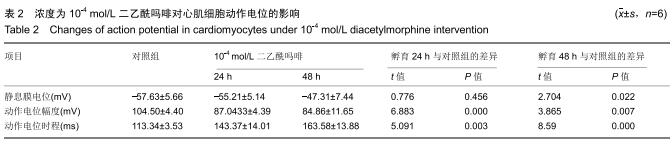
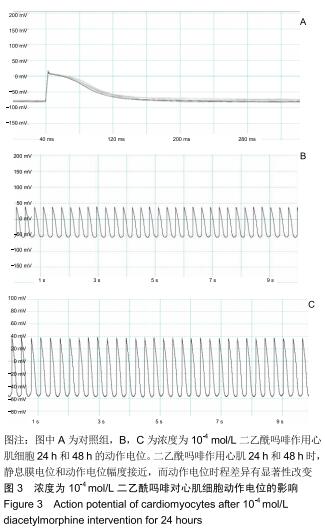
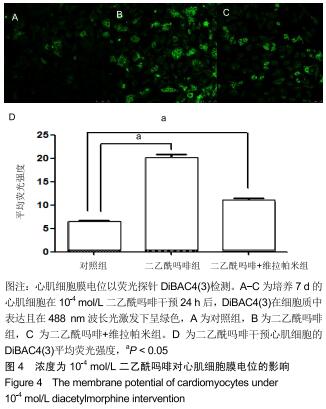
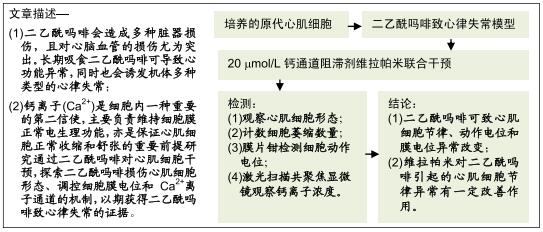
|
[1] 黄万麒,李利华,李桢,等.20例海洛因滥用相关死亡案例的法医学分析[J].法医学杂志,2016,32(4):266-268.
[2] KIM J, IM HI, MOON C.Intravenous morphine self-administration alters accumbal microRNA profiles in the mouse brain.Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(1):77-85.
[3] 梁纲,黄绍标,李飞,等.海洛因依赖者中抗-HIV抗体阳性人群的心电图分析[J].广西医科大学学报,2012,29(5):702-704.
[4] 彭云蓉,黎明,罗燕萍.海洛因依赖者左心室功能的评价[J].中国实用医药,2017,12(19):29-31.
[5] KRUTETSKAYA ZI, MILENINA LS, NAUMOVA AA, et al. Trifluoperazine Attenuates Store-Dependent Ca2+ Entry in Macrophages. Dokl Biochem Biophys. 2018;478(1):44-46.
[6] 何蕾,张莉,黄靖香,等.乳鼠心肌细胞的体外培养及生物学特性研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2007(5):506-507.
[7] 胡夏韵.钙通道相关基因CASQ2与RYR2在二乙酰吗啡致心律失常中的作用研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2019.
[8] 苏丽萍. C-jun基因与caspase-8基因在海洛因致小脑颗粒神经元细胞凋亡中的作用机制研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学, 2015.
[9] BUTLER B, RUBIN G, LAWRANCE A, et al. Estimating the risk of fatal arrhythmia in patients in methadone maintenance treatment for heroin addiction. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2011; 30(2): 173-180.
[10] PHILLIPS KA, HIRSCH GA, EPSTEIN DH, et al. Cardiac complications of unwitting co-injection of quinine/quinidine with heroin in an intravenous drug user. J Gen Intern Med. 2012;27(12):1722-1725.
[11] SZTAJZEL J, KARPUZ H, RUTISHAUSER W. Heroin abuse and myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 1994;47(2):180-182.
[12] PAVLIDIS P, DEFTEREOU TE, KARAKASI MV, et al. Intravenous Heroin Abuse and Acute Myocardial Infarction: Forensic Study. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2016;37(2):95-98.
[13] RUAN X, TIEMANN DD, KAYE AD. Intravenous Heroin Abuse and Acute Myocardial Infarction: Association or Causality? Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2016;37(4):317-318.
