| [1] Hagen EM.Acute complications of spinal cord injuries.World J Orthop.2015;6(1):17-23.[2] Merghati Khoi E,Latifi S,Rahdari F,et al.The effect of injury-related characteristics on changes in marital status after spinal cord injury.Iran J Public Health.2015;44(10): 1395-1402.[3] Dedeepiya VD,William JB,Parthiban JK,et al.The known-unknowns in spinal cord injury, with emphasis on cell-based therapies - a review with suggestive arenas for research.Expert Opin Biol Ther.2014;14(5):617-634.[4] Dolbow DR,Gorgey AS,Recio AC,et al.Activity-based restorative therapies after spinal cord injury: inter-institutional conceptions and perceptions.Aging Dis.2015;6(4):254-261.[5] Hagen EM,Rekand T.Management of neuropathic pain associated with spinal cord injury. Pain Ther.2015;4(1):51-65.[6] Y?lmaz T,Kaptano?lu E.Current and future medical therapeutic strategies for the functional repair of spinal cord injury.World J Orthop.2015;6(1):42-55.[7] Sezer N,Akku? S,U?urlu FG.Chronic complications of spinal cord injury.World J Orthop.2015; 6(1):24-33.[8] Wang J,Pearse DD.Therapeutic hypothermia in spinal cord injury: the status of its use and open questions.Int J Mol Sci.2015;16(8):16848-16879.[9] Schroeder GD,Kepler CK,Vaccaro AR.The Use of Cell Transplantation in Spinal Cord Injuries. J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2016;24(4):266-275.[10] Goel A.Stem cell therapy in spinal cord injury: Hollow promise or promising science? J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2016; 7(2):121-126.[11] Marichal N,Fabbiani G,Trujillo-Cenoz O,et al.Purinergic signalling in a latent stem cell niche of the rat spinal cord. Purinergic Signal.2016;12(2):331-341.[12] Guo L,Rolfe AJ,Wang X,et al.Rescuing macrophage normal function in spinal cord injury with embryonic stem cell conditioned media.Mol Brain.2016;9(1):48.[13] Neirinckx V,Agirman G,Coste C,et al.Adult bone marrow mesenchymal and neural crest stem cells are chemoattractive and accelerate motor recovery in a mouse model of spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther.2015;6:211.[14] Li J,Lepski G.Cell transplantation for spinal cord injury: a systematic review.Biomed Res Int.2013;2013:786475.[15] Ades AE,Caldwell DM,Reken S,et al.Evidence synthesis for decision making 7: a reviewer's checklist.Med Decis Making. 2013;33(5):679-691.[16] 张拓,佟旭,刘晨.骨髓间充质干细胞对脉冲低剂量效率放射性脊髓损伤细胞修复作用的研究[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2015, 15(A0):64-65.[17] 郭志松,秦秉玉,代荣钦,等.骨髓问充质干细胞治疗脊髓损伤的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014, 31(11):2605-2607.[18] 张效北,李江涛,赵和泰,等.间质干细胞治疗脊髓损伤的临床分析[J].亚太传统医药,2012,8(3):116-117.[19] 肖以磊,朱建新,李忠民,等.两种不同途径移植自体骨髓间充质干细胞治疗早期脊髓损伤疗效观察[J].中国医师进修杂志,2012, 35(14):24-28.[20] 郭钢花,申利坊,李哲.脐血间充质干细胞治疗脊髓损伤临床研究[J].中国实用医刊,2012, 39(10):58-60.[21] 崔贵祥,宋成忠,李义召,等.自体骨髓单个核细胞治疗脊髓损伤的临床研究[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2009,24(4):304-312.[22] 谢遵伟,崔贵祥,李义召,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞治疗脊髓损伤疗效观察[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(7):1277-1279.[23] 肖以磊,李忠民,朱建新,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞治疗早期脊髓损伤疗效观察[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2014,20(1):7-11.[24] Cheng H,Liu X,Hua R,et al.Clinical observation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in treatment for sequelae of thoracolumbar spinal cord injury.J Transl Med. 2014; 12:254.