1.1 试验目的 观察牙髓血管再生术用于临床治疗年轻恒牙牙髓坏死、牙根发育停滞的疗效,为该新技术在临床上大规模应用提供经验和证据。
1.2 试验方法选择及理由 ①牙髓血管再生术作为一项治疗年轻恒压牙髓坏死的新技术,具有其他方法不可比拟的优势:刺激出血前,根管内20 mL,17%EDTA冲洗液能抑制生物膜的形成,还可使牙本质基质暴露,使其中生长因子释放,有利于促进根管壁新组织的附着;刺激出血后,血凝块形成,导致肉芽组织形成,是组织再生的必需成分;此为技术上的创新;②牙髓血管再生术在国内刚刚开展,目前基本没有多样本的随机对照试验研究,因此课题组开展此次随机对照试验。
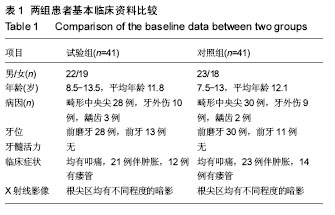
1.3 减少、避免偏倚的措施 ①试验组和对照组患者基线资料均衡;②实验室指标的测量统一进行,为不参与试验的专业人士盲法进行;③患牙治疗由同一组医生进行,尽量减少操作方面的差异。
1.4 试验设计类型 前瞻性随机对照临床试验。
1.5 试验完成地点 中国,陕西省西安市,西安交通大学附属口腔医院。
1.6 受试者选择
1.6.1 纳入标准
(1)患牙均为年轻恒牙:牙齿发育处于Nolla分期的 7、8或9期。Nolla 分期方法如下:0期,牙囊未出现;1期,牙囊影像出现;2期,牙尖开始钙化;3期,牙冠形成 1/3;4期,牙冠形成 2/3;5期,牙冠接近形成;6期,牙冠形成,牙根开始发育;7期,牙根形成 1/3;8期,牙根形成 2/3;9期:牙根接近形成,根尖孔未闭合;10期,牙根形成,根尖孔闭合。
(2)因畸形中央尖折断、外伤或龋病等原因致牙髓坏死或急、慢性根尖周炎。
(3)无药物过敏史及系统性疾病史。
(4)患者及其监护人同意该治疗方案,签署知情同意书并具有良好的依从性。
1.6.2 排除标准
(1)不符合以上纳入标准者。
(2)治疗后(2年内)急需进行桩冠或桩核冠修复的患牙。
(3)患者依从性不佳,不能遵守医嘱、按时复诊者。
1.6.3 入组时间 2013年12月至2016年12月。
1.6.4 临床试验预期总体持续时间及其确定理由 病例收集时间为3年,病例随访时间为18个月,后期数据整理、统计分析及论文写作需6个月,所以临床试验预期总体持续时间为5年。
1.6.5 每位受试者的预期参与持续时间 因每位患者治疗后需随访18个月,加上治疗时间,所以每位受试者的预期参与持续时间为2年左右。
1.7 招募 医生在西安交通大学附属口腔医院牙体牙髓科就诊的牙髓坏死或根尖周炎根尖未发育完全的年轻恒牙患者及家属群中宣传此次试验的招募条件,有感兴趣的患者或家属可通过主治医生,以电话、e-mail或微信的形式联系项目负责人,招募至研究组进行筛选。符合要求的患者及其监护人被告知相关治疗计划和费用,签署试验知情同意书后入组。
1.8 试验分组
1.8.1 产生序列分配的方法 应用计算机随机数字法进行随机分组。
1.8.2 分配隐藏及实施 计算机产生的2组随机名单装入密封的不透明的信封中,由指定的不参与手术干预的课题组成员保存。
1.8.3 盲法 患者不知道分组;评估人员不知道患者的分组;数据的统计分析由不清楚分组的专业统计人员进行。
1.9 干预措施
1.9.1 试验组治疗方法 试验组采用牙髓血管再生术:用阿替卡因注射液对患牙进行局部浸润麻醉,橡皮障隔离,开髓形成直线通路;用 20 mL 1.0% NaClO在根管上2/3处轻柔地冲洗(采用侧开孔钝头冲洗针),建议使用较低浓度的NaOCl(1.5%,20 mL/cancal,5 min),然后针头位于距离根尖至少1 mm,避免影响根尖周组织中的干细胞;纸尖干燥根管;将三联抗生素糊剂(triple antibiotic paste,TAP)(米诺环素︰甲硝唑︰环丙沙星=1︰1︰1,终浓度为0.1 g/L)置于根管内(糊剂位于釉牙骨质界下方);冠部用玻璃离子水门汀暂封,1-4周后复诊;不适随诊。
