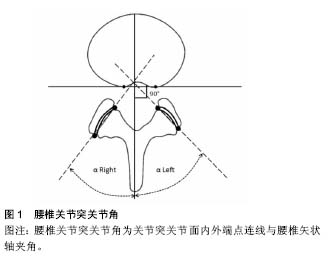
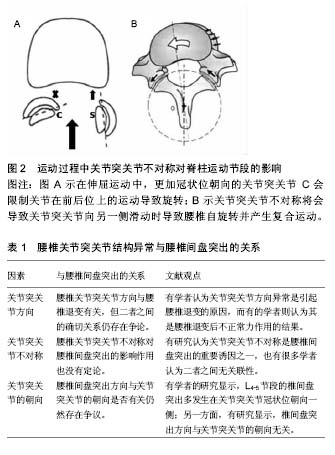
| [1] Adams MA, Hutton WC. The effect of posture on the role of the apophysial joints in resisting intervertebral compressive forces. J Bone Joint Surg. 1980; 62: 358-362.?[2] Kalichmanand L, Hunter DJ. Lumbar facet joint osteoarthritis: a review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 37: 69-80. ?[3] Leonid K, Pradeep S, Ali G, et al. Facet tropism and orientation: associations with facet joint osteoarthritis and degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2009; 34(16): E579-E585.[4] Cohen Steven P, Raja Srinivasa N. Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of lumbar zygapophysial (facet) joint pain. Anesthesiology. 2007; 106:591-614.[5] Masharawi Y, Rothschild B, Salame K, et al. Facet tropism and interfacet shape in the thoracolumbar vertebrae: characterization and biomechanical interpretation. Spine. 2005;30:281-292.[6] Veres SP, Robertson PA, Broom ND. The influence of torsion on disc herniation when combined with flexion. Eur Spine J. 2010;19:1468-1478.[7] Fazey PJ, Song S, Monsas S, et al. An MRI investigation of intervertebral disc deformation in response to torsion. Clin Biomech. 2006;21:538-542.[8] Schmidt H, Kettler A, Heuer F, et al. Intradiscal pressure, shear strain, and fiber strain in the intervertebral disc under combined loading. Spine. 2007;32:748-755.[9] Drake JD, Aultman CD, McGill SM, et al. The influence of static axial torque in combined loading on intervertebral joint failure mechanics using a porcine model. Clin Biomech. 2005;20:1038-1045.[10] Karacan I, Aydin T, Sahin Z, et al. Facet angles in lumbar disc herniation: their relation to anthropometric features. Spine. 2004;29:1132-1136.[11] Cyron BM, Hutton WC. Articular tropism and stability of the lumbar spine. Spine. 1980;5:168-172.[12] Kunakornsawat S, Ngamlamaidt K, Tungsiripat R, et al. The relationship of facet tropism to lumbar disc herniation . J Med Assoc Thai. 2007;90(27):1337-1341.[13] Lee DY, Ahn Y, Lee SH. The influence of facet tropism on herniation of the lumbar disc in adolescents and adults . J Bone Jt Surg Br. 2006; 8:520-523.[14] Park JB, Chang H, Kim KW, et al. Facet tropism: a comparison between far lateral and posterolateral lumbar disc herniations. Spine, 2001; 26:677-679.[15] Adams MA, Hutton WC; The relevance of torsion to the mechanical derangement of the lumbar spine. Spine. 1981;6: 241-248.[16] Fitzgerald JA, Newman PH. Degenerative spondylolisthesis . J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1976; 58:184-192.[17] Grobler LJ, Robertson PA, Novotny JE, et al. Etiology of spondylolisthesis. Assessment of the role played by lumbar facet joint morphology . Spine.1993;18:80-91. [18] Kim NH, Lee JW. The relationship between isthmic and degenerative spondylolisthesis and the configuration of the lamina and facet joints . Eur Spine J. 1995; 4:139-144.[19] Nagaosa Y, Kikuchi S, Hasue M, et al. Pathoanatomic mechanisms of degenerative spondylolisthesis. A radiographic study. Spine.1998; 23:1447-1451.[20] Sato K, Wakamatsu E, Yoshizumi A, et al. The configuration of the laminas and facet joints in degenerative spondylolisthesis. A clinicoradiologic study. Spine. 1989;14: 1265-1271.