| [1]Zhang B, Gu J, Zhang X, et al. Biomechanical Measurement of Rabbit Cornea by a Modified Scheimpflug Device. J Ophthalmol. 2016;2016:8271762.[2]Zhang F, Wu J, Kang D, et al. Development of a complex hydrogel of hyaluronan and PVA embedded with silver nanoparticles and its facile studies on Escherichia coli. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013;24(12):1410-1425.[3]Yusong P, Qianqian S, Chengling P, et al. Prediction of mechanical properties of multilayer gradient hydroxyapatite reinforced poly(vinyl alcohol) gel biomaterial. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(5):729-735.[4]D'Amico DJ. New methods for retinal examination in eyes with a Boston keratoprosthesis. Retina. 2013;33(6): 1097-1098.[5]Du LQ, Chen HM, Yan Y, et al. In vivo biological stability of chemically pretreated silicone gel inserts intended for use in keratoprostheses. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012;125(23): 4239-4244.[6]Jiang H, Zuo Y, Zhang L, et al. Property-based design: optimization and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) hydrogel and PVA-matrix composite for artificial cornea. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(3):941-952.[7]Bakhshandeh H, Soleimani M, Hosseini SS, et al. Poly (epsilon-caprolactone) nanofibrous ring surrounding a polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel for the development of a biocompatible two-part artificial cornea. Int J Nanomedicine. 2011;6:1509-1515.[8]Wang L, Ma R, Du G, et al. Biocompatibility of helicoidal multilamellar arginine-glycine-aspartic acid-functionalized silk biomaterials in a rabbit corneal model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(1):204-211.[9]Liu Y, Ren L, Wang Y. Crosslinked collagen-gelatin-hyaluronic acid biomimetic film for cornea tissue engineering applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(1): 196-201. [10]Hicks CR, Chirila TV, Vijayasekaran S, et al. PHEMA as a keratoprosthesis material. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006;90(1):124.[11]Carreira AS, Ferreira P, Ribeiro MP, et al. New drug-eluting lenses to be applied as bandages after keratoprosthesis implantation. Int J Pharm. 2014;477(1-2):218-226.[12]Hwang Y, Kim G. Evaluation of stability and biocompatibility of PHEMA-PMMA keratoprosthesis by penetrating keratoplasty in rabbits. Lab Anim Res. 2016;32(4):181-186.[13]Vajaranant TS, Liu J, Wilensky J, et al. Innovative approaches to glaucoma management of Boston keratoprosthesis type 1. Curr Ophthalmol Rep. 2016;4(3):147-153.[14]Huhtinen R, Sandeman S, Rose S, et al. Examining porous bio-active glass as a potential osteo-odonto-keratoprosthetic skirt material. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013;24(5):1217-1227.[15]Viitala R, Franklin V, Green D, et al. Towards a synthetic osteo-odonto-keratoprosthesis. Acta Biomater. 2009;5(1): 438