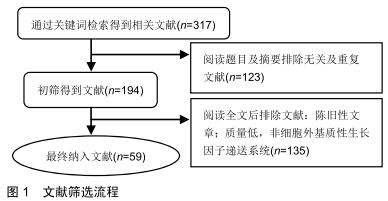
|
[1] DIMITRIOU R, JONES E, MCGONAGLE D, et al. Bone regeneration: current concepts and future directions.BMC Med.2011;9:66.
[2] AUDIGE L, GRIFFIN D, BHANDARI M, et al. Path analysis of factors for delayed healing and nonunion in 416 operatively treated tibial shaft fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;438: 221-232.
[3] CALCIOLARI E, MARDAS N, DEREKA X, et al. The effect of experimental osteoporosis on bone regeneration: part 2, proteomics results. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2017;28(9): e135-e45.
[4] ILYAS A, ODATSU T, SHAH A, et al. Amorphous Silica: A New Antioxidant Role for Rapid Critical-Sized Bone Defect Healing. Adv Healthc Mater.2016;5(17):2199-2213.
[5] LI M, WANG W, ZHU Y, et al. Molecular and cellular mechanisms for zoledronic acid-loaded magnesium-strontium alloys to inhibit giant cell tumors of bone. Acta Biomater. 2018; 77:365-379.
[6] LYNCH JR, TAITSMAN LA, BAREI DP, et al. Femoral nonunion: risk factors and treatment options.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008;16(2):88-97.
[7] MARTIN V, BETTENCOURT A. Bone regeneration: Biomaterials as local delivery systems with improved osteoinductive properties. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater. 2018;82:363-371.
[8] GRIFFIN KS, DAVIS KM, MCKINLEY TO, et al. Evolution of Bone Grafting: Bone Grafts and Tissue Engineering Strategies for Vascularized Bone Regeneration.Clin Rev Bone Miner. 2015;13(4):232-244.
[9] SOKOLSKY-PAPKOV M, AGASHI K, OLAYE A, et al. Polymer carriers for drug delivery in tissue engineering.Adv Drug Deliver Rev.2007;59(4-5):187-206.
[10] SHRIVATS AR, MCDERMOTT MC, HOLLINGER JO. Bone tissue engineering: state of the union.Drug Discov Today. 2014;19(6):781-786.
[11] LI YH, WANG ZD, WANG W, et al. The biocompatibility of calcium phosphate cements containing alendronate-loaded PLGA microparticles in vitro.Exp Biol Med. 2015;240(11): 1465-1471.
[12] DANG PN, DWIVEDI N, PHILLIPS LM, et al. Controlled Dual Growth Factor Delivery From Microparticles Incorporated Within Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Aggregates for Enhanced Bone Tissue Engineering via Endochondral Ossification. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;5(2): 206-217.
[13] AZEVEDO HS, PASHKULEVA I. Biomimetic supramolecular designs for the controlled release of growth factors in bone regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;94:63-76.
[14] NI M, LI G, TANG PF, et al. rhBMP-2 not alendronate combined with HA-TCP biomaterial and distraction osteogenesis enhance bone formation.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(11):1469-1476.
[15] WANG C, ZHAO Q, WANG M. Cryogenic 3D printing for producing hierarchical porous and rhBMP-2-loaded Ca-P/PLLA nanocomposite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Biofabrication. 2017;9(2):025031.
[16] EVEN J, ESKANDER M, KANG J. Bone morphogenetic protein in spine surgery: current and future uses.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2012;20(9):547-552.
[17] KITAMURA M, AKAMATSU M, MACHIGASHIRA M, et al. FGF-2 stimulates periodontal regeneration: results of a multi-center randomized clinical trial.J Dent Res. 2011;90(1): 35-40.
[18] BALOOCH G, BALOOCH M, NALLA RK, et al. TGF-beta regulates the mechanical properties and composition of bone matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2005;102(52):18813-18818.
[19] VOGEL V, SHEETZ M. Local force and geometry sensing regulate cell functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(4):265-275.
[20] TRAPPMANN B, GAUTROT JE, CONNELLY JT, et al. Extracellular-matrix tethering regulates stem-cell fate. Nat Mater. 2012;11(7):642-649.
[21] 王之发.细胞外基质支架材料在软骨组织再生和骨组织工程中应用的初步探讨[D].西安:第四军医大学,2016.
[22] HYNES RO. The extracellular matrix: not just pretty fibrils. Science. 2009;326(5957):1216-1219.
[23] AMORIM S, PIRES RA, DA COSTA DS, et al. Interactions between Exogenous FGF-2 and Sulfonic Groups: in Situ Characterization and Impact on the Morphology of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Langmuir. 2013;29(25):7983-7992.
[24] 池玉磊,卜宪敏,查玉梅,等.骨髓间充质干细胞复合支架材料治疗骨缺损:研究现状及前景展望[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(29): 4749-4756.
