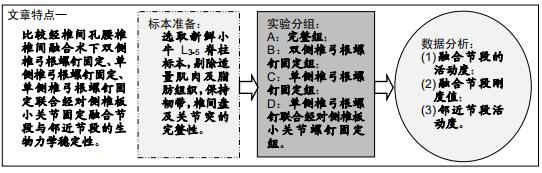
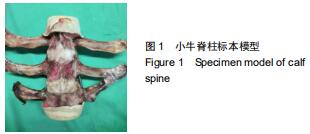
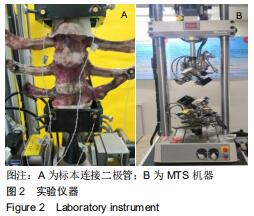
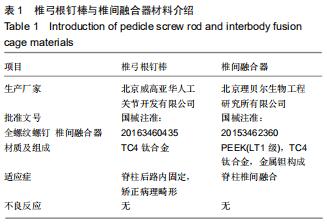
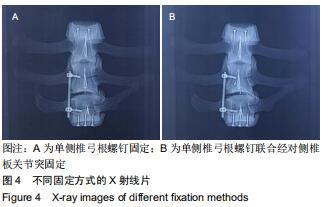
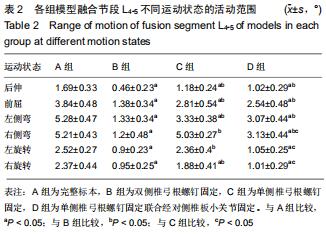
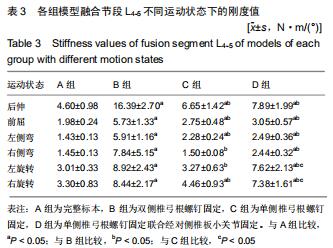
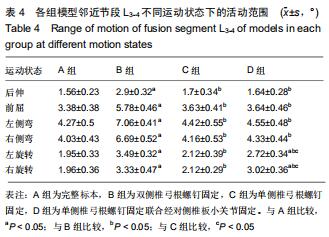
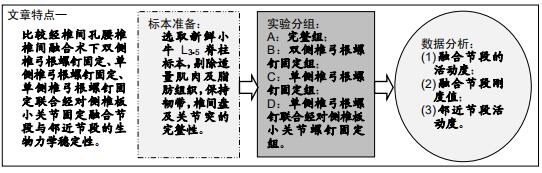
|
[1] LIU HY, ZHOU J, WANG B, et al. Comparison of Topping-off and posterior lumbar interbody fusion surgery in lumbar degenerative disease: a retrospective study.Chin Med J (Engl). 2012;125(22): 3942-3946.
[2] ELIYAS JK, KARAHALIOS D. Surgery for degenerative lumbar spine disease.Dis Mon. 2011;57(10):592-606.
[3] TCHAKO A, SADEGH AM. Stress changes in intervertebral discs of the cervical spine due to partial discectomies and fusion.J Biomech Eng.2009;131(5):51013.
[4] CHO CB, RYU KS, PARK CK. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion with stand-alone interbody cage in treatment of lumbar intervertebral foraminal stenosis : comparative study of two different types of cages.J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2010;47(5):352-357.
[5] 董健文,邱奕雁,赵卫东,等.单侧椎弓根钉棒固定单节段腰椎及其邻近节段生物力学研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2010,28(1):85-89.
[6] HU Y, ZHU BK, KEPLER CK, et al.A Comparison Study of Three Posterior Fixation Strategies in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Lumbar for the Treatment of Degenerative Diseases. Indian J Orthop.2019;53(4):542-547.
[7] CHEN DJ, YAO C, SONG Q, et al. Unilateral versus Bilateral Pedicle Screw Fixation Combined with Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for the Treatment of Low Lumbar Degenerative Disc Diseases: Analysis of Clinical and Radiographic Results. World Neurosurg.2018;115:e516-e522.
[8] LU P, PAN T, DAI T, et al. Is unilateral pedicle screw fixation superior than bilateral pedicle screw fixation for lumbar degenerative diseases: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res.2018;13(1):296.
[9] ZENG ZY, WU P, SONG YX, et al. Unilateral pedicle screw fixation combined with contralateral percutaneous translaminar facet screw fixation and lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of lower lumbar diseases: an analysis of complications.Zhongguo Gu Shang.2016;29(3):232-241.
[10] KABINS MB, WEINSTEIN JN, SPRATT KF, et al. Isolated L4-L5 fusions using the variable screw placement system: unilateral versus bilateral.J Spinal Disord.1992;5(1):39-49.