[21] Dai LY. Orientation and tropism of lumbar facet joints in degenerative spondylolisthesis. Int Orthop. 2001;25:40-42.[22] Fujiwara A, Tamai K, An HS, et al. Orientation and osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joint. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;385:88-94.[23] Linova L, Klindukhova A, Lib L, et al. Lumbar facet joint orientation and osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional study. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2013;26:421-426.[24] Brailsford JF. Deformities of the lumbosacral region of the spine . Br J Surg. 1928;16:562-627.[25] Farfan HF, Sullivan JD. The relation of facet orientation to intervertebral disc failure . Can J Surg. 1967;10:179-185.[26] Noren R, Trafimow J, Andersson GB, et al. he role of facet joint tropism and facet angle in disc degeneration . Spine. 1991;16:530-32.[27] Boden SD, Riew KD, Yamaguchi K, et al. Orientation of the lumbar facet joints: association with degenerative disc disease. J Bone Jt Surg Am. 1996;78: 403-411.[28] Cassidy JD, Loback D, Yong-Hing K, et al. Lumbar facet joint asymmetry. Intervertebral disc herniation. Spine. 1992;17: 570-574.[29] Hagg O, Wallner A. Facet joint asymmetry and protrusion of intervertebral disc. Spine. 1990;15:356-359.[30] Vanharanta H, Floyd T, Ohnmeiss D. The relationship of facet tropism to degenerative disc disease. Spine. 1993;18: 1000-1005.[31] Ishihara H, Matsui H, Osada R, et al. Facet joint asymmetry as a radiologic feature of lumbar intervertebral disc herniation in children and adolescents. Spine. 1997;22:2001-2004.[32] Ko HY, Park BK. Facet tropism in lumbar motion segments and its significance in disc herniation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1997;78:1211-214.[33] 戴力扬,贾连顺.腰椎关节突关节不对称[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 1996,6(3):106-108.[34] Loback D, Young-Hing K, Cassidy D, et al. The relationship between facet orientation and lumbar disc herniation: the role of torsion in intervertebral disc failure. Orthop Trans. 1985; 9:560-563.[35] Kénési C, Lesur E. Orientation of the articular processes at L4, L5, and S1. Possible role in pathology of the intervertebral disc. Anat Clin. 1985;7:43-47.[36] 张光铂,绳厚福,史振才. 腰椎关节突关节不对称与椎间盘变性[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,1997,7(5):199-201.[37] Manish C, Gaurav S, Shobha SA, et al. Association of facet tropism with lumbar disc herniation. Eur Spine J. 2013; 22(5): 1045-1052.[38] Wang JX, Yang XY. Age-Related Changes in the Orientation of Lumbar Facet Joints. Spine. 2009; 34: E596-E598.[39] 王大林,吴小涛,王黎明. 腰椎关节突关节不对称与青少年腰椎间盘突出症[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2005,15(6):341-344.[40] Wang H, Zhou YJ. Facet tropism: possible role in the pathology of lumbar disc herniation in adolescents. Neurosurg Pediatr. 2016 ;18(1):111-115. [41] Wang H, Zhang Z, Zhou Y. Irregular Alteration of Facet Orientation in Lumbar Segments: Possible Role in Pathology of Lumbar Disc Herniation in Adolescents. World Neurosurg. 2016; 86:321-327.[42] Grogan J, Nowicki BH, Schmidt TA, et al. Lumbar facet joint tropism does not accelerate degeneration of the facet joints. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1997;18(7):1325-1329. |
.jpg)
.jpg)