中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (22): 3602-3608.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.22.026
• 生物材料循证医学 evidence-based medicine of biomaterials • 上一篇
脱细胞神经支架联合干细胞构建组织工程神经修复坐骨神经缺损的meta分析
向飞帆1,阳运康1,谭小琦2,魏代清1,杨 琨2,孙远林2,周 举2
- 1西南医科大学附属医院骨与关节外科,四川省泸州市 646000; 2西南医科大学,四川省泸州市 646000
Effect of combination of acellular nerve grafts and stem cells for sciatic nerve regeneration: a Meta-analysis
Xiang Fei-fan1, Yang Yun-kang1, Tan Xiao-qi2, Wei Dai-qing1, Yang Kun2, Sun Yuan-lin2, Zhou Ju2
- 1Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
脱细胞神经支架:通过化学或物理方法去除天然神经的髓鞘等组织,保留基底膜及原有空间三维纤维管道结构,具有低免疫原性,是目前神经替代物的研究热点。
组织工程神经:运用材料科学、工程学、生物学的原理和方法,研发有活力的人体组织替代物,借以修复、维持或增强组织的功能,组织工程化的有活力的神经替代物称为组织工程神经。
背景:研究表明,脱细胞神经支架不仅具有天然神经的空间三维结构,而且具有低免疫原性,但对于长段神经缺损的修复效果仍不理想。为此,有学者将脱细胞神经支架复合种子细胞构建组织工程神经,以提高其治疗效果。
目的:系统评价脱细胞神经支架联合间充质干细胞或许旺细胞移植修复大鼠坐骨神经缺损的疗效。
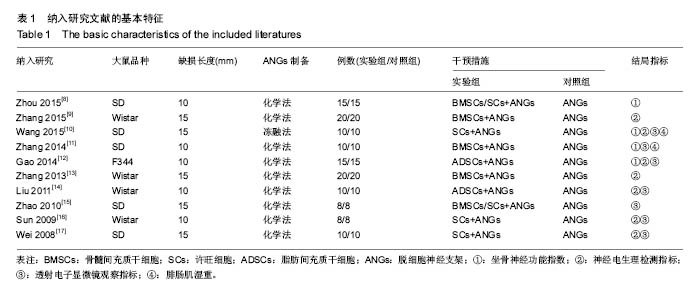
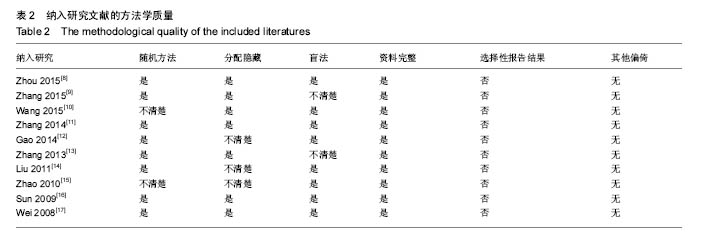
方法:检索PubMed、The Cochrane Library、EMbase、CNKI、WanFang和VIP数据库,查阅关于脱细胞神经支架联合间充质干细胞或许旺细胞修复大鼠坐骨神经缺损的随机对照实验,检索时限均为建库至2016年7月。由3名研究员按纳入和排除标准独立筛选文献、提取数据和评价文献的方法学质量,采用Review Manger5.3软件进行meta分析。
