| [1] Stevens JA, Rudd RA. The impact of decreasing U.S. hip fracture rates on future hip fracture estimates. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(10):2725-2728.[2] Ong T, Anand V, Tan W, et al. Patient characteristics and outcomes of a hip fracture and comconitant fracture compared with hip fracture alone: results from a United Kingdom teaching hospital. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016; 136(4):463-467.[3] Bretherton CP, Parker MJ. Femoral medialization, fixation failures, and functional outcome in trochanteric hip fractures treated with either a sliding hip screw or an intramedullary nail from within a randomized trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30(12): 642-646.[4] Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51(4):737-755.[5] Dawson J, Fitzpatrick R, Carr A, et al. Questionnaire on the perceptions of patients about total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998;80-B:63-69.[6] Tsuda Y, Yasunaqa H, Horiquchi H, et al. Association between dementia and postoperative complications after hip fracture surgery in the elderly: analysis of 87,654 patients using a national administrative database. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(11):1511-1517.[7] Switzer JA, Bozic KJ, Kates SL. Geriatric fracture care: Future trajectories: A 2015 AOA critical issues symposium. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(8):e40.[8] Hotchen AJ, Vonberg FW, Ironside EC, et al. Predictors of infective outcomes following hip fracture:a cohort study. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2016;2:2333721416649488.[9] Sheikh HQ, Hossain FS, Aqil A, et al. A comprehensive analysis of the causes and predictors of 30-day mortality following hip fracture surgery. Clin Orthop Surg. 2017;9(1): 10-18.[10] Siegmeth AW, Gurusamy K, Parker MJ. Delay to surgery prolongs hospital stay in patients with fractures of the proximal femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(8): 1123-1126.[11] Novack V, Jotkowitz A, Etzion O, et al. Does delay in surgery after hip fracture lead to worse outcomes? A multicenter survey. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007;19(3):170-176.[12] Curtis EM, van der Velde R, Moon RJ, et al. Epidemiology of fractures in the United Kingdom 1988-2012: Variation with age, sex, geography, ethnicity and socioeconomic status. Bone. 2016;87:19-26.[13] Dudko S, Kosior P, Kusz D, et al. Factors influencing treatment of proximal femoral fractures. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2017;19(1):45-54.[14] Kaufer H. Mechanics of the treatment of hip injuries. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980;(146):53-61.[15] Adams CI, Robinson CM, Court-Brown CM, et al. Prospective randomized controlled trial of an intramedullary nail versus dynamic screw and plate for intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(6):394-400.[16] Sadowski C, Lubbeke A, Saudan M, et al. Treatment of reverse oblique and transverse intertrochanteric fractures with use of an intramedullary nail or a 95 degrees screw-plate: a prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(3):372-381.[17] Zhu Q, Xu X, Yang X, et al. Intramedullary nails versus sliding hip screws for AO/OTA 31-A2 trochanteric fractures in adults: A meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2017;43:67-74.[18] Socci AR, Casemyr NE, Leslie MP, et al. Implant options for the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures of the hip: rationale, evidence, and recommendations. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(1): 128-133.[19] Bretherton CP, Parker MJ. Femoral medialization, fixation failures, and functional outcome in trochanteric hip fractures treated with either a sliding hip screw or an intramedullary nail from within a randomized trial. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30(12): 642-646.[20] Queally JM, Harris E, Handoll HH, et al. Intramedullary nails for extracapsular hip fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(9):CD004961.[21] Cho HM, Lee K. Clinical and functional outcomes of treatment for Type A1 intertrochanteric femoral fracture in elderly patients: Comparison of dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nail antirotation. Hip Pelvis. 2016;28(4):232-242.[22] Zeng X, Zhang N, Zeng D, et al. Proximal femoral nail antirotation versus dynamic hip screw fixation for treatment of osteoporotic type 31-A1 intertrochanteric femoral fractures in elderly patients. J Int Med Res. 2017;45(3):1109-1123.