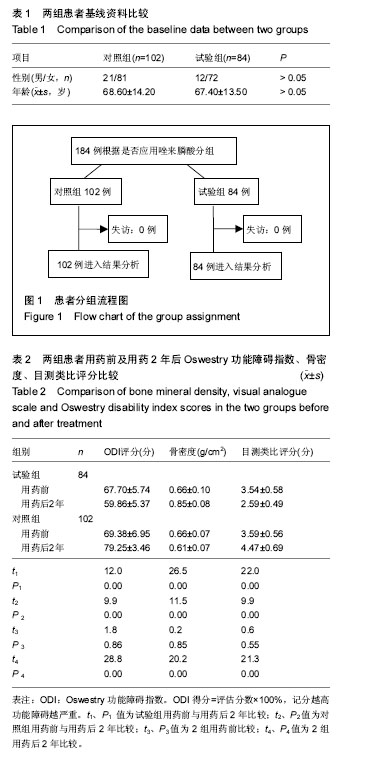
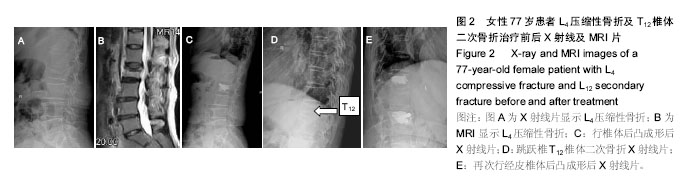
| [1] Marlin E, Nathoo N, Mendel E.Use of percutaneous kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty in spinal surgery.J Neurosurg Sci. 2012,56(2):105-112.[2] Itshayek E, Fraifeld S, Vargas AA.Efficacy and safety of vertebral stenting for painful vertebral compression fractures in patients with metastatic disease.Neurol Res.2014;36(12): 1086-1093.[3] 温晓阳,余凯龙,何东生,等.PKP与PVP治疗陈旧性骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折效果对比观察[J].山东医药 2016,56(42),59-61.[4] Trout AT,Kallmes DF,Kaufmann TJ.New frautures after vertebroplasty:adjacent fractures occur significantly sooner.Am J Neuroradiol,2006; 27: 217-223.[5] Kim YY, Rhyu KW.Recompression of vertebral body after balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Eur Spine J.2010;19(11):1907-1912.[6] Cheng X, Long HQ, Xu JH.Comparison of unilateral versus bilateral percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of patients withosteoporosis vertebral compression fracture (OVCF): a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Spine J.2016 25(11):3439-3449.[7] Frank AJ, Moll JM, Hort JF. A comparison of three ways of measuring pain.Rheumatol Rehabil.1982;21(4):211-217.[8] Fairbank JC, Couper J, Davies JB, et al. The Oswestry low back pain disability questionnaire. Physiotherapy.1980; 66(8):271-273. [9] Fairbank JC, Pynsent PB. The oswestry disability index. Spine.2000;25: 2940-2953.[10] 钟远鸣,付拴虎,张家立,等.经皮穿刺椎体成形术中骨水泥渗漏的原因及预防[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(4):294-298.[11] Yeom JS,Kim WJ,Choy WS,et al.Leakage of cement percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic compression fractures.J.Bone Joint Surg Br,2003,85(1):83-89.[12] Steven Boonen, Dennis M. Black, Cathleen S, et al. Efficacy and Safety of a Once-Yearly Intravenous Zoledronic Acid 5 mg for Fracture Prevention in Elderly Postmenopausal Women with Osteoporosis Aged 75 and Older J Am Geriatr Soc. 2010; 58(2): 292–299. [13] Kenneth W. Lyles, Cathleen S. Colón-Emeric, et al. Zoledronic Acid in Reducing Clinical Fracture and Mortality after Hip Fracture N Engl J Med. 2007, 357(18) 1799-1809. [14] Longo UG1, Loppini M, Denaro L, et al. Conservative management of patients with an osteoporotic vertebral fracture: a review of the literature.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2012;94(2):152-157.[15] Longo UG, Loppini M, Denaro L, et al. Osteoporotic vertebral fractures: current concepts of conservative care.Br Med Bull. 2012;102(6):171-189.[16] Vondracek SF. Managing osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2010;67(7 Suppl 3):S9-19.[17] 常睿洁. 骨质疏松症的中西药治疗进展[J]. 中国新药杂志, 2015,24(13):1498-1503.[18] 张鑫,刘波,刘辉.运动疗法配合物理疗法治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折[J].中医正骨,2014,26(9):43-45.[19] Newman M,Minns Lowe C,Barker K.Spinal Orthoses for Vertebral Osteoporosis and Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture: A Systematic Review.Arch Phys Med Rehabil.2016; 97(6): 1013-1025.[20] Yuan WH,Hsu HC,Lai KL.Vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty versus conservative treatment for osteoporoticvertebral compression fractures:A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(31):e4491.[21] Bailey CS,Urquhart JC, Dvorak MF, et al.Orthosis versus no orthosis for the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures without neurologic injury: a multicenter prospective randomized equivalence trial.Spine J.2014;14(11):2557-2564.[22] Rzewuska M, Ferreira M, McLachlan AJ, et al. The efficacy of conservative treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures on acute pain relief: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Eur Spine J.2015;24(4):702-714.