[11] SUK KS, LEE HM, KIM NH, et al. Unilateral versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation in lumbar spinal fusion.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(14):1843-1847.
[12] FERNANDEZ-FAIREN M, SALA P, RAMIREZ H, et al. A prospective randomized study of unilateral versus bilateral instrumented posterolateral lumbar fusion in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2007;32(4):395-401.
[13] BERINGER WF, MOBASSER JP. Unilateral pedicle screw instrumentation for minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion.Neurosurg Focus.2006;20(3):E4.
[14] TUTTLE J, SHAKIR A, CHOUDHRI HF. Paramedian approach for transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with unilateral pedicle screw fixation. Technical note and preliminary report on 47 cases. Neurosurg Focus.2006;20(3):E5.
[15] SLUCKY AV, BRODKE DS, BACHUS KN, et al. Less invasive posterior fixation method following transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a biomechanical analysis.Spine J.2006;6(1): 78-85.
[16] KASAI Y, INABA T, KATO T, et al. Biomechanical study of the lumbar spine using a unilateral pedicle screw fixation system.J Clin Neurosci.2010;17(3):364-367.
[17] BEST NM, SASSO RC. Efficacy of translaminar facet screw fixation in circumferential interbody fusions as compared to pedicle screw fixation.J Spinal Disord Tech.2006;19(2):98-103.
[18] WILKE HJ, WENGER K, CLAES L. Testing criteria for spinal implants: recommendations for the standardization of in vitro stability testing of spinal implants.Eur Spine J.1998;7(2):148-154.
[19] GODZIK J, MARTINEZ-DEL-CAMPO E, NEWCOMB A, et al. Biomechanical Stability Afforded by Unilateral Versus Bilateral Pedicle Screw Fixation with and without Interbody Support Using Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion.World Neurosurg. 2018;113: e439-e445.
[20] PHILLIPS FM, TZERMIADIANOS MN, VORONOV LI, et al. Effect of the Total Facet Arthroplasty System after complete laminectomy-facetectomy on the biomechanics of implanted and adjacent segments. Spine J.2009;9(1):96-102.
[21] GONG Z, CHEN Z, FENG Z, et al. Finite element analysis of 3 posterior fixation techniques in the lumbar spine.Orthopedics. 2014;37(5):e441-e448.
[22] LUO B, YAN M, HUANG J, et al. Biomechanical study of unilateral pedicle screw combined with contralateral translaminar facet screw in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon).2015;30(7):657-661.
[23] 张昊,胡亚威,菅新民,等.两种不同椎弓根螺钉内固定术式对腰椎稳定性影响的生物力学对比研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志, 2016,34(2): 220-223.
[24] YANG M, SUN G, GUO S, et al. The Biomechanical Study of Extraforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Three-Dimensional Finite-Element Analysis.J Healthc Eng.2017;2017:9365068.
[25] 何蔚,张桦,何海龙,等.腰椎单侧及双侧椎弓根螺钉固定椎间融合器的生物力学研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2009,34(4):405-408.
[26] ZHAO C, WANG X, CHEN C, et al. Finite element analysis of minimal invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion.Cell Biochem Biophys.2014;70(1):609-613.
[27] 陈志明,马华松,赵杰,等.腰椎单侧椎弓根螺钉固定的三维有限元分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2010,20(8):684-688.
[28] 邵高海,焦春燕,余雨,等.单侧椎弓根螺钉置入并椎间融合对邻近椎间盘节段退变的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011, 15(13):2317-2321.
[29] 何蔚,张桦,何海龙,等.腰椎单侧及双侧椎弓根螺钉固定椎间融合器的生物力学研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2009,34(4):405-408.
[30] OKUDA S, IWASAKI M, MIYAUCHI A, et al. Risk factors for adjacent segment degeneration after PLIF.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(14):1535-1540.
[31] SHONO Y, KANEDA K, ABUMI K, et al. Stability of posterior spinal instrumentation and its effects on adjacent motion segments in the lumbosacral spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(14): 1550-1558.
[32] 曾忠友,吴鹏,宋永兴,等.小切口单侧椎弓根螺钉联合对侧经皮椎板关节突螺钉固定并椎间融合治疗腰椎病变的并发症分析[J].中国骨伤,2016,29(3):232-241.
[33] 曾忠友,吴鹏,孙德弢,等.两种不同固定方式并椎间融合治疗腰椎双节段病变的临床对比研究[J].中国骨伤,2015,28(10):903-909.
[34]曾忠友,吴鹏,毛克亚,等.单侧椎弓根螺钉固定与联合对侧椎板关节突螺钉固定应用于下腰椎单节段病变的临床研究[J].中国骨伤, 2015,28(4):306-312.
|