中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (36): 5835-5840.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.36.017
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
纳美芬改善大面积脑梗死预后:随机对照前瞻性临床试验方案
孙 晶1,李小平2,王婷婷3,侯玮琛4
- 1华北电力大学医院口腔科,北京市 102206;吉林大学第一医院,2儿科,4神经内科,吉林省长春市 130021;3淄博市第一医院中西医结合科,山东省淄博市 255200
Nalmefene improves prognosis in patients with a large cerebral infarction: study protocol for a randomized controlled prospective trial
Sun Jing1, Li Xiao-ping2, Wang Ting-ting3, Hou Wei-chen4
- 1Department of Stomatology, North China Electric Power University Hospital, Beijing 102206, China; 2Department of Pediatrics, 4Department of Neurology, First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China; 3Department of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine, Zibo First Hospital, Zibo 255200, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
盐酸纳美芬作用:主要用于已知或疑似阿片类药物过量或中毒的急救促醒、急性颅脑与脊髓损伤、脑缺血、脑梗塞等神经功能损坏性疾病、昏迷、休克及术后麻醉催醒、酒精中毒、戒毒后防复吸治疗等症状。
基质金属蛋白酶:是最重要的金属酶之一。至今已发现至少19种,是一种依赖金属锌离子的金属酶,因其作用底物广泛,表达细胞众多而备受重视。在正常生理情况下,能够切断任何细胞外基质成分,调节细胞黏附,作用于细胞外成分或其他蛋白成分而启动潜在生物学功能,直接或间接参与胚胎发育、组织模型再塑及创伤修复等正常生理功能。
文题释义:
盐酸纳美芬作用:主要用于已知或疑似阿片类药物过量或中毒的急救促醒、急性颅脑与脊髓损伤、脑缺血、脑梗塞等神经功能损坏性疾病、昏迷、休克及术后麻醉催醒、酒精中毒、戒毒后防复吸治疗等症状。
基质金属蛋白酶:是最重要的金属酶之一。至今已发现至少19种,是一种依赖金属锌离子的金属酶,因其作用底物广泛,表达细胞众多而备受重视。在正常生理情况下,能够切断任何细胞外基质成分,调节细胞黏附,作用于细胞外成分或其他蛋白成分而启动潜在生物学功能,直接或间接参与胚胎发育、组织模型再塑及创伤修复等正常生理功能。
.jpg) 文题释义:
盐酸纳美芬作用:主要用于已知或疑似阿片类药物过量或中毒的急救促醒、急性颅脑与脊髓损伤、脑缺血、脑梗塞等神经功能损坏性疾病、昏迷、休克及术后麻醉催醒、酒精中毒、戒毒后防复吸治疗等症状。
基质金属蛋白酶:是最重要的金属酶之一。至今已发现至少19种,是一种依赖金属锌离子的金属酶,因其作用底物广泛,表达细胞众多而备受重视。在正常生理情况下,能够切断任何细胞外基质成分,调节细胞黏附,作用于细胞外成分或其他蛋白成分而启动潜在生物学功能,直接或间接参与胚胎发育、组织模型再塑及创伤修复等正常生理功能。