[25] MARTINO MM, BRIQUEZ PS, MARUYAMA K, et al. Extracellular matrix-inspired growth factor delivery systems for bone regeneration.Adv Drug Deliver Rev.2015;94:41-52.
[26] 肖统光,张一民,郭维民,等.细胞外基质来源支架在软骨组织工程中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,38(20):5737-5744.
[27] WU CH, KO JL, PAN HH, et al. Ni-induced TGF-beta signaling promotes VEGF-a secretion via integrin beta3 upregulation.J Cell Physiol.2019;234(12):22093-22102.
[28] MARTINO MM, BRIQUEZ PS, RANGA A, et al. Heparin- binding domain of fibrin(ogen) binds growth factors and promotes tissue repair when incorporated within a synthetic matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2013;110(12):4563-4568.
[29] DE LAPORTE L, RICE JJ, TORTELLI F, et al. Tenascin C promiscuously binds growth factors via its fifth fibronectin type III-like domain.PloS One.2013;8(4):e62076.
[30] MACRI L, SILVERSTEIN D, CLARK RA. Growth factor binding to the pericellular matrix and its importance in tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2007;59(13):1366-1381.
[31] NAKATO H, LI JP. Functions of Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans in Development: Insights From Drosophila Models.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol.2016;325:275-293.
[32] BENTMANN A, KAWELKE N, MOSS D, et al. Circulating fibronectin affects bone matrix, whereas osteoblast fibronectin modulates osteoblast function.J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25(4): 706-715.
[33] VASCONCELOS DM, GONCALVES RM, ALMEIDA CR, et al. Fibrinogen scaffolds with immunomodulatory properties promote in vivo bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2016;111:163-178.
[34] HAWKINS AG, JULIAN CM, KONZEN S, et al. Microenvironmental Factors Drive Tenascin C and Src Cooperation to Promote Invadopodia Formation in Ewing Sarcoma. Neoplasia. 2019;21(10):1063-1072.
[35] CHO CB, JUNG SY, PARK CY, et al. A Vitronectin-Derived Bioactive Peptide Improves Bone Healing Capacity of SLA Titanium Surfaces. Materials.2019;12(20).pii: E3400.
[36] MARTINO MM, BRIQUEZ PS, GUC E, et al. Growth factors engineered for super-affinity to the extracellular matrix enhance tissue healing. Science.2014;343(6173):885-888.
[37] KIM SH, TURNBULL J, GUIMOND S. Extracellular matrix and cell signalling: the dynamic cooperation of integrin, proteoglycan and growth factor receptor.J Endocrinol. 2011; 209(2):139-151.
[38] ZHU J, CLARK RAF. Fibronectin at Select Sites Binds Multiple Growth Factors and Enhances their Activity: Expansion of the Collaborative ECM-GF Paradigm.J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134(4):895-901.
[39] FURUYA H, TABATA Y, KANEKO K. Bone regeneration for murine femur fracture by gelatin hydrogels incorporating basic fibroblast growth factor with different release profiles.Tissue Eng Part A.2014;20(9-10):1531-1541.
[40] VO TN, KASPER FK, MIKOS AG. Strategies for controlled delivery of growth factors and cells for bone regeneration. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2012;64(12):1292-1309.
[41] LEE K, SILVA EA, MOONEY DJ. Growth factor delivery- based tissue engineering: general approaches and a review of recent developments.J R Soc Interface.2011;8(55):153-170.
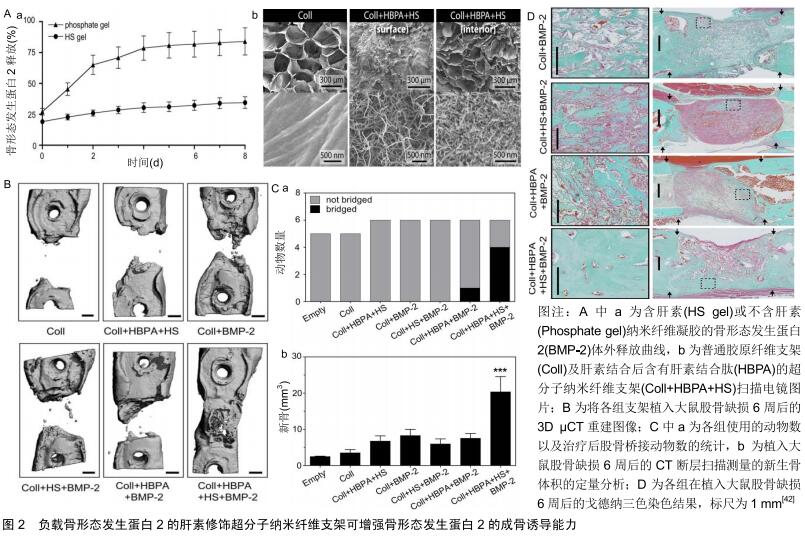
[42] LEE SS, HUANG BJ, KALTZ SR, et al. Bone regeneration with low dose BMP-2 amplified by biomimetic supramolecular nanofibers within collagen scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2013;34(2): 452-459.
