| [1] Witjes S, Schrier JC, Gardeniers JW,et al.Comlications with in two years after revision of total hip prostheses.Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd.2007;151(35):1928-1934.[2] 周建生,王志岩,肖玉周,等.人工髋关节翻修旋转中心重建的临床研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2013.31 (5):475-480.[3] Lennon AB,Britton JR,Mac Niocaill RF,et al.Predicting revision risk for aseptic lossening of femoral components in total hip arthroplasty in individual patients a finite element study. J Orthop Res.2007;25(6):779-788. [4] Harris WH.Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty.An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1969;51(4);57-70. [5] 裴福兴.髋关节翻修术若干问题探讨[J].中华外科杂志,2009, 47:161-163[6] 孙俊英.人工髋关节翻修手术学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2012. [7] Minoda Y, Kobayashi A, Sakawa A, et al. Wear particle analysis of highly crosslinked polyethylene isolated from a failed total hip arthroplasty.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;86(2):501-505.[8] Min BW, Song KS, Bae KC, er al.Second-generation cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients with osteonecrosis of the femoral head.J Arthroplasty. 2008; 23(6):902-910. [9] Ingham E,Fisher J.Biological reactions to wear debris in total ioint replacement.Proc Inst Mech Eng H.2000;214(1):21-37.[10] Paprosky WG,Magnus RE.Principles of bone grafting in revision total hip arthroplasty: acetabular technique. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1994;298:147-155.[11] Simon JP, Fowler JL, Gie GA, et al. Impaction cancellous grafting of the femur in cemented total hip reVision arthroplasty. In: Proceedings of the British Orthopaedic Association. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1991;73(Suppl 1): 73.[12] Buttaro MA, Costantini J, Comba F, et al. The use of femoral struts and impacted cancellous bone allograft in patients with seVere femoral bone loss who undergo reVision total hip replacement: a three- to nine-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(2):167-172.[13] Halliday BR, English HW, Timperley AJ, et al. Femoral impaction grafting with cement in reVision total hip replacement: eVolution of the techniques and results. J Bone Joint Surg [Br],2003;85-B:809-817.[14] Haddad FS, Duncan CP,Berry DJ,er al. Periprosthetic femoral fractures around well- fixed implants : ues of cortical onlay allografts with or without a plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 6: 945-950.[15] 周永刚,金志刚,王岩,等,异体皮质骨骨支撑植骨在髋关节股骨翻修术中的应用[J/CD] .中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2008,2: 484-490. [16] Lin YY, Yoo MC, Pei FX, et al. Cementless hemispheric acetabular component for acetabular revision arthroplasty . A 5-to 19-year follow-up study. J Arthroplasty .2008;23:376 -382.[17] Romano CL, Gala L,Logoluso N,er al.Two-stage revison of septic knee prosthesis with articulating knee spacers yields better infection eradication rate than one-stage or two-stage revision with static spacers. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2012;20(12):2445-2453.[18] Van Diemen MP, Colen S ,Dalemans AA, er al. Two-stage revision of an infected total hip arthroplasty : a follow-up of 136 patients. Hip Int.2013 [Epubb ahead of print]. [19] Choi HR, Kwon YM , Freiberg AA ,er al. Comparison of one-stage revision with antibiotic cement versus two-stage revision results for infected total hip arthroplasty . J Arthroplasty. 2013 [Epub ahead of print].[20] Klouche S, Leonard P, Zeller V, et al. Infected total hip arthroplasty revision : one-or two-stage procedure? Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2012;98:144-150.[21] Singer J, Merz A,Frommelt L, er al. High rage of infection with one-stage revision of septic knee prostheses excluding MRSA and MRSE. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012 ;470:1461-1471.[22] Lange J, Troelsen A, Thomsen RW, et al.Chronic infections in hip arthroplasties : comparing risk of reinfection following one -stage and two- stage revision:a systematic review and meta -analysis. Clin Epidemiol .2012;4:57-73. |
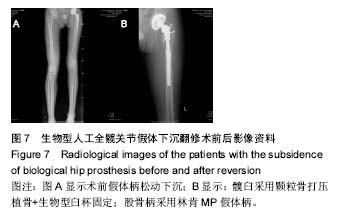
.jpg)
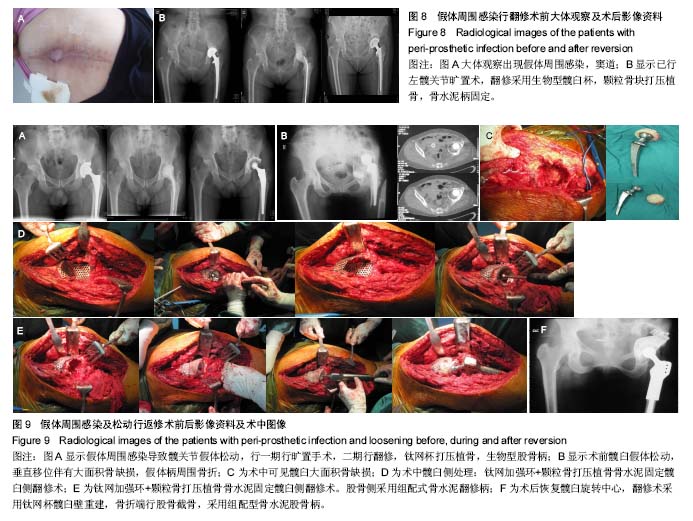
.jpg)
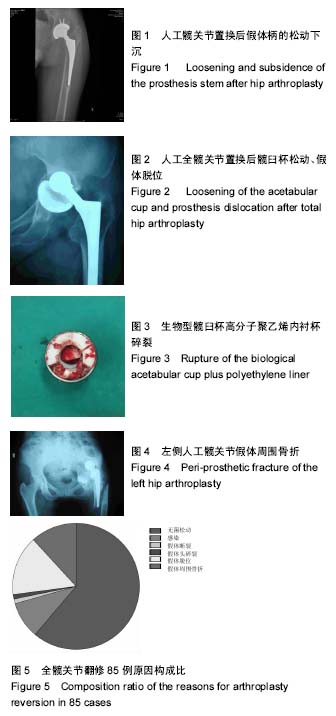
.jpg)