[25] Dai G,Liu X,Zhang Z,et al.Transplantation of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of complete and chronic cervical spinal cord injury. Brain Res.2013; 1533: 73-79.[26] 赵琳,杨彦玲,韩继明.细胞移植及细胞联合移植修复脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].神经解剖学杂志,2014,30(5):605-608.[27] 彭岱,王汉东.干细胞在脊髓损伤治疗现状与进展[J].医学研究生学报,2013,26(11):1226-1229.[28] Alkabie S,Boileau AJ.The role of therapeutic hypothermia after traumatic spinal cord injury-A systematic review.World Neurosurg.2016;86:432-449.[29] Gomez-Villafuertes R.Contribution of purinergic receptors to spinal cord injury repair: stem cell-based neuroregeneration. Neural Regen Res.2016;11(3):418-419.[30] Pati S,Pilia M,Grimsley JM,et al.Cellular therapies in trauma and critical care medicine: forging new frontiers. Shock. 2015;44(6):505-523.[31] Batista CE,Mariano ED,Marie SK,et al. Stem cells in neurology - current perspectives.Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2014;72(6):457-465.[32] Lin XY,Lai BQ,Chen MT,et al.Cell transplantation and neuroengineering approach for spinal cord injury treatment: a summary of current laboratory findings and review of literature. Cell Transplant.2016;25(8):1425-1438.[33] Myers SA,Bankston AN,Burke DA,et al.Does the preclinical evidence for functional remyelination following myelinating cell engraftment into the injured spinal cord support progression to clinical trials? Exp Neurol.2016;283(Pt B): 560-572.[34] Mendonca MV,Larocca TF,de Freitas SB,et al.Safety and neurological assessments after autologous transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in subjects with chronic spinal cord injury.Stem Cell Res Ther.2014;5(6):126.[35] Ra JC,Shin IS,Kim SH,et al.Safety of intravenous infusion of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in animals and humans.Stem Cells Dev.2011;20(8):1297-1308.[36] Lima C,Pratas-Vital J,Escada P,et al.Olfactory mucosa autografts in human spinal cord injury: a pilot clinical study.J Spinal Cord Med.2006;29(3):191-203.[37] Shroff G.Human embryonic stem cell therapy in chronic spinal cord injury: A retrospective study. Clin Transl Sci.2016;9(3): 168-175.[38] Cheng I,Githens M,Smith RL,et al.Local versus distal transplantation of human neural stem cells following chronic spinal cord injury.Spine J.2016;16(6):764-769.[39] Oh SK,Choi KH,Yoo JY,et al.A Phase III Clinical Trial Showing Limited Efficacy of Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury. Neurosurgery. 2016;78(3): 436-447.[40] Oraee-Yazdani S,Hafizi M,Atashi A,et al.Co-transplantation of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and Schwann cells through cerebral spinal fluid for the treatment of patients with chronic spinal cord injury: safety and possible outcome.Spinal Cord.2016; 54(2):102-109.[41] Lin XY,Lai BQ,Zeng X,et al.Cell transplantation and neuroengineering approach for spinal cord injury treatment: A summary of current laboratory findings and review of literature.Cell Transplant.2016;25(8):1425-1438.[42] Aras Y,Sabanci PA,Kabatas S,et al.The effects of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation during the acute and subacute phases following spinal cord injury. Turk Neurosurg.2016;26(1):127-139. |

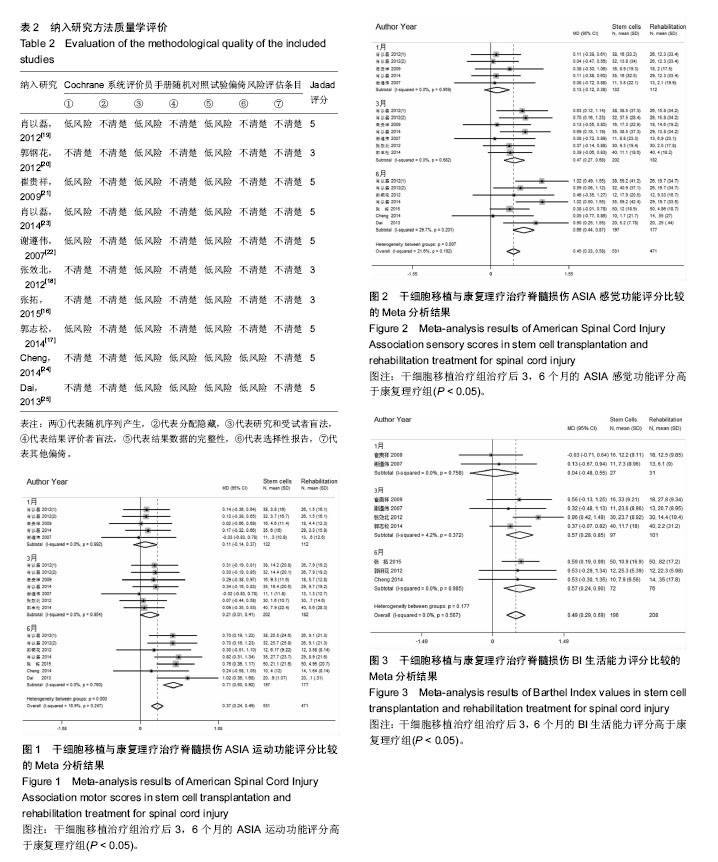
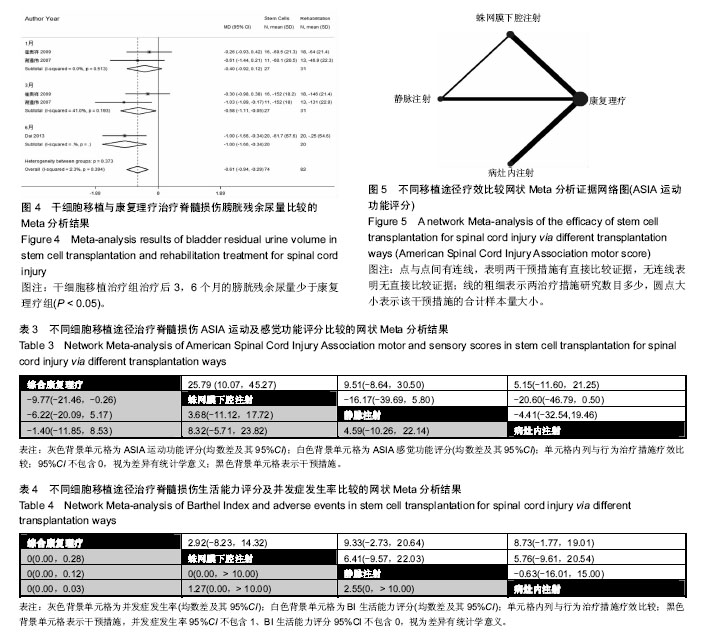
.jpg)