[23] Wang Q, Yang X, He HZ, et al. Comparative study of InterTan and dynamic hip screw in treatment of femoral intertrochanteric injury and wound. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014; 7(12):5578-5582.[24] Sanders D, Bryant D, Tieszer C, et al. A multicenter randomized control trial comparing a novel intramedullary device (InterTan) versus convertional treatment (sliding hip screw) of geriatric hip fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2017; 31(1): 1-8.[25] Huang Y, Zhang C, Luo Y. A comparative biomechanical study of proximal femoral nail(InterTan) and proximal femoral nail antirotation for interchanteric fractrues. Int Orthop. 2013; 37(12):2465-2473.[26] Zhang S, Zhang K, Jia Y, et al. InterTan nail versus Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation-Asia in the treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures. Orthopedics. 2013;36(3):e288-294.[27] Queally JM, Harris E, Handoll HH, et al. Intramedullary nails for extracapsular hip fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;9:CD004961.[28] Seyhan M, Turkmen I, Unay K, et al. Do PFNA devices and Intertan nails both have the same effects in the treatment of trochanteric fractures? A prospective clinical study. J Orthop Sci. 2015;20(6):1053-1061.[29] Zehir S, Sahin E, Zehir R. Comparison of clinical outcomes with three different intramedullary nailing devices in the treatment of unstable trochanteric fractures. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derq. 2015;21(6):469-476.[30] Yu W, Zhang X, Zhu X, et al. A retrospective analysis of the InterTan nail and proximal femoral nail anti-rotation-Asia in the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric femur fractures in the elderly. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11:10.[31] Luo X, He S, Zeng D, et al. Proximal femoral nail antirotation versus hemiarthroplasty in the treatment of senile intertrochanteric fractures: Case report. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2017;38:37-42. [32] Jia L, Zhang K, Wang ZG, et al. Proximal femoral nail antirotation internal fixation in treating intertrochanteric femoral fractures of elderly subjects. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2017;31(2):329-334.[33] Shin WC, Seo JD, Lee SM, et al. Radiographic Outcomes of Osteosynthesis Using Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation (PFNA) System in Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture: Has PFNA II Solved All the Problems? Hip Pelvis. 2017;29(2): 104-112. [34] Zhang H, Zeng X, Zhang N, et al. INTERTAN nail versus proximal femoral nail antirotation-Asia for intertrochanteric femur fractures in elderly patients with primary osteoporosis. J Int Med Res. 2017;45(4):1297-1309. [35] Shin YS, Chae JE, Kang TW, et al. Prospective randomized study comparing two cephalomedullary nails for elderly intertrochanteric fractures: Zimmer natural nail versus proximal femoral nail antirotation II. Injury. 2017;48(7): 1550-1557. [36] Esen E, Dur H, Atao?lu MB, et al. Evaluation of proximal femoral nail-antirotation and cemented, bipolar hemiarthroplasty with calcar replacement in treatment of intertrochanteric femoral fractures in terms of mortality and morbidity ratios. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2017;28(1):35-40. [37] Sonmez MM, Camur S, Erturer E, et al. Strategies for Proximal Femoral Nailing of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractures: Lateral Decubitus Position or Traction Table. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25(3):e37-e44. [38] Zeng X, Zhan K, Zhang L,et al. Conversion to total hip arthroplasty after failed proximal femoral nail antirotations or dynamic hip screw fixations for stable intertrochanteric femur fractures: a retrospective study with a minimum follow-up of 3 years. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18(1):38. [39] Park BJ, Cho HM, Min WB.Surgical Treatment of Undisplaced Femur Neck Fractures in Dementia Patients Using Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation.Hip Pelvis. 2015;27(3):164-172. [40] Jiang X, Wang Y, Ma X, et al. Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation Versus Reverse Less Invasive Stabilization System-distal Femur for Treating Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(14):e3168. |
.jpg)
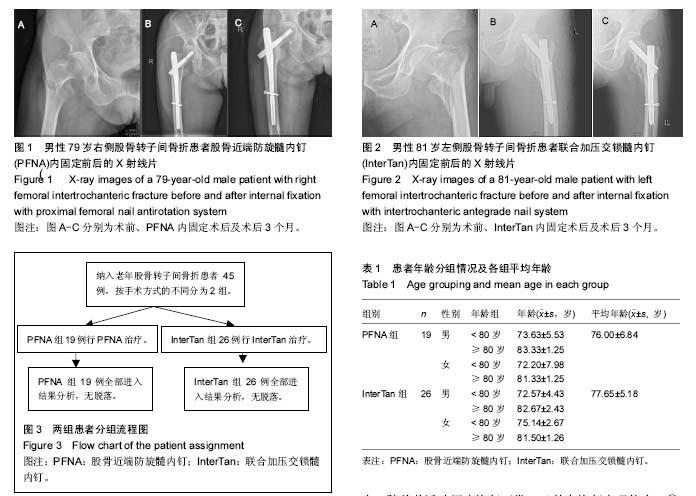
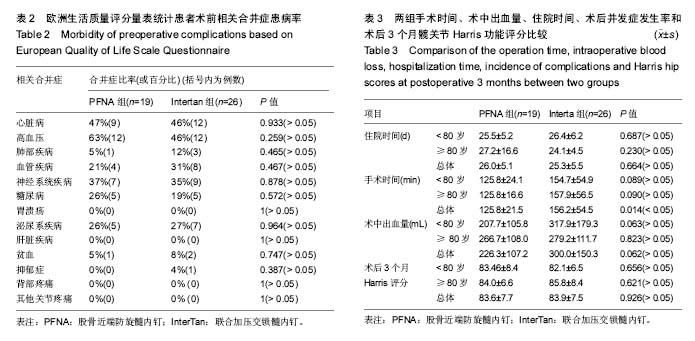
.jpg)