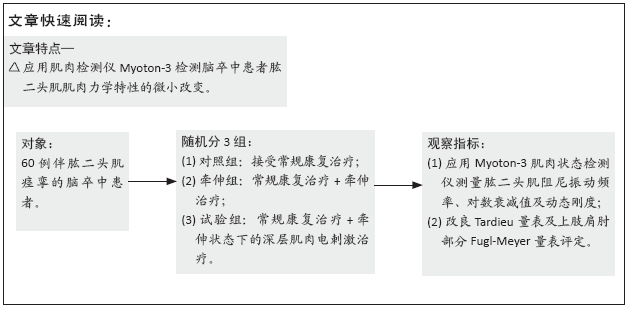
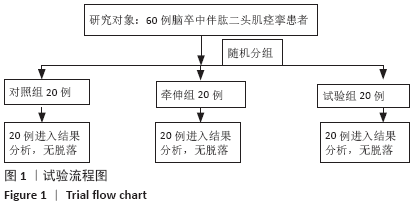
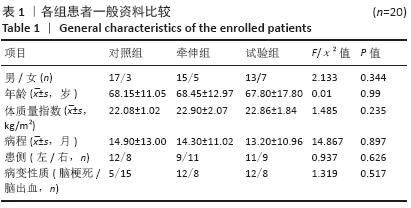
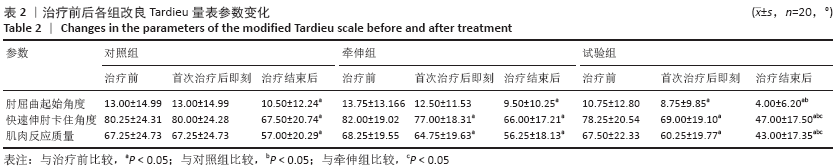
[1] 崔利华,山磊,杨宇琦.首次脑卒中后 6 个月内肢体痉挛情况调查 1[J].中国康复理论与实践,2014,20(12):1144-1146.
[2] 陆敏,彭军,尤春景,等.脑卒中患者肢体痉挛的发生率及其与功能的关系[J].中国康复,2005,20(5):281-282.
[3] KATALINIC OM, HARVEY LA, HERBERT RD. Effectiveness of stretch for the treatment and prevention of contractures in people with neurological conditions: a systematic review. Phys Ther. 2011;91(1):11-24.
[4] THIBAUT A, CHATELLE C, ZIEGLER E, et al. Spasticity after stroke: physiology, assessment and treatment. Brain Inj. 2013;27(10):1093-1105.
[5] RÄTSEP T, ASSER T. Changes in viscoelastic properties of skeletal muscles induced by subthalamic stimulation in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2011;26(2):213-217.
[6] MARUSIAK J, KISIEL-SAJEWICZ K, JASKÓLSKA A, et al. Higher muscle passive stiffness in Parkinson’s disease patients than in controls measured by myotonometry. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010;91(5):800-802.
[7] 赵丹.电动深层肌肉刺激仪联合热磁治疗慢性非特异性颈痛疗效观察[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2016,18(8):225-227.
[8] GAPEYEVA H, VAIN A. Principles of applying Myoton in physical medicine and rehabilitation. Methodical Guide. Muomeetria, Tartu, Estonia. 2008.
[9] ANSARI NN, NAGHDI S, HASSON S, et al. The Modified Tardieu Scale for the measurement of elbow flexor spasticity in adult patients with hemiplegia. Brain Inj. 2008;22(13-14):1007-1012.
[10] AARRESTAD DD, WILLIAMS MD, FEHRER SC, et al. Intra-and interrater reliabilities of the myotonometer when assessing the spastic condition of children with cerebral palsy. J Child Neurol. 2004;19(11):894-901.
[11] SINGH P, JOSHUA AM, GANESHAN S, et al. Intra-rater reliability of the modified Tardieu scale to quantify spasticity in elbow flexors and ankle plantar flexors in adult stroke subjects. Ann Indian Acad Neurol. 2011;14(1):23.
[12] TRIANDAFILOU KM, KAMPER DG. Investigation of hand muscle atrophy in stroke survivors. Clin Biomech(Bristol, Avon). 2012;27(3):268-272.
[13] REKAND T. Clinical assessment and management of spasticity: a review. Acta Neurol Scand. 2010;122:62-66.
[14] MORRIS S. Ashworth and Tardieu Scales: Their clinical relevance for measuring spasticity in adult and paediatric neurological populations. Phys Ther Rev. 2002; 7(1):53-62.
[15] AGYAPONG-BADU S, WARNER M, SAMUEL D, et al. Measurement of ageing effects on muscle tone and mechanical properties of rectus femoris and biceps brachii in healthy males and females using a novel hand-held myometric device. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2016;62:59-67.
