中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (35): 5668-5672.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.35.015
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
改良经跗骨窦微创小切口空心钉内固定与传统外侧L形切口钢板内固定治疗跟骨骨折
黄 晟,沈鹏程,徐 浩,朱立帆,翁峰标,侯青凡
- 南通大学附属吴江医院,苏州市吴江区第一人民医院,江苏省苏州市 215200
Modified minimally invasive internal fixation with cannulated screws through tarsal sinus versus traditional extended lateral “L-shape” incision with plate fixation for calcaneal fractures
Huang Sheng, Shen Peng-cheng, Xu Hao, Zhu Li-fan, Weng Feng-biao, Hou Qing-fan
- Wujiang Hospital Affiliated to Nantong University, Wujiang First People’s Hospital of Suzhou, Suzhou 215200, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
Sanders分型:根据CT 30°半冠状位扫描,最大程度显示距下关节后关节面,将跟骨平均分为3柱,跟骨后关节面由平行于跟骨纵轴的A.B两线分为3个等大的区域,产生3种潜在的骨折块,外侧、中央、内侧。Ⅰ型:所有无移位的关节内骨折;Ⅱ型:后关节面2片段骨折,根据骨折线的位置分为A.B.C3个亚型;Ⅲ型:后关节面3片段骨折,按照2个骨折线的位置分为AB.AC或BC3个亚型;Ⅳ型:后关节面4片段骨折,为严重的粉碎性关节内骨折,常不止4个骨块。
改良经跗骨窦微创小切口空心钉内固定:先行2 cm的跗骨窦切口,切口由后关节面顶部延续到跟骨前突,切口走向与足底平行,锐性分离组织,暴露关节面,并设置另一辅助小切口1 cm,通过此小切口插入大血管钳于骨折断端,撬拨内侧壁,予复位跟骨内侧壁的对位对线及跟骨高度,于跗骨窦切口植入固定载距突空心钉一枚,最后通过手法挤压复位外侧壁的膨出,由跟骨后方靠近跟骨结节处往跟骰方向植入空心螺钉固定骨折块及维持高度。
摘要
背景:目前切开复位内固定术是临床最常见的跟骨骨折治疗方案,但是手术并发症一直困扰着临床工作者,因此选择合适的手术方案对于减少术后并发症、提高患者疗效具有重要意义。
目的:比较改良经跗骨窦微创小切口空心钉内固定与传统外侧L形切口钢板内固定治疗跟骨骨折的效果。
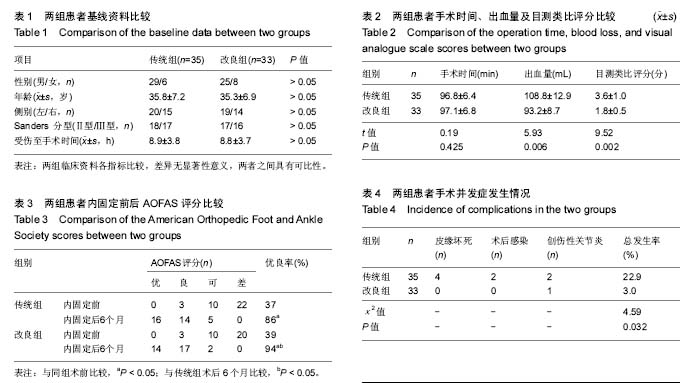
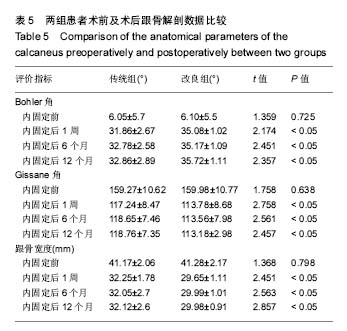
方法:选择单侧跟骨骨折(SandersⅡ、Ⅲ型)患者68例,其中改良经跗骨窦微创小切口入路空心钉内固定治疗33例(改良组),经传统外侧L形切口入路钢板内固定治疗35例(传统组)。比较两组手术时间、出血量及目测类比评分,及两组手术前后AOFAS 评分、Bohler角、Gissane角及术后并发症发生情况的差异,分别对患者内固定后疼痛、关节活动度、踝关节稳定性等进行评价。
结果与结论:①两组内固定后6月AOFAS评分优良率均高于内固定前(P < 0.05),且改良组AOFAS评分高于传统组(P < 0.05);②改良组内固定后1周、6个月、12个月的Bohler角、Gissane角及跟骨宽度与传统组同期相比较有明显改善(P < 0.05);③两组手术时间的比较相差不大,但在出血量、手术时间与目测类比评分上,改良组相比传统组均显著改善(P < 0.05);④改良组内固定后并发症发生率明显少于传统组(P < 0.05);⑤结果说明,与传统L形切口钢板内固定相比,改良经跗骨窦微创小切口空心钉内固定治疗跟骨骨折在减轻疼痛、提供关节活动度等方面能够取得更好的临床效果,使跟骨关节面有更强的稳定性。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-5768-4755(黄晟)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)