[1] REN N, ZHANG S, LI Y, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell functions on the hierarchical micro/nanotopographies of the Ti-6Al-7Nb alloy. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;52(10):907-912.
[2] SUN L, FAN X, ZHANG L, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell transplantation via four routes for the treatment of acute liver failure in rats. Int J Mol Med. 2014;34(4):987-996.
[3] FRIEDENSTEIN AJ, DERIGLASOVA UF, KULAGINA NN, et al. Precursors for fibroblasts in different populations of hematopoietic cells as detected by the in vitro colony assay method. Exp Hematol. 1974; 2(2):83-92.
[4] LAFLAMME MA, MURRY CE. Heart regeneration. Nature. 2011;473 (7347):326-335.
[5] DENZER K, KLEIJMEER MJ, HEIJNEN HF, et al. Exosome: from internal vesicle of the multivesicular body to intercellular signaling device. J Cell Sci. 2000;113 Pt 19:3365-3374.
[6] RAPOSO G, NIJMAN HW, STOORVOGEL W, et al. B lymphocytes secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med. 1996;183(3): 1161-1172.
[7] THÉRY C, AMIGORENA S, RAPOSO G, et al. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. 2006;Chapter 3:Unit 3.22.
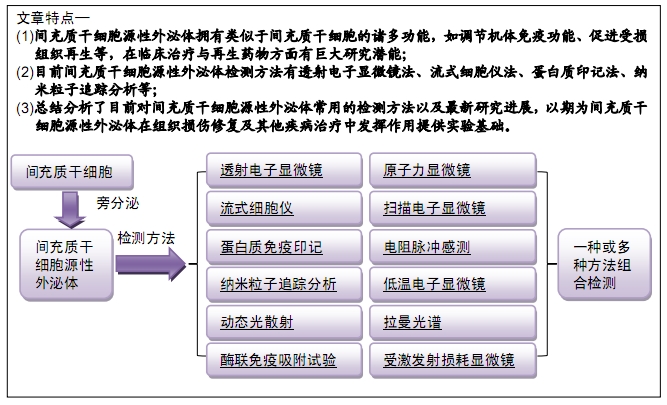
[8] 许文荣,孙瑶湘.外泌体内分子标志物检测及其临床应用[J].临床检验杂志,2017,35(3):161-164.
[9] LI T, YAN Y, WANG B, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate liver fibrosis. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(6):845-854.
[10] BRUNO S, GRANGE C, DEREGIBUS MC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived microvesicles protect against acute tubular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20(5):1053-1067.
[11] GATTI S, BRUNO S, DEREGIBUS MC, et al. Microvesicles derived from human adult mesenchymal stem cells protect against ischaemia-reperfusion-induced acute and chronic kidney injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(5):1474-1483.
[12] 李梦芸,刘德伍,毛远桂.干细胞源性外泌体在创面修复中的作用研究进展[J].中华烧伤杂志,2017,33(3):180-184.
[13] 杨前,刁波.间充质干细胞源性外泌体研究进展[J].华南国防医学杂志, 2018,32(2):137-141.
[14] 刘青武,陈佳,蒙玉娇,等.间充质干细胞源性外泌体及其在创面修复中的研究进展[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2019,24(7):826-832.
[15] KHATUN Z, BHAT A, SHARMA S, et al. Elucidating diversity of exosomes: biophysical and molecular characterization methods. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2016;11(17):2359-2377.
[16] SOKOLOVA V, LUDWIG AK, HORNUNG S, et al. Characterisation of exosomes derived from human cells by nanoparticle tracking analysis and scanning electron microscopy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011; 87(1):146-150.
[17] MOKARIZADEH A, DELIREZH N, MORSHEDI A, et al. Microvesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells: potent organelles for induction of tolerogenic signaling. Immunol Lett. 2012;147(1-2):47-54.
[18] 肖漓,白剑,陈文,等.脐带间充质干细胞外泌体的分离和鉴定[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版),2016,6(4):236-239.
[19] PAOLINI L, ZENDRINI A, DI NOTO G, et al. Residual matrix from different separation techniques impacts exosome biological activity. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23550.
