9] 林欣谕.肌内效贴在康复领域应用及发展研究[J].当代体育科技, 2018,8(19):11-13.
[10] CARNABY MANN GD,CRARY MA. McNeill dysphagia therapy program: a case-control study.Arch Phys Med Rehabil.2010;91(5):743-749.
[11] MYUNG SP,JIN YC,YOUNG JS,et al.Systematic Review of Behavioral Therapy to Improve Swallowing Functions of Patients With Parkinson's Disease.Gastroenterol Nurs. 2019; 42(1):65-78.
[12] 刘佩婉,葛丽君,王思远,等.肌内效贴改善脑卒中吞咽障碍的疗效观察[J].中日友好医院学报,2016,30(3):175-176.
[13] 杨立.表面肌电生物反馈联合吞咽训练在脑梗死恢复期吞咽障碍患者康复中的应用[J].临床合理用药杂志,2018,11(2): 100-101.
[14] 李沛,冯卫星,闫菲菲,等.穴位按摩配合进食训练治疗卒中后吞咽障碍36例[J].河北中医,2017,39(2):273-276.
[15] GRAWBURG M,HOWE T,WORRALL L,et al.Family-Centered Care in Aphasia.Topics in Language Disorders.2019;39(1): 29-54.
[16] MARINDA B,EMMA M,NORA S. Expiratory muscle strength training improves swallowing and respiratory outcomes in people with dysphagia:A systematic review.Int J Speech Lang Pathol. 2019;21(1):89-100.
[17] WILMSKOETTER J,HERBERT TL,BONILHA H.Factors Associated With Gastrostomy Tube Removal in Patients With Dysphagia After Stroke.Nutr Clin Pract. 2017;32(2):166-174.
[18] KIMURA Y,KISHIMOTO S,SUMI T,et al.Improving the Quality of Life of Patients With Severe Dysphagia by Surgically Closing the Larynx.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol.2019;128(2): 96-103.
[19] CLAIRE F,MATT G. Kinesiology tape mediates soccer-simulated and local peroneal fatigue in soccer players. Res Sports Med.2017;25(3):313-321.
[20] CHRISTOPHE C,SUSANA L,RAFAEL G,et al.Kinesiology taping does not change fibularis longus latency time and postural sway.Journal of bodywork and movement therapies. 2016;20(1):132-138.
[21] SHIH YF,LEE YF,CHEN WY.Effects of Kinesiology Taping on Scapular Reposition Accuracy, Kinematics, and Muscle Activity in Athletes With Shoulder Impingement Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Study.J Sport Rehabil.2018;27(6): 560-569.
[22] 陈怡,胥方元.肌内效贴联合功能训练对脑卒中患者的疗效[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2018,13(5):265-266.
[23] MIKAMI DLY, FURIA CLB, WELKER AF. Addition of Kinesio Taping of the orbicularis oris muscles to speech therapy rapidly improves drooling in children with neurological disorders. Dev Neurorehabil.2019;22(1):13-18.
[24] 罗子芮,林广勇,陈子波,等.表面肌电生物反馈疗法联合吞咽训练对鼻咽癌放疗后吞咽困难患者的影响[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2019,41(8):601-605.
[25] 吴正波.表面肌电生物反馈疗法联合吞咽康复训练对脑卒中后吞咽障碍功能恢复的影响[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2017, 20(9):69-71.
|