[14] 刘小山,陈玉川,李朝晖,等.海洛因成瘾大鼠心电图及心肌超微结构改变的研究[J].法医学杂志,2004,20(3):129-132,135.
[15] MELANDRI R, DE TOMMASO I, ZELE I, et al. Myocardial involvement in rhabdomyolysis caused by acute heroin intoxication. Recenti Prog Med. 1991;82(6):324-327.
[16] 刘小山,吴敬东,蒿自睿,等.二醋吗啡对大鼠心肌细胞游离Ca~ (2+)浓度的作用[J].法医学杂志,2007(6):424-427.
[17] 王广勇,刘小山,王小宇,等.维拉帕米对海洛因诱发的乳鼠心肌细胞钙活动异常的作用[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2011, 32(5): 566-570.
[18] SOLIS E JR, CAMERON-BURR KT, SHAHAM Y, et al. Intravenous Heroin Induces Rapid Brain Hypoxia and Hyperglycemia that Precede Brain Metabolic Response. eNeuro. 2017;4(3):ENEURO.0151-17.2017.
[19] SOLIS E JR, BOLA RA, FASULO BJ, et al. Brain Hyperglycemia Induced by Heroin: Association with Metabolic Neural Activation. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2017;8(2):265-271.
[20] MALEKI-BALAJOO S, HOSSEIN-ZADEH GA, SOLTANIAN-ZADEH H, et al. Locally Estimated Hemodynamic Response Function and Activation Detection Sensitivity in Heroin-Cue Reactivity Study. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2016;7(4):299-314.
[21] DUNN KE, BRANDS B, MARSH DC, et al. Characterizing the subjective, observer-rated, and physiological effects of hydromorphone relative to heroin in a human laboratory study. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018;235(4):971-981.
[22] MARKS AR. Calcium cycling proteins and heart failure: mechanisms and therapeutics. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(1): 46-52.
[23] 江洁冰,周培岚,郑志兵,等.阿片受体泛素化机制及其对受体功能的影响[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2015,29(2):302-309.
[24] LUTZ PE, AYRANCI G, CHU-SIN-CHUNG P, et al. Distinct mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptor mechanisms underlie low sociability and depressive-like behaviors during heroin abstinence. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014;39(11): 2694-2705.
[25] GIULIANO C, ROBBINS TW, WILLE DR, et al. Attenuation of cocaine and heroin seeking by μ-opioid receptor antagonism. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2013;227(1):137-147.
[26] LUTZ PE, AYRANCI G, CHU-SIN-CHUNG P, et al. Distinct mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptor mechanisms underlie low sociability and depressive-like behaviors during heroin abstinence. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014;39(11): 2694-2705.
[27] 彭丹晖,邓玲燕,黎阳.阿片受体最新研究进展[J].医学综述,2015, 21(24):4444-4447.
[28] 王萌,张冬梅,张冰,等.δ、κ阿片受体对舒芬太尼预处理大鼠心肌缝隙连接蛋白43的影响[J].临床麻醉学杂志, 2015,31(10): 996-999.
[29] FRANKLIN C, FORTEPIANI L, NGUYEN T, et al. Renal responses produced by microinjection of the kappa opioid receptor agonist, U50-488H, into sites within the rat lamina terminalis. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2015;3(2):e00117.
[30] PRZEWŁOCKI R, PRZEWŁOCKA B. Opioids in chronic pain. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001;429(1-3):79-91.
[31] MINAMI M, ONOGI T, NAKAGAWA T, et al. DAMGO, a mu-opioid receptor selective ligand, distinguishes between mu-and kappa-opioid receptors at a different region from that for the distinction between mu- and delta-opioid receptors. FEBS Lett. 1995;364(1):23-27.
[32] YAMAZAKI T, AKIYAMA T, MORI H. Effects of nociceptin on cardiac norepinephrine and acetylcholine release evoked by ouabain. Brain Res. 2001;904(1):153-156.
[33] ZIMLICHMAN R, GEFEL D, ELIAHOU H, et al. Expression of opioid receptors during heart ontogeny in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Circulation. 1996;93(5):1020-1025.
[34] SUN B, WEI J, ZHONG X, et al. The cardiac ryanodine receptor, but not sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase, is a major determinant of Ca2+ alternans in intact mouse hearts. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(35):13650-13661.
|