文题释义:
盐酸纳美芬作用:主要用于已知或疑似阿片类药物过量或中毒的急救促醒、急性颅脑与脊髓损伤、脑缺血、脑梗塞等神经功能损坏性疾病、昏迷、休克及术后麻醉催醒、酒精中毒、戒毒后防复吸治疗等症状。
基质金属蛋白酶:是最重要的金属酶之一。至今已发现至少19种,是一种依赖金属锌离子的金属酶,因其作用底物广泛,表达细胞众多而备受重视。在正常生理情况下,能够切断任何细胞外基质成分,调节细胞黏附,作用于细胞外成分或其他蛋白成分而启动潜在生物学功能,直接或间接参与胚胎发育、组织模型再塑及创伤修复等正常生理功能。摘要
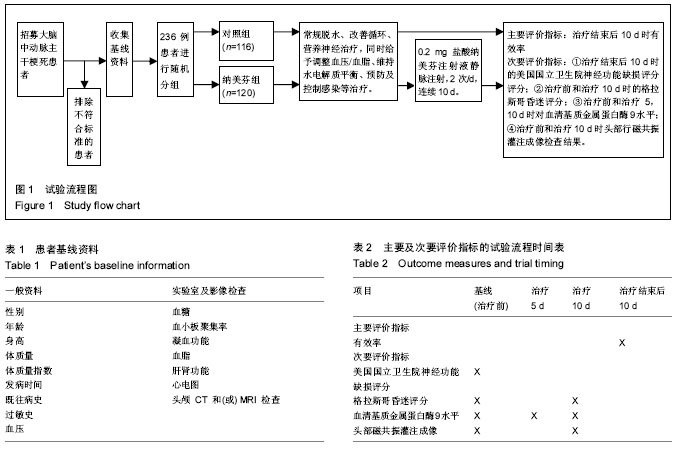
背景:大脑中动脉主干梗死会造成大面积脑梗死,临床上常采用溶栓、降纤、血管扩张以及手术等方法进行治疗,但这些方法对患者预后的疗效存在争议。纳美芬是一种特异性吗啡受体阻断剂,具有神经保护作用。但是目前尚无其治疗大面积脑梗死有效性的临床研究。
目的:以常规治疗为对照,观察纳美芬对大脑中动脉主干脑梗死患者的神经功能恢复作用。
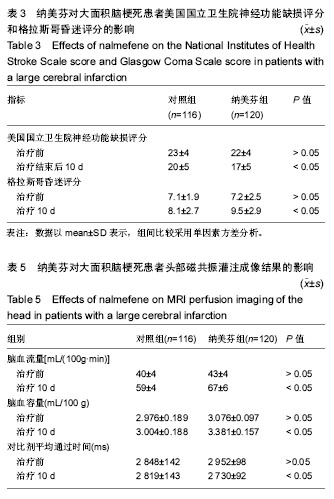
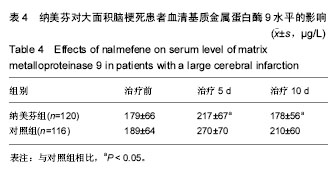
方法:随机对照前瞻性试验选取中国吉林大学第一医院收治的大脑中动脉主干梗死患者236例,随机分为对照组(n=116)和纳美芬组(n=120)。对照组采取常规治疗方法,纳美芬组在常规治疗基础上连续10 d静脉注射盐酸纳美芬注射液。试验以治疗结束后10 d时有效率作为主要评价指标。次要评价指标为:①治疗结束后10 d时的美国国立卫生院神经功能缺损评分;治疗前和治疗后10 d时的格拉斯哥昏迷评分;③治疗前和治疗5,10 d时对血清基质金属蛋白酶9水平;④治疗前和治疗10 d时头部行磁共振灌注成像检查结果。试验方案已在中国临床试验注册中心注册,注册号为ChiCTR-IOR-17013871。
结果与结论:已完成的预试验结果显示,与对照组相比,治疗后纳美芬组患者美国国立卫生院神经功能缺损评分明显降低,治疗有效率增加,格拉斯哥昏迷评分明显升高,血清基质金属蛋白酶9水平下降,头部磁共振灌注病灶侧脑血流量和脑血容量明显增加,对比剂平均通过时间显著缩短。试验将为纳美芬联合常规治疗大面积脑梗死提供试验证据,为改善大面积脑梗死预后提供试验数据支持。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-8592-0775(孙晶)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
盐酸纳美芬作用:主要用于已知或疑似阿片类药物过量或中毒的急救促醒、急性颅脑与脊髓损伤、脑缺血、脑梗塞等神经功能损坏性疾病、昏迷、休克及术后麻醉催醒、酒精中毒、戒毒后防复吸治疗等症状。
基质金属蛋白酶:是最重要的金属酶之一。至今已发现至少19种,是一种依赖金属锌离子的金属酶,因其作用底物广泛,表达细胞众多而备受重视。在正常生理情况下,能够切断任何细胞外基质成分,调节细胞黏附,作用于细胞外成分或其他蛋白成分而启动潜在生物学功能,直接或间接参与胚胎发育、组织模型再塑及创伤修复等正常生理功能。
文题释义:
盐酸纳美芬作用:主要用于已知或疑似阿片类药物过量或中毒的急救促醒、急性颅脑与脊髓损伤、脑缺血、脑梗塞等神经功能损坏性疾病、昏迷、休克及术后麻醉催醒、酒精中毒、戒毒后防复吸治疗等症状。
基质金属蛋白酶:是最重要的金属酶之一。至今已发现至少19种,是一种依赖金属锌离子的金属酶,因其作用底物广泛,表达细胞众多而备受重视。在正常生理情况下,能够切断任何细胞外基质成分,调节细胞黏附,作用于细胞外成分或其他蛋白成分而启动潜在生物学功能,直接或间接参与胚胎发育、组织模型再塑及创伤修复等正常生理功能。