复诊时,评估初步治疗效果,如果有持续感染的症状或体征,考虑再一次抗生素封药或更换抗生素种类,使用不含血管收缩剂的3%甲哌卡因进行局麻,上橡皮障,使用20 mL 17%EDTA缓慢冲洗根管,纸尖拭干根管。采用高压灭菌 25# K锉刺激根尖周组织引起根管内出血,待血液充盈至牙颈部时,用无菌小棉球(直径大约3 mm)蘸生理盐水略微挤干,置于根管内(约15 min),在釉牙骨质界下3 mm处形成血凝块。在血凝块上方放置矿化三氧化物聚合体(mineral trioxide aggregate,MTA),将湿棉球置于MTA 上方,并用Cavit暂时封闭冠部2 h;去除暂封物,自酸蚀、3M Filtek Z350 Flowable 纳米流动树脂、3M Filtek Z350复合树脂永久充填;治疗操作结束后,常规拍X射线片,以检查治疗操作的情况。
1.9.2 对照组治疗方法 对照组采用根尖诱导成形术:常规备洞开髓,根管预备:去除根管内感染坏死牙髓组织,并用3%过氧化氢溶液。生理盐水反复冲洗,清除残留的感染组织。根管消毒:吸干根管,封消毒力强刺激性小的药物于根管内,每周更换1次,至无渗出无症状为止。有根尖周病变的患牙,可封入抗生素糊剂,每1-3个月更换1次,至根尖周炎症被控制为止。药物诱导:根管内填入可诱导根尖成形的药物——氢氧化钙制剂。逐层填入,填满根管。使其接触根尖部组织或根髓断面。暂时充填龋洞,随访观察:3-6个月随访一次,使根尖形成或根端闭合为止。常规根管充填。当X射线片显示根尖延长或有钙化组织沉积并将根端闭合时,可行常规根管充填。
1.10 有效性和安全性评价方法
1.10.1 有效性评价方法
(1)主要评价指标:治疗成功率,通过临床检查和X射线片来评价术后疗效。
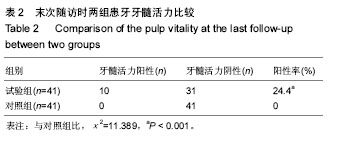
(2)次要评价指标:患者的满意度及牙髓活力。
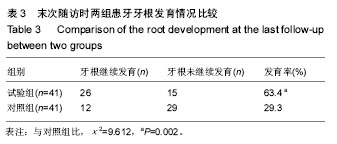
(3)评价、记录和分析有效性参数的方法和时间选择:治疗后的 3,6,9,12,18个月进行复诊;复诊内容包括:①拍摄根尖X射线片(标准平行投照法), 观察患牙牙根情况(根尖周暗影是否消失、根尖有无闭合、管壁有无增厚、根长有无变化);②牙髓活力测试(电活力和冷热诊);③口腔常规检查(视诊、叩诊、扪诊、牙齿松动度);④有无临床症状及体征(有无疼痛、瘘管);⑤患者的满意度。
疗效评定标准:①治愈:患牙的临床症状完全消失;X射线片显示根尖周暗影消失,牙根继续发育,牙根长度增加,根管壁增厚,根尖闭合,甚至出现牙髓活力测试阳性反应;②好转:患牙的临床症状完全消失;X射线片显示根尖周暗影缩小或消失,但牙根无明显继续发育;③失败:患牙临床症状无明显改善或症状加重;X射线片未见根尖周暗影缩小,牙根无明显继续发育。治愈和好转均为成功病例。
牙髓活力评价标准:0-40为活髓,41-80为部分坏死。
1.10.2 安全性评价方法 观察不良事件和材料宿主反应。不良反应按肯定有关、很可能有关、可能有关、可能无关及无关5级标准判断,前3者视为试验的不良反应,计算不良反应发生率。
1.11 试验流程 试验流程图见
图1。
.jpg)
1.12 监查计划
1.12.1 试验启动初期 任命监察员,在试验开始前制定监察计划,确定监察的频率以及每次监察的时长。
1.12.2 试验过程中 定期进行监察访视。监察员与研究人员会面,了解试验进程;检查试验档案文件,通过检查病例报告表和原始记录进行数据核查;了解药物及口腔材料使用情况,及时进行补充或更新;与研究人员讨论监察中发现的问题及解决方法;更新试验项目进度表。
1.12.3 试验收尾阶段 监察员完成监察报告,上交项目负责人。
1.13 统计学考虑
1.13.1 样本量的计算 结合作者以往经验,试验假设对照组患牙采用根尖诱导成形术治疗成功率为75%,试验组患牙采用牙髓血管再生术治疗成功率为95%,设β=0.1,power=90%,显著性水准为双侧α=0.05,采用PASS 11.0软件计算后样本量为每组61例,按15%的脱落率计算,每组应纳入72例。最终按入选标准和排除标准筛选后,实际每组纳入41例,共82例患者参加试验。
1.13.2 预期脱落率 预期脱落率为15%。
1.13.3 数据的统计方法 所有数据应用SPSS 22.0统计软件进行分析,计量数据描述采用x±s表示。正态分布资料采用两样本独立t 检验,计数资料比较采用卡方检验,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。