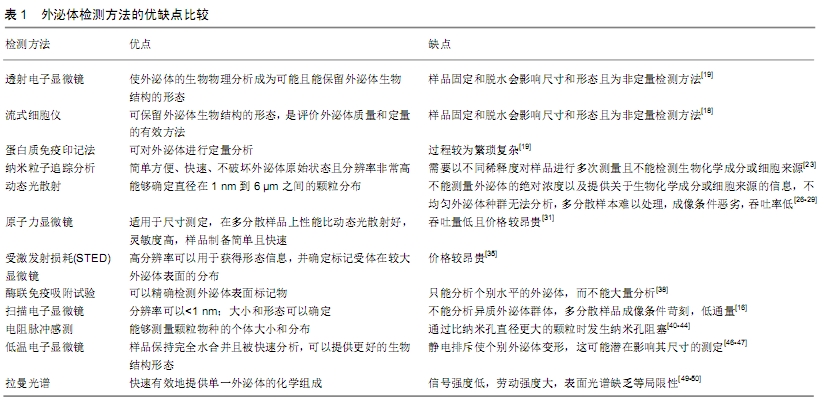
[20] 边素艳,刘宏斌.细胞外囊泡的分离及鉴定方法[J].新医学, 2019,50(9): 658-662.
[21] 郭莹,王秀伟,牛玉虎,等.人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体提取方法的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(9):1382-1388.
[22] TIAN Y, MA L, GONG M, et al. Protein Profiling and Sizing of Extracellular Vesicles from Colorectal Cancer Patients via Flow Cytometry. ACS Nano. 2018;12(1):671-680.
[23] 张娟,刘峰,张薇,等.人脐血间充质干细胞来源的外泌体:分离鉴定及生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(37):5955-5960.
[24] 梁亚会,郭子宽,王芳,等.PEG 6000快速提取间充质干细胞外泌体[J].空军医学杂志,2017,33(3):176-179.
[25] 胡国文,李青,牛鑫,等.旋转超滤:一种提取细胞外泌体的新方法[J].第二军医大学学报,2014,35(6):598-602.
[26] FRANQUESA M, HOOGDUIJN MJ, RIPOLL E, et al. Update on controls for isolation and quantification methodology of extracellular vesicles derived from adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells. Front Immunol. 2014;5:525.
[27] CLARK NA, LUNACEK JH, BENEDEK GB. A Study of Brownian Motion Using Light Scattering. Amer J Phys. 1970;38(6):575-585.
[28] DIECKMANN Y, CÖLFEN H, HOFMANN H, et al. Particle size distribution measurements of manganese-doped ZnS nanoparticles. Anal Chem. 2009;81(10):3889-3895.
[29] BRYANT G, THOMAS JC. Improved Particle Size Distribution Measurements Using Multiangle Dynamic Light Scattering. Langmuir. 1995;11(7):2480-2485.
[30] FILELLA M, JINGWU Z, NEWMAN ME, et al. Analytical applications of photon correlation spectroscopy for size distribution measurements of natural colloidal suspensions: capabilities and limitations. Colloids & Surfaces A Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects. 1997; 120(1-3): 27-46.
[31] HOO CM, STAROSTIN N, WEST P, et al. A comparison of atomic force microscopy (AFM) and dynamic light scattering (DLS) methods to characterize nanoparticle size distributions. Journal of Nanoparticle Research. 2008;10(1 Supplement): 89-96.
[32] HOEKSTRA AG, SLOOT PMA. Biophysical and Biomedical Applications of Nonspherical Scattering. London: Academic Press, 2000:585-602.
[33] BINNIG G, QUATE CF, GERBER C. Atomic force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1986;56(9):930-933.
[34] SIEDLECKI CA, WANG IW, HIGASHI JM, et al. Platelet-derived microparticles on synthetic surfaces observed by atomic force microscopy and fluorescence microscopy. Biomaterials. 1999;20(16): 1521-1529.
[35] YUANA Y, OOSTERKAMP TH, BAHATYROVA S, et al. Atomic force microscopy: a novel approach to the detection of nanosized blood microparticles. J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8(2):315-323.
[36] WESTPHAL V, HELL SW. Nanoscale resolution in the focal plane of an optical microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 2005;94(14):143903.
[37] WILLIG KI, RIZZOLI SO, WESTPHAL V, et al. STED microscopy reveals that synaptotagmin remains clustered after synaptic vesicle exocytosis. Nature. 2006;440(7086):935-939.