[43] YANG HS, LA WG, BHANG SH, et al. Heparin-conjugated fibrin as an injectable system for sustained delivery of bone morphogenetic protein-2. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(4): 1225-1233.
[44] ZHU JY, HUANG BL, DING S, et al. Tethering of rhBMP-2 upon calcium phosphate cement via alendronate/heparin for localized, sustained and enhanced osteoactivity.Rsc Adv. 2017;7(33):20281-20292.
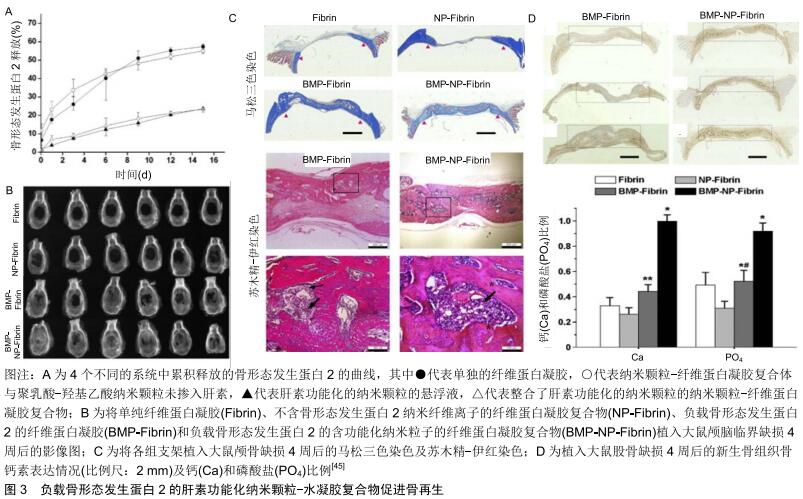
[45] CHUNG YI, AHN KM, JEON SH, et al. Enhanced bone regeneration with BMP-2 loaded functional nanoparticle- hydrogel complex. J Control Release. 2007;121(1-2):91-99.
[46] SCHMOEKEL HG, WEBER FE, SCHENSE JC, et al. Bone repair with a form of BMP-2 engineered for incorporation into fibrin cell ingrowth matrices. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2005;89(3): 253-262.
[47] ARRIGHI I, MARK S, ALVISI M, et al. Bone healing induced by local delivery of an engineered parathyroid hormone prodrug. Biomaterials. 2009;30(9):1763-1771.
[48] CHEN B, LIN H, WANG J, et al. Homogeneous osteogenesis and bone regeneration by demineralized bone matrix loading with collagen-targeting bone morphogenetic protein-2. Biomaterials. 2007;28(6):1027-1035.
[49] HAN X, ZHANG W, GU J, et al. Accelerated postero-lateral spinal fusion by collagen scaffolds modified with engineered collagen-binding human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in rats. PloS One. 2014;9(5):e98480.
[50] TOKUNOU T, MILLER R, PATWARI P, et al. Engineering insulin-like growth factor-1 for local delivery.FASEB J. 2008; 22(6):1886-1893.
[51] MEINEL L, KAPLAN DL. Silk constructs for delivery of musculoskeletal therapeutics.Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2012; 64(12):1111-1122.
[52] LIN FB, REN XD, PAN Z, et al. Fibronectin Growth Factor-Binding Domains Are Required for Fibroblast Survival. J Invest Dermatol.2011;131(1):84-98.
[53] ANONYMOUS. Fibronectin in human bone tissue remodelling. Virchows Arch. 2005;447(2):434-434.
[54] MIN SK, KANG HK, JUNG SY, et al. A vitronectin-derived peptide reverses ovariectomy-induced bone loss via regulation of osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation.Cell Death Differ. 2018;25(2):268-281.
[55] ALAM N, GOEL HL, ZARIF MJ, et al. The integrin - Growth factor receptor duet. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213(3):649-653.
[56] COMOGLIO PM, BOCCACCIO C, TRUSOLINO L. Interactions between growth factor receptors and adhesion molecules: breaking the rules. Curr Opin Cell Biol.2003;15(5): 565-571.
[57] KISIEL M, MARTINO MM, VENTURA M, et al. Improving the osteogenic potential of BMP-2 with hyaluronic acid hydrogel modified with integrin-specific fibronectin fragment. Biomaterials. 2013;34(3):704-712.
[58] MARTINO MM, TORTELLI F, MOCHIZUKI M, et al. Engineering the growth factor microenvironment with fibronectin domains to promote wound and bone tissue healing.Sci Transl Med. 2011;3(100):100ra89.
SHEKARAN A, GARCIA JR, CLARK AY, et al. Bone regeneration using an alpha 2 beta 1 integrin-specific hydrogel as a BMP-2 delivery vehicle. Biomaterials. 2014;35(21):5453-5461
|