1.14 数据管理
1.14.1 病例报告表填写与移交 试验开始前由课题组成员讨论设计统一的病例报告表,并指定2名专门的数据录入人员填写,要求及时并严格遵照方案填写,并保证数据真实完整且与原始资料一致,监察员需定期核对原始数据,所有的数据收集完成后,核对无误,交给项目负责人。
1.14.2 数据录入与修改 所有的资料以双重录入的形式转化为电子版文件。数据只有在监察员、数据录入人员均确认数据有误时方能修改。
1.14.3 数据库锁定 当所有患者的数据收集完成后,核对文件的数据,由项目负责人对数据库进行锁定,之后数据不允许再作变动,该文件需做备份。所有与本次临床试验有关的研究资料均由西安交通大学附属口腔医院保存。
1.14.4 数据处理 将数据库交给专业统计人员进行统计分析,并由统计分析人员写出统计分析报告,交付项目负责人,写出研究报告。
1.15 研究的可行性分析 西安交通大学附属口腔医院作为三甲口腔专科医院,患者量大,病例收集能达到预期结果,并且本院儿童口腔科、牙体牙髓病科、急诊科医护人员具有较高的业务素质,能按照标准完成病例的治疗。
1.16 临床试验的质量控制
1.16.1 总要求 通过制定临床试验标准操作规程(SOP),确保试验遵循临床试验方案和管理法规,保证受试者的权益,确保试验记录和报告数据准确、完整可信。
1.16.2 机构和人员要求 建立独立于临床试验部门的质量保证部门,设立监察员、稽查员。监察员需具备一定的医学、药学及统计学的知识,并经过培训。稽查员不直接参与本次临床试验,只进行每年一两次的系统稽查。
1.16.3 临床试验培训要求 临床试验开始前应对所有的参与人员进行相关的临床试验标准操作规程(SOP)培训,并进行统一的技术考核。
1.16.4 病例报告表的填写 病例报告表由2名专门的数据录入人员填写,要求及时并严格遵照方案填写,并保证数据真实完整且与原始资料一致。
1.16.5 原始资料的保存 原始资料由指定的专门资料管理员保存,不得随意修改。
1.16.6 临床试验的监查 监察员定期进行监察访视,核对原始数据,发现问题、解决问题。
1.17 临床试验的伦理问题及知情同意 试验方案经西安交通大学附属口腔医院伦理委员会批准实施,批准号为JDKY015-02。临床试验研究的实施符合《赫尔辛基宣言》和医院对人体研究的相关伦理要求。参与试验的患病个体及其家属为自愿参加,均对试验过程完全知情同意,在充分了解本治疗方案的前提下签署“知情同意书”。
1.18 对不良事件报告的规定
1.18.1 不良事件定义 受试者接受牙髓血管再生术治疗后出现的不良医学事件,但不一定与治疗有因果关系。
1.18.2 严重不良事件 试验过程中发生需住院治疗、延长住院时间、伤残、影响工作能力、危及生命或死亡等事件。
1.18.3 报告程序 医师做好不良事件的记录,包括不良事件的描述,发生时间,终止时间,程度及发作频度,是否需要治疗,如需要,记录给予的治疗。
发生严重不良事件时,除了采取必要的治疗措施以外,应在24 h内如实分别向当地食品药品监督管理局和国家食品药品监督管理局报告,并及时向伦理委员会报告,并在报告上注明日期,严重不良事件处理结束后,应提交受试者情况的后续报道。
1.18.4 不良事件的预测及采取的措施 与牙髓血管再生术治疗相关的常见不良反应有疼痛、材料宿主反应等,一般对症处理即可。
1.19 保密原则
1.19.1 受试者资料的保密 受试者参加试验及个人试验资料为个人隐私,受试者的全名不会出现在所有记录及文件中,患者姓名用拼音缩写表示。
1.19.2 研究数据的保密 电子版数据必须由专门计算机储存,设定开机密码,由资料管理员专人操作和管理;书面数据存放于固定地点并加锁,钥匙由资料管理员和项目负责人保管。
1.20 试验结果发表约定 研究结束后,由主要研究者编写研究总结报告,研究报告中将包括研究目的描述、研究中所使用的方法以及结果和结论,并投稿。
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)