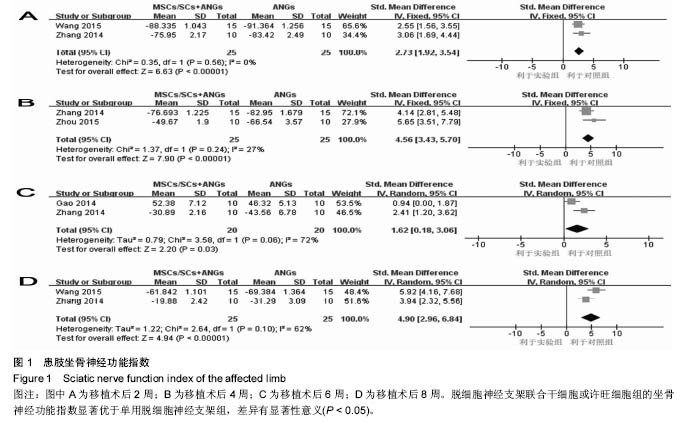
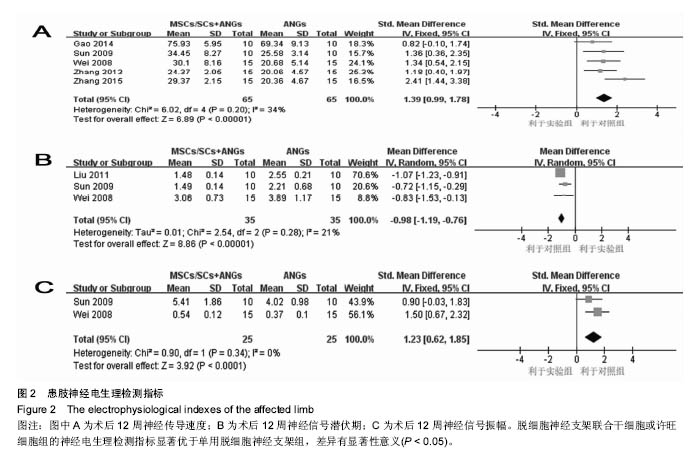
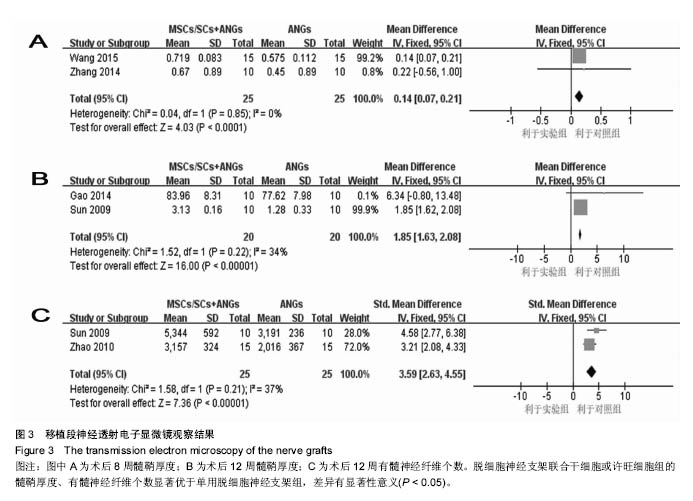
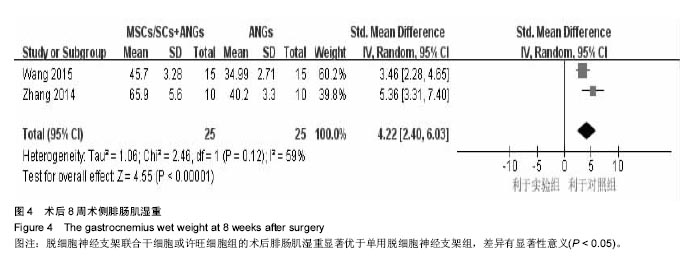
结果与结论:最终10篇文献纳入研究,共计252只大鼠。Meta分析结果显示:①脱细胞神经支架联合间充质干细胞或许旺细胞组的坐骨神经功能指数均优于单纯脱细胞神经支架组:2周[SMD=2.73,95%CI(1.92,3.54),P < 0.000 01],4周[SMD=4.57,95%CI(3.43,5.70),P < 0.000 01],6周[SMD=1.62,95%CI(0.18,3.06),P=0.03],8周[SMD=4.90,95%CI(2.96,6.84),P < 0.000 01];②术后12周脱细胞神经支架联合间充质干细胞或许旺细胞组神经传导速度、潜伏期、振幅优于脱细胞神经支架组:神经传导速度[SMD=1.39,95%CI(0.99,1.78),P < 0.000 01],潜伏期[MD=-0.98,95%CI(-1.19,-0.76),P < 0.000 01],振幅[SMD=1.23,95%CI(0.62,1.85),P < 0.000 1];③脱细胞神经支架联合间充质干细胞或许旺细胞组髓鞘厚度均优于单纯脱细胞神经支架组:术后8周髓鞘厚度[MD=0.14,95%CI(0.07,0.21),P < 0.000 1],术后12周髓鞘厚度[SMD=1.85,95%CI(1.63,2.08),P < 0.000 01],术后12周有髓神经纤维数[SMD=3.59,95%CI(2.63,4.55),P < 0.000 01];④术后8周脱细胞神经支架联合间充质干细胞或许旺细胞组腓肠肌湿重优于单纯脱细胞神经支架组[SMD=4.22,95%CI(2.40,6.03),P < 0.000 01];⑤当前证据表明,脱细胞神经支架联合间充质干细胞或许旺细胞治疗大鼠坐骨神经缺损较单纯脱细胞神经支架更有助于神经再生和功能恢复。受纳入文献质量的限制,以上结论需更高质量、更大样本的随机对照实验加以验证。
中图分类号:
.jpg)