[38] HEIN B, WILLIG KI, HELL SW. Stimulated emission depletion (STED) nanoscopy of a fluorescent protein-labeled organelle inside a living cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(38):14271-14276.
[39] VAN DER POL E, HOEKSTRA AG, STURK A, et al. Optical and non-optical methods for detection and characterization of microparticles and exosomes. J Thromb Haemost. 2010;8(12): 2596-2607.
[40] OSUMI K, OZEKI Y, SAITO S, et al. Development and assessment of enzyme immunoassay for platelet-derived microparticles. Thromb Haemost. 2001;85(2):326-330.
[41] ERDBRÜGGER U, LANNIGAN J. Analytical challenges of extracellular vesicle detection: A comparison of different techniques. Cytometry A. 2016;89(2):123-134.
[42] GRAHAM MD. The Coulter principle: Imaginary origins. Cytometry A. 2013;83(12):1057-1061.
[43] ANDERSON W, KOZAK D, COLEMAN VA, et al. A comparative study of submicron particle sizing platforms: accuracy, precision and resolution analysis of polydisperse particle size distributions. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2013;405:322-330.
[44] LANE RE, KORBIE D, ANDERSON W, et al. Analysis of exosome purification methods using a model liposome system and tunable-resistive pulse sensing. Sci Rep. 2015;5:7639.
[45] KO J, CARPENTER E, ISSADORE D. Detection and isolation of circulating exosomes and microvesicles for cancer monitoring and diagnostics using micro-/nano-based devices. Analyst. 2016;141(2): 450-460.
[46] MAAS SL, DE VRIJ J, BROEKMAN ML. Quantification and size-profiling of extracellular vesicles using tunable resistive pulse sensing. J Vis Exp. 2014;(92):e51623.
[47] XU R, GREENING DW, ZHU HJ, et al. Extracellular vesicle isolation and characterization: toward clinical application. J Clin Invest. 2016; 126(4):1152-1162.
[48] POSPICHALOVA V, SVOBODA J, DAVE Z, et al. Simplified protocol for flow cytometry analysis of fluorescently labeled exosomes and microvesicles using dedicated flow cytometer. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:25530.
[49] PETERSEN KE, MANANGON E, HOOD JL, et al. A review of exosome separation techniques and characterization of B16-F10 mouse melanoma exosomes with AF4-UV-MALS-DLS-TEM. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014;406(30):7855-7866.
[50] YUANA Y, KONING RI, KUIL ME, et al. Cryo-electron microscopy of extracellular vesicles in fresh plasma. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013;2(1): 21494.
[51] GREY M, DUNNING CJ, GASPAR R, et al. Acceleration of α-synuclein aggregation by exosomes. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(5):2969-2982.
[52] SMITH ZJ, LEE C, ROJALIN T, et al. Single exosome study reveals subpopulations distributed among cell lines with variability related to membrane content. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:28533.
[53] LEE C, CARNEY RP, HAZARI S, et al. 3D plasmonic nanobowl platform for the study of exosomes in solution. Nanoscale. 2015;7(20): 9290-9297.
[54] BARNES WL, DEREUX A, EBBESEN TW. Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature. 2003;424(6950):824-830.
[55] NORDIN JZ, LEE Y, VADER P, et al. Ultrafiltration with size-exclusion liquid chromatography for high yield isolation of extracellular vesicles preserving intact biophysical and functional properties. Nanomedicine. 2015;11(4):879-883.
[56] BÖING AN, VAN DER POL E, GROOTEMAAT AE, et al. Single-step isolation of extracellular vesicles by size-exclusion chromatography. J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3.
[57] LAI RC, YEO RW, TAN KH, et al. Exosomes for drug delivery - a novel application for the mesenchymal stem cell. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31(5): 543-551.
[58] YEO RW, LAI RC, ZHANG B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell: an efficient mass producer of exosomes for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(3):336-341.
[59] PAOLINI L, ZENDRINI A, DI NOTO G, et al. Residual matrix from different separation techniques impacts exosome biological activity. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23550.
[60] SÓDAR BW, KITTEL Á, PÁLÓCZI K, et al. Low-density lipoprotein mimics blood plasma-derived exosomes and microvesicles during isolation and detection. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24316.
|