中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (26): 4217-4221.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.26.020
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
量子点与巨噬细胞的生物相容性
李 翀1,严 成2,金慧敏2,吴水芸2,强叶涛2,颜楠楠2,肖腾飞2,夏 圣2
- 1江苏大学附属昆山医院,江苏省昆山市 215300;2江苏大学医学院,江苏省镇江市 212013
Biocompatibility of macrophages with quantum dots
Li Chong1, Yan Cheng2, Jin Hui-min2, Wu Shui-yun2, Qiang Ye-tao2, Yan Nan-nan2, Xiao Teng-fei1, Xia Sheng2
- 1Kunshan Hospital of Jiangsu University, Kunshan 215300, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Immunology and Immunoassay, Jiangsu University Medical School, Zhenjiang 212013, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
量子点:是一类新的半导体纳米荧光材料,含Ⅲ-Ⅴ族、Ⅱ-Ⅵ族或Ⅳ族元素。研究表明,量子点有宽吸收光谱、较窄发射光谱、光稳定性强等特点,而且不同粒径的量子点在受到同一光源激发后可产生不同波长的发射光。因此,与传统的有机荧光染料相比,量子点呈现出良好的生物标记特性,尤其在细胞标记、临床靶向生物成像等领域呈现出其独特的光学特性。
背景:与传统的有机荧光染料相比,量子点呈现出良好的生物标记特性,尤其在细胞标记、临床靶向生物成像等领域呈现出独特的光学特性。
目的:观察CdSe/ZnS量子点与单核-巨噬细胞的生物相容性。
方法:将巨噬细胞RAW264.7接种于96孔板中,分3组培养,分别加入0,50,100 mg/L的CdSe/ZnS量子点干预,培养1 h或2 h,流式细胞仪检测荧光信号;培养0-24 h,流式细胞仪检测50 mg/L CdSe/ZnS量子点标记巨噬细胞的荧光信号强度;培养18 h,定量PCR检测巨噬细胞内肿瘤坏死因子α及白细胞介素1β的水平;培养18 h,MTT法检测巨噬细胞增殖,流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡。
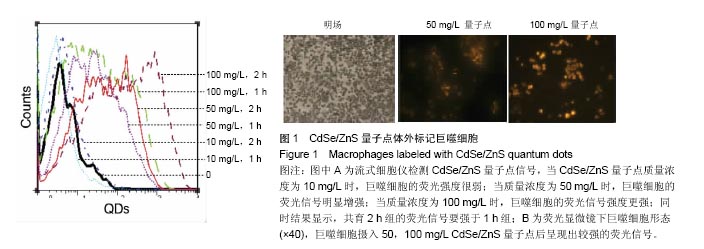
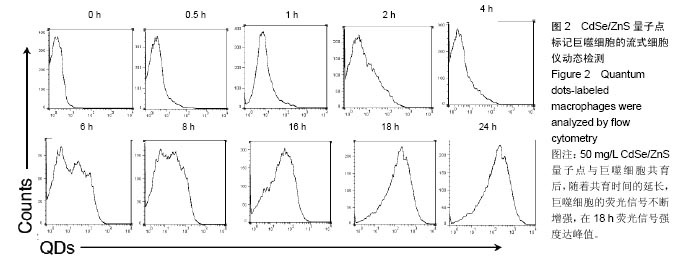
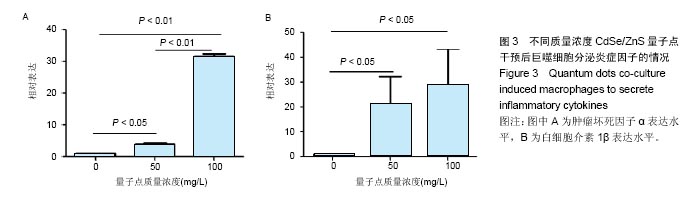
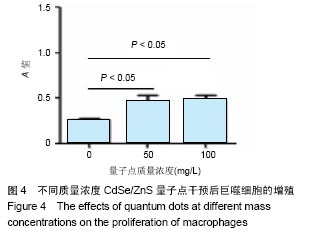
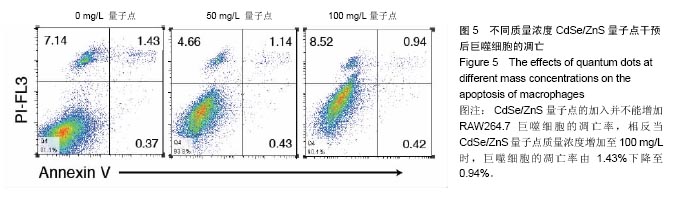
结果与结论:①荧光信号强度与CdSe/ZnS量子点的质量浓度呈正相关,并且随着标记时间的延长,荧光信号强度增强;②经50 mg/L CdSe/ZnS量子点标记后,随着时间的延长,巨噬细胞的荧光信号不断增强,在18 h达到峰值;③与0 mg/L量子点组比较,50,100 mg/L量子点组可显著促进巨噬细胞内肿瘤坏死因子α及白细胞介素1β的表达(P < 0.01或P < 0.05);100 mg/L量子点组肿瘤坏死因子α表达高于50 mg/L量子点组(P < 0.01);50,100 mg/L量子点组白细胞介素1β表达无差异;④50,100 mg/L CdSe/ZnS量子点组细胞增殖强于0 mg/L量子点组(P < 0.05),50,100 mg/L CdSe/ZnS量子点组细胞增殖无差异;⑤50,100 mg/L CdSe/ZnS量子点对巨噬细胞的凋亡无明显影响;⑥结果表明,CdSe/ZnS量子点可活化巨噬细胞,促其增殖与分泌炎症因子,但不影响其凋亡。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)