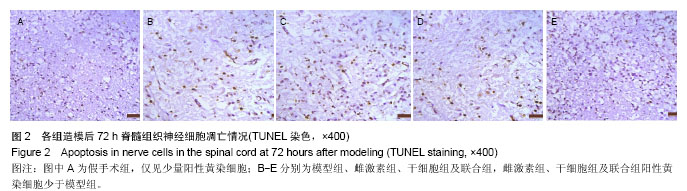
| [1] Mosquera L,Jennifer M,Colón,José M,et al.Tamoxifen and estradiol improved locomotor function and increased spared tissue in rats after spinal cord injury: their antioxidant effect and role of estrogen receptor alpha.Brain Res.2014;1561(2):成11-22.[2] Lin CW,Chen B,Huang KL,et al.Inhibition of autophagy by estradiol promotes locomotor recovery after spinal cord injury in rats.Neurosci Bull.2016;32(2):137-144.[3] Letaif OB,Cristante AF,Barros Filho TE,et al.Effects of estrogen on functional and neurological recovery after spinal cord injury: An experimental study with rats.Clinics(Sao Paulo).2015; 70(10):700-705.[4] Okuda A,Horii-Hayashi N,Sasagawa T,et al.Bone marrow stomal cell sheets may promote axonal regeneration and functional recovery with suppression of glial scar formation after spinal cord transection injury in rats.J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;25:1-8.[5] Han S,Wang B,Li X,et al.Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in three-dimensional culture promote neuronal regeneration by neurotrophic protection and immunomodulation. J Biomed Mater Res A.2016;104(7):1759-1769.[6] Baydin A,Cokluk C,Aydin K.A new minimally invasive experimental spinal cord injury model in rabbits.Minim Invasive Neurosurg.2007;50(3):170-172.[7] Basso DM,Beattie MS,Bresnahan JC.A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating seale for open field testing in rats.J Neurotrauma.1995;12(1):1-21.[8] 王继猛,梁卓文,胡文昱,等.激光照射对脊髓损伤大鼠TNF-α、IL-6和IL-10表达的影响[J].中国激光,2014,2(2):0204003,1-5.[9] Yin X,Yin Y,Cao FL,et al.Tanshinone IIA attenuates the inflammatory response and apoptosis after traumatic injury of the spinal cord in adult rats.PLoS One.2012;7(6):e38381.[10] Gokce EC,Kahveci R,Gokce A,et al.Neuroprotective effects of thymoquinone against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury by attenuation of inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis.J Neurosurg Spine.2016;24(6):949-959.[11] Sullivan PG,Krishnamurthy S,Petel SP,et al.Temporal characterization of mitochondrial bioenergetics sfter spinal cord injury.J Neurotrauma.2007;24(6):991-999.[12] Pan W,Kastin AJ.Spinal cord injury changes cytokine transport.Neurol Disord Drug Targets.2016;15(9):1139-1150.[13] Han D,Wu C,Xiong Q,et al.Anti-inflammatory mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in rat model of spinal cord injury.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2015; 71(3):1341-1347.[14] Yan P,Li Q,Kim JM,et al.Cellular localization of tumornecrosis factor-α following acute spinal cord injury in adult rats.J Neurotrauma.2001;18(5):563-568.[15] Ankeny DP,Mctigue DM,Jakeman LB.Bone marrow transplants provide tissue protection and directional guidance for axons after contusive spinal cord injury in rats.Exp Neurol. 2004;190(1):17-31.[16] Patel SP,Sullivan PG,Pandya JD,et al.Differential effects of the mitochondrial uncoupling agent,2,4-dinitrophenol,or the nitroxide antioxidant,Tempol,on synaptic or nonsynaptic mitochondria after spinal cord injury.J Neurosci Res.2009; 87(1):130-140. [17] Roozbehi A,Joghataie MT,Mehdizadeh M,et al.The effects of cyclosporin-A on functional outcome and axonal regrowth following spinal cord injury in adult rats.Acta Med Iran.2012; 50(4):226-232.[18] Ritfeld GJ,Patel A,Chou A,et al.The role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in bone marrow stromal cell-mediated spinal cordrepair.Cell Transplant.2015;24(11):2209-20. [19] 任义行,杨新明,孟宪勇,等.白细胞介素6受体单克隆抗体与骨髓间充质干细胞可减少急性脊髓损伤神经元的凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(14):1981-1988.[20] 李洪秋,王哲,阿良,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠脊髓损伤后氧化应激的影响[J].脊柱外科杂志,2010,8(3):157-161.[21] 边立功,刘承杏,李兴国,等.17-β雌二醇提高巯醇抗氧化物(酶)治疗脊髓损伤的作用[J].解剖学报,2010,41(2):185-190.[22] Ray SK,Samntaray S,Banik NL.Future directions for using estrogen receptor agonists in the treatment of acute and chronic spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(9): 1418-1419. [23] Li XM,Yang Q,Li XB,et al.Estrogen-like neuroprotection of isopsoralen against spinal cord injury through estrogen receptor ERα.Metab Brain Dis.2017;32(1):259-265. [24] Cheng Q,Meng J,Wang XS,et al.G-1 exerts neuroprotective effects through G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 following spinal cord injury in mice.Biosci Rep.2016;36(4). pii:e00373. [25] Amini Pishva A,Akbari M,Farahabadi A,et al.Effect of Estrogen Therapy on TNF-α and iNOS Gene Expression in Spinal Cord Injury Model.Acta Med Iran.2016;54(5):296-301.[26] Brotfain E,Gruenbaum SE,Boyko M,et al.Neuroprotection by Estrogen and Progesterone in Traumatic Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury.Curr Neuropharmacol.2016;14(6):641-653.[27] Letaif OB,Cristante AF,Barros Filho TE,et al.Effects of estrogen on functional and neurological recovery after spinal cord injury: An experimental study with rats.Clinics(Sao Paulo). 2015;70(10):700-705. [28] Chakrabarti M,Das A,Samantaray S,et al.Molecular mechanisms of estrogen for neuroprotection in spinal cord injury and traumatic brain injury.Rev Neurosci. 2016;27(3): 271-281. [29] Chen J,Hu R,Ge H,et al.G-protein-coupled receptor 30-mediated antiapoptotic effect of estrogen on spinal motor neurons following injury and its underlying mechanisms.Mol Med Rep.2015;12(2):1733-1740. [30] Lee JY,Choi HY,Na WH,et al.17β-estradiol inhibits MMP-9 and SUR1/TrpM4 expression and activation and thereby attenuates BSCB disruption/hemorrhage after spinal cord injury in male rats.Endocrinology.2015;156(5):1838-1850. [31] Hu JZ,Long H,Wu TD,et al.The effect of estrogen-related receptor α on the regulation of angiogenesis after spinal cord injury.Neuroscience.2015;290:570-580. [32] Mosquera L,Colón JM,Santiago JM,et al.Tamoxifen and estradiol improved locomotor function and increased spared tissue in rats after spinal cord injury: their antioxidant effect and role of estrogen receptor alpha.Brain Res. 2014; 1561: 11-22. [33] Prossnitz ER.G protein-coupled estrogen receptor: a new therapeutic target in stroke and traumatic brain/spinal cord injury?Crit Care Med.2012;40(12):3323-3325. [34] Samantaray S,Das A,Matzelle DC,et al.Administration of low dose estrogen attenuates persistent inflammation, promotes angiogenesis, and improves locomotor function following chroni spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurochem.2016; 137(4): 604-617. [35] Cox A,Varma A,Barry J,et al.Nanoparticle estrogen in rat spinal cord injury elicits rapid anti-inflammatory effects in plasma,cerebrospinal fluid,and tissue.J Neurotrauma. 2015; 32(18):1413-1421.[36] 程姝丽,丁寅.雌激素对小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞凋亡的抑制作用及其机制研究[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2012,28(5):514-516. |
.jpg)
.jpg)