[16] CHUANG L, WU C, LIN K, et al. Quantitative mechanical properties of the relaxed biceps and triceps brachii muscles in patients with subacute stroke: a reliability study of the myoton-3 myometer. Stroke Res Treat. 2012;2012:617694.
[17] 刘春龙,徐凯,张志杰,等.肌肉状态检测系统评估脑卒中患者肌肉张力的信度研究[J].中国康复,2014,29(2):99-100.
[18] 廖长艳,张佳佳.电动深层肌肉刺激仪降低脑卒中患者上肢肌张力的疗效观察[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(12):112-113.
[19] NOMA T, MATSUMOTO S, ETOH S, et al. Anti-spastic effects of the direct application of vibratory stimuli to the spastic muscles of hemiplegic limbs in post-stroke patients. Brain Inj. 2009;23(7-8):623-631.
[20] MARCONI B, FILIPPI GM, KOCH G, et al. Long-term effects on cortical excitability and motor recovery induced by repeated muscle vibration in chronic stroke patients. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair. 2011;25(1):48-60.
[21] NOMA T, MATSUMOTO S, SHIMODOZONO M, et al. Anti-spastic effects of the direct application of vibratory stimuli to the spastic muscles of hemiplegic limbs in post-stroke patients: a proof-of-principle study. J Rehabil Med. 2012; 44(4): 325-330.
[22] BOVEND’EERDT TJ, NEWMAN M, BARKER K, et al. The effects of stretching in spasticity: a systematic review. Arch Phys Med Rehab. 2008;89(7):1395-1406.
[23] NARO A, LEO A, RUSSO M, et al. Breakthroughs in the spasticity management: Are non-pharmacological treatments the future? J Clin Neurosci. 2017; 39: 16-27.
[24] Palisano R, Rosenbaum P, Walter S, et al. Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1997;39(4):214-223.
[25] LO WLA, ZHAO JL, LI L, et al. Relative and Absolute Interrater Reliabilities of a Hand-Held Myotonometer to Quantify Mechanical Muscle Properties in Patients with Acute Stroke in an Inpatient Ward. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:4294028.
[26] 徐海洋,王立峰.针刺联合 DMS 治疗脑卒中后上肢肌张力增高的疗效分析[J].临床医学研究与实践,2017,2(32):128-129.
[27] SCHMID AA, VAN PUYMBROECK M, ALTENBURGER PA, et al. Balance and balance self-efficacy are associated with activity and participation after stroke: a cross-sectional study in people with chronic stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehab. 2012;93(6):1101-1107.
[28] 沈显山,吴建贤,洪永锋,等.局部振动在脑卒中康复的应用进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2018,33(11):26.
[29] 张小满,石萍,喻洪流.振动疗法在康复中的研究及应用[J].北京生物医学工程,2016,35(5):538-543,548.
[30] COCHRANE DJ, STANNARD SR. Acute whole body vibration training increases vertical jump and flexibility performance in elite female field hockey players. Br J Sports Med. 2005;39(11):860-865.
[31] PAOLONI M, TAVERNESE E, FINI M, et al. Segmental muscle vibration modifies muscle activation during reaching in chronic stroke: A pilot study. NeuroRehabilitation. 2014;35(3):405-414.
[32] TSAI KH, YEH CY, CHANG HY, et al. Effects of a single session of prolonged muscle stretch on spastic muscle of stroke patients. Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub China B. 2001;25(2):76-81.
[33] BAE SH, KIM KY. Effects of vibration stimulation method on upper limbs spasticity in patients with brain lesion. J Korea Acad Industr Coop Soc. 2011;12(7):3109-3116.
[34] 关兴荣.头针结合 DMS 治疗脑卒中后上肢肌张力增高的临床观察[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2018.
[35] PEER KS, BARKLEY JE, KNAPP DM. The acute effects of local vibration therapy on ankle sprain and hamstring strain injuries. Phys Sportsmed. 2009; 37(4): 31-38.
[36] BISHOP B. Vibratory stimulation: Part II. Vibratory stimulation as an evaluation tool. Phys Ther. 1975;55(1):28-34.
[37] CONSTANTINO C, GALUPPO L, ROMITI D. Efficacy of mechano-acoustic vibration on strength, pain, and function in poststroke rehabilitation: a pilot study. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2014;21(5):391-399.
[38] HAGBARTH KE, EKLUND G. Tonic vibration reflexes (TVR) in spasticity. Brain Res. 1966;2(2):201-203.
[39] BAE SH, KIM KY. The effect of vibratory stimulation on tissue compliance and muscle activity in elbow flexor spasticity. J Phys Ther Sci. 2012;24(8):751-754.
[40] BIZZINI M, MANNION AF. Reliability of a new, hand-held device for assessing skeletal muscle stiffness. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2003;18(5):459-461. |