[23] Folman Y,Shabat S.A comparison of two new technologies for percutaneous vertebral augmentation: confidence vertebroplasty vs. sky kyphoplasty.Isr Med Assoc J.2011; 13(7):394-397.[24] Foo LS,Yeo W,Fook S.Results,experience and technical points learnt with use of the SKy Bone Expander kyphoplastysystem for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a prospective study of 40 patients with a minimum of 12 months of follow-up.Eur Spine J.2007; 16(11): 1944-1950.[25] Inamasu J, Guiot BH, Uribe JS.Flexion-distraction injury of the L1 vertebra treated with short-segment posterior fixation andOptimesh.J Clin Neurosci.2008;15(2):214-218.[26] Sun ZY,Li XF,Zhao H,Percutaneous Balloon Kyphoplasty in Treatment of Painful Osteoporotic Occult Vertebral Fracture: A Retrospective Study of 89 Cases.Med Sci Monit. 2017; 23:1682-1690.[27] 蒙连新,许宗菊,康盼.密固达对老年骨质疏松患者疼痛及生活质量的效果观察及分析[J].医学信息 2015,28,(14)39-40.[28] 贾璞,唐海.骨水泥强化术后椎体再骨折的相关因素研究进展[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2013, 6(1):83-88.[29] Klazen CA,Venmans A,De Vries J,et al. Percutaneousvertebroplasty is not a risk factor for new osteoporotic compression fractures: results from VERTOSⅡ.Am J Neuroradiol.2010;31:1447-1450.[30] Bliemel C, Oberkircher L, Buecking B, et al. Higher incidence of new vertebral fractures following percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty--fact or fiction?. Acta Orthop Belg.2012;78(2): 220-229.[31] Hayashi Y. Bone diseases with Pain. Osteoporosis Clin Calcium.2007;17(4):606-612.[32] Dyck R,Karunanayake C,Pahwa P,et al.Prevalence, risk factors and co-morbidities of diabetes among adults in rural Saskatchewan: the influence of farm residence and agriculture-related exposures. BMC Public Health.2013;13: 7-10.[33] Mattei TA.Cavitational kyphoplasty: a new technique for reducing the rates of cement extravasation through targeted low-pressure cement injection.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2017 Apr 5.[34] 赵杰,袁义,蒋国强.骨质疏松性椎体骨折PKP治疗后相邻椎体再发骨折的原因分析及治疗策略[J].浙江创伤外科,2015,20(2): 338-340.[35] Watts NB,Harris ST,Genant HK. Treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty.Osteoporos Int. 2001;12: 29-37.[36] Polikeit A,Noltel P,Ferguson SJ.The effect of cement augmentation on the load transfer in an osteoporotic functional spinal unit:finite-element analysis.Spine( Phila Pa 1976),2003;28: 991-996.[37] Lewiecki EM. Bisphosphonates for the treatment of osteoporosis: insights for clinicians. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2010;1(3):115-128.[38] 范靖雪,姜礼红,孟佳.双膦酸盐的作用机制和急性时相反应[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(9):28-31.[39] Gaines JM, Marx KA.Older men’s knowledge about osteoporosis and educational intervenetions to increase osteoporosis knowledge in older men: a systematic review J.Maturitas,2011,68(1):5-12.[40] Nancollas GH,Tang R,Phipps RJ,et al.Novel insights into actions of bisphosphonates on bone: differences in interactions with hydroxyapatite. Bone. 2006; 38(5):617-627[41] Rout AT, Kallmes DF, Kaufmann TJ. New fractures after vertebroplasty: adjacent fractures occur significantly sooner. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.2006;27(1):217-223.[42] Harrop JS,Prpa B,Reinhardt MK,et al.Primary and secondary osteoporosis' incidence of subsequent vertebral compression fractures after kyphoplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2004;29(19): 2120-2125.[43] Bouza C, López-Cuadrado T, Almendro N. Safety of balloon kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in Europe: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur Spine J. 2015,24(4): 715-723. |
.jpg)
.jpg)