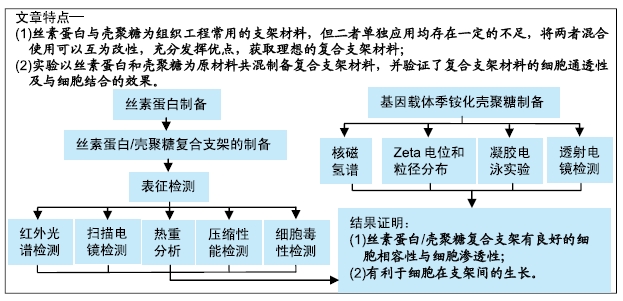
1.1 设计 细胞学体外实验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2017年12月至2018年12月在广西中医药大学动物实验室完成。
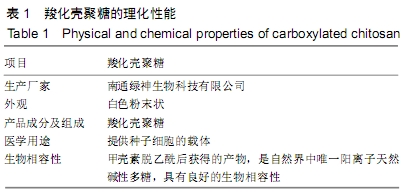
1.3 材料 蚕茧由浙江大学提供;兔骨髓间充质干细胞由武汉普诺赛生命科技有限公司提供;ZIP1质粒由赛业(广州)生物科技有限公司合成;羧化壳聚糖由南通绿神生物科技有限公司合成,见表1。
实验用主要试剂:氯化钠、淀粉试纸、0.25%胰酶消化液、CCK-8检测试剂盒、琼脂糖、6×loading buffer、TAE电泳液、碳酸钠、溴化锂、冰乙酸、碘化钾、1-甲基-2-吡咯烷酮、氢氧化钠、碘甲烷(碧云天);无水乙醇(国药集团化学试剂有限公司);溴乙锭(广州化学试剂厂);PBS(Hyclone)。
实验用主要仪器:恒温水浴锅(上海亚荣生化仪器厂);真空干燥箱(上海一恒科学仪器有限公司);磁力搅拌器(德国艾卡);台式高速离心机(湖南湘仪集团);冷冻干燥机(宁波新芝生物);傅里叶红外光谱仪(德国布鲁克);热重分析仪(德国耐驰仪器公司);博士ElectroForce®3220高精度生物材料试验机(美国Bose公司);场发射扫描电子显微镜(FS-SEM,日立高新技术公司);酶标仪(Thermo Fisher
Scientific);Zeta电位仪(马尔文公司);水平电泳槽、电泳仪、电泳装置(Tanon)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 丝素蛋白的制备 将剪碎的蚕茧加入到0.02 mol/L的Na2CO3水溶液中,加热煮沸1 h,用去离子水不断进行冲洗直到样本pH值接近中性,再去除多余的丝胶,随后将标本放入到60 ℃的烘箱进行烘干。将干燥后的丝素蛋白与浓度为9.3 mol/L的LiBr溶液按1∶10的比例结合,将溶液温度调至60 ℃加热5 h。然后将所得到的溶液用透析袋(截留分子质量为10 kD)透析3 d,并且每天换一次水。将透析后的丝素蛋白溶液在室温下进行离心(5 000
r/min离心 10 min),提取丝素蛋白溶液(浓度约为3.5%),保存至4 ℃环境中备用。
1.4.2 丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架的制备 将壳聚糖溶于浓度为1%的冰乙酸,制备成质量浓度为35 g/L的壳聚糖溶液并与丝素蛋白溶液融合,将丝素蛋白与羧化壳聚糖按照8∶2体积比混合,再将混合溶液注入48孔板中,每孔注入1 mL。最后通过冷冻干燥得到丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架。
1.4.3 基因载体季铵化壳聚糖的合成 将5 g壳聚糖、13 g碘化钾、27.5 mL NaOH(15%)、28.75 mL碘甲烷依次倒入180 mL的1-甲基-2-吡咯烷酮,保持在60 ℃的水浴下搅拌融合并静置2 h。然后将反应液倒入足量的乙醇中沉淀并用乙醇清洗2遍,将所得产物用NaCl水溶液溶解,用透析袋(截留相对分子质量3 500)分别以1 mol/L的NaCl溶液与三蒸水透析4 d与3 d(每天更换2次透析液),最后淀粉是指检测无碘残留后,将产物冻干标记为季铵化壳聚糖。
1.4.4 支架及材料表征和检测
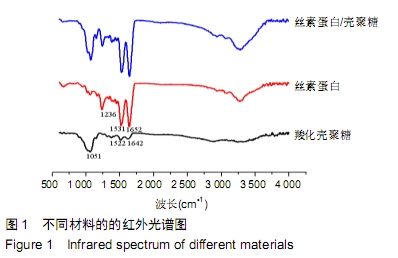
丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架的红外光谱检测:采用KBr片法,以傅里叶红外光谱仪表征丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架、丝素蛋白、壳聚糖的红外吸收特征,扫描范围为500-
4 000 cm-1。
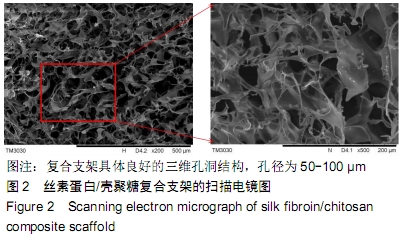
丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架扫描电镜检测:将干燥好的丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架固定在铜台上并喷金处理,运用场发射扫描电子显微镜观察。
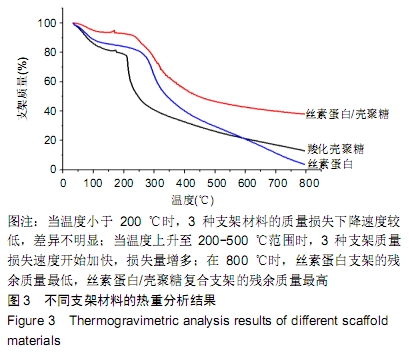
丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架热重分析:将羧化壳聚糖、丝素蛋白、丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架进行热重分析。将 10 mg待检验的样品放于氮气环境下进行检测,测试度升高控制范围为30-800 ℃,温度上升速度为10 ℃/min。
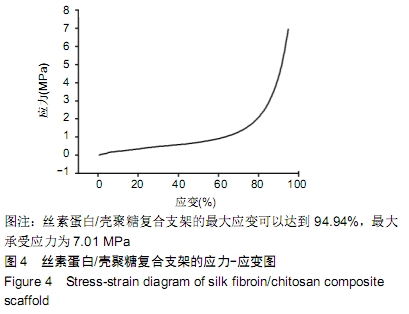
丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架的压缩性能检测:在正常条件下,用博士ElectroForce®3220生物材料检测机对丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架进行压缩应力和压缩模量测试。测试样品:丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架支架。样品大小:直径为 6 mm,高度为5-7 mm。测试条件为:以225 N的附加压力与1 mm/min的线速度将支架压缩至原先高度的一半。
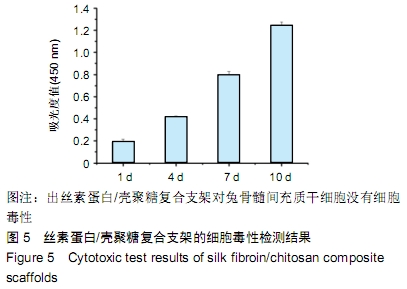
丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架的细胞毒性检测:画好培养板加样分布图,取培养良好的兔骨髓间充质干细胞,消化离心,配好细胞悬液,计数、传代,按500 µL体积特定细胞数来配制细胞悬液(全培)。取24孔板,一个浓度设置两三个平行组,另留2个空白对照,每孔铺5万-10万个细胞,每孔500 µL,培养12 h;移出全培,吸走5孔加5孔,不用PBS洗,加入已配好的OPTI-MEM培养基+体积分数10%胎牛血清,每孔400 µL,处理一二小时,移出液体,PBS洗2次;饥饿1 h时进行材料和DNA复合,编号,每子弹头取2 µg
DNA(ZIP1质粒,每孔需2 µg),轻微吹打,复合 30 min后再向复合物中加入OPTI-MEM凑齐100 µL;向复合体中加入OPTI-MEM培养基+体积分化10%胎牛血清(总体积达到500 µL),移出培养板液体,移入该液体,每孔 500 µL,培养1,4,7,10 d时移出培养板液体,PBS洗2次,移入已配好的DMEM+体积分数10%胎牛血清500 µL,培养24-48 h观察,采用CCK-8试剂盒对细胞毒性进行检查。
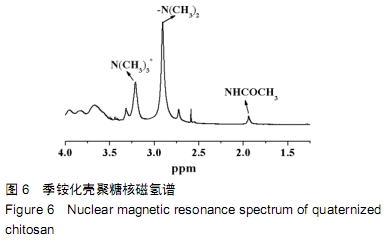
季铵化壳聚糖的核磁氢谱:将所制得的季铵化壳聚糖溶解于D2O中,用核磁共振仪表征季铵化壳聚糖的核磁氢谱。
季铵化壳聚糖的Zeta电位和粒径分布:用Zeta电位仪对所制得的季铵化壳聚糖的电位和粒径分布进行检测。
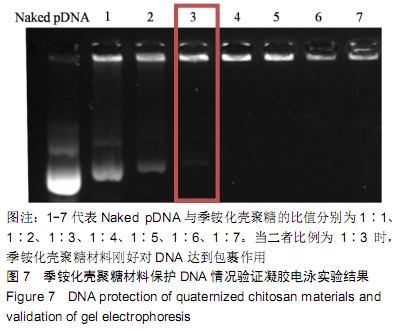
季铵化壳聚糖材料保护DNA情况验证凝胶电泳实验:将1 g琼脂糖溶于100 mL 1×TAE溶液配制1%凝胶电泳胶,在微波炉中加热使其充分溶解,待温度降至60 ℃左右加入5 µL溴乙啶(10 g/L),摇晃均匀倒入已插好梳子的制胶架中,室温下水平放置30 min左右使其凝固;按照所需比例吸取不同体积的材料溶液与10 µL质粒DNA(2 mg/L),室温孵育30 min;将已凝固的凝胶放入加满1×TAE溶液的电泳槽内(没过胶面2 mm为宜),加样,每孔加入10 µL复合材料,样本需预先加入2 µL
loading buffer;插上电泳仪电源,设置电流强度300 mA,电压强度140 V,时间设置35 min;待loading buffer跑至接近凝胶底部时关闭电泳仪,取出凝胶,在凝胶电泳成像仪中成像。
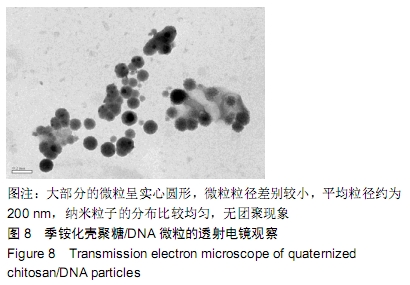
季铵化壳聚糖/DNA的透射电镜检测:将适量鱼精DNA溶于PBS中,配成质量浓度为0.5 g/L的DNA溶液,置于37 ℃恒温水容易备用;在5 mL离心管中,加入以上鱼精DNA溶液(0.5 g/L)0.2 mL,然后加入0.8 mL含0.5 g/L季铵化壳聚糖的PBS溶液(0.8 g/L,经0.22 μm滤膜过滤,37 ℃预热),混合后保持在37 ℃恒温水箱中震荡搅拌10 min后取出。最后将溶液放置于有聚合物薄膜的铜网上以37 ℃烘干,在透射电镜下进行观察粒子的形貌和大小。
1.5 主要观察指标 丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架的热重分析、力学性能及细胞毒性;季铵化壳聚糖的电位和粒径分布、保护DNA及与DNA结合的情况。
实验用主要试剂:氯化钠、淀粉试纸、0.25%胰酶消化液、CCK-8检测试剂盒、琼脂糖、6×loading buffer、TAE
电泳液、碳酸钠、溴化锂、冰乙酸、碘化钾、1-甲基-2-吡咯烷酮、氢氧化钠、碘甲烷(碧云天);无水乙醇(国药集团化学试剂有限公司);溴乙锭(广州化学试剂厂);PBS(Hyclone)。
实验用主要仪器:恒温水浴锅(上海亚荣生化仪器厂);真空干燥箱(上海一恒科学仪器有限公司);磁力搅拌器(德国艾卡);台式高速离心机(湖南湘仪集团);冷冻干燥机(宁波新芝生物);傅里叶红外光谱仪(德国布鲁克);热重分析仪(德国耐驰仪器公司);博士ElectroForce®3220高精度生物材料试验机(美国Bose公司);场发射扫描电子显微镜(FS-SEM,日立高新技术公司);酶标仪(Thermo Fisher
Scientific);Zeta电位仪(马尔文公司);水平电泳槽、电泳仪、电泳装置(Tanon)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 丝素蛋白的制备 将剪碎的蚕茧加入到0.02 mol/L的Na2CO3水溶液中,加热煮沸1 h,用去离子水不断进行冲洗直到样本pH值接近中性,再去除多余的丝胶,随后将标本放入到60 ℃的烘箱进行烘干。将干燥后的丝素蛋白与浓度为9.3 mol/L的LiBr溶液按1∶10的比例结合,将溶液温度调至60 ℃加热5 h。然后将所得到的溶液用透析袋(截留分子质量为10 kD)透析3 d,并且每天换一次水。将透析后的丝素蛋白溶液在室温下进行离心(5 000
r/min离心 10 min),提取丝素蛋白溶液(浓度约为3.5%),保存至4 ℃环境中备用。
1.4.2 丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架的制备 将壳聚糖溶于浓度为1%的冰乙酸,制备成质量浓度为35 g/L的壳聚糖溶液并与丝素蛋白溶液融合,将丝素蛋白与羧化壳聚糖按照8∶2体积比混合,再将混合溶液注入48孔板中,每孔注入1 mL。最后通过冷冻干燥得到丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架。
1.4.3 基因载体季铵化壳聚糖的合成 将5 g壳聚糖、13 g碘化钾、27.5 mL NaOH(15%)、28.75 mL碘甲烷依次倒入180 mL的1-甲基-2-吡咯烷酮,保持在60 ℃的水浴下搅拌融合并静置2 h。然后将反应液倒入足量的乙醇中沉淀并用乙醇清洗2遍,将所得产物用NaCl水溶液溶解,用透析袋(截留相对分子质量3 500)分别以1 mol/L的NaCl溶液与三蒸水透析4 d与3 d(每天更换2次透析液),最后淀粉是指检测无碘残留后,将产物冻干标记为季铵化壳聚糖。
1.4.4 支架及材料表征和检测
丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架的红外光谱检测:采用KBr片法,以傅里叶红外光谱仪表征丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架、丝素蛋白、壳聚糖的红外吸收特征,扫描范围为500-
4 000 cm-1。
丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架扫描电镜检测:将干燥好的丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架固定在铜台上并喷金处理,运用场发射扫描电子显微镜观察。
丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架热重分析:将羧化壳聚糖、丝素蛋白、丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架进行热重分析。将 10 mg待检验的样品放于氮气环境下进行检测,测试度升高控制范围为30-800 ℃,温度上升速度为10 ℃/min。
丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架的压缩性能检测:在正常条件下,用博士ElectroForce®3220生物材料检测机对丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架进行压缩应力和压缩模量测试。测试样品:丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架支架。样品大小:直径为 6 mm,高度为5-7 mm。测试条件为:以225 N的附加压力与1 mm/min的线速度将支架压缩至原先高度的一半。
丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架的细胞毒性检测:画好培养板加样分布图,取培养良好的兔骨髓间充质干细胞,消化离心,配好细胞悬液,计数、传代,按500 µL体积特定细胞数来配制细胞悬液(全培)。取24孔板,一个浓度设置两三个平行组,另留2个空白对照,每孔铺5万-10万个细胞,每孔500 µL,培养12 h;移出全培,吸走5孔加5孔,不用PBS洗,加入已配好的OPTI-MEM培养基+体积分数10%胎牛血清,每孔400 µL,处理一二小时,移出液体,PBS洗2次;饥饿1 h时进行材料和DNA复合,编号,每子弹头取2 µg
DNA(ZIP1质粒,每孔需2 µg),轻微吹打,复合 30 min后再向复合物中加入OPTI-MEM凑齐100 µL;向复合体中加入OPTI-MEM培养基+体积分化10%胎牛血清(总体积达到500 µL),移出培养板液体,移入该液体,每孔 500 µL,培养1,4,7,10 d时移出培养板液体,PBS洗2次,移入已配好的DMEM+体积分数10%胎牛血清500 µL,培养24-48 h观察,采用CCK-8试剂盒对细胞毒性进行检查。
季铵化壳聚糖的核磁氢谱:将所制得的季铵化壳聚糖溶解于D2O中,用核磁共振仪表征季铵化壳聚糖的核磁氢谱。
季铵化壳聚糖的Zeta电位和粒径分布:用Zeta电位仪对所制得的季铵化壳聚糖的电位和粒径分布进行检测。
季铵化壳聚糖材料保护DNA情况验证凝胶电泳实验:将1 g琼脂糖溶于100 mL 1×TAE溶液配制1%凝胶电泳胶,在微波炉中加热使其充分溶解,待温度降至60 ℃左右加入5 µL溴乙啶(10 g/L),摇晃均匀倒入已插好梳子的制胶架中,室温下水平放置30 min左右使其凝固;按照所需比例吸取不同体积的材料溶液与10 µL质粒DNA(2 mg/L),室温孵育30 min;将已凝固的凝胶放入加满1×TAE溶液的电泳槽内(没过胶面2 mm为宜),加样,每孔加入10 µL复合材料,样本需预先加入2 µL
loading buffer;插上电泳仪电源,设置电流强度300 mA,电压强度140 V,时间设置35 min;待loading buffer跑至接近凝胶底部时关闭电泳仪,取出凝胶,在凝胶电泳成像仪中成像。
季铵化壳聚糖/DNA的透射电镜检测:将适量鱼精DNA溶于PBS中,配成质量浓度为0.5 g/L的DNA溶液,置于37 ℃恒温水容易备用;在5 mL离心管中,加入以上鱼精DNA溶液(0.5 g/L)0.2 mL,然后加入0.8 mL含0.5 g/L季铵化壳聚糖的PBS溶液(0.8 g/L,经0.22 μm滤膜过滤,37 ℃预热),混合后保持在37 ℃恒温水箱中震荡搅拌10 min后取出。最后将溶液放置于有聚合物薄膜的铜网上以37 ℃烘干,在透射电镜下进行观察粒子的形貌和大小。
1.5 主要观察指标 丝素蛋白/壳聚糖复合支架的热重分析、力学性能及细胞毒性;季铵化壳聚糖的电位和粒径分布、保护DNA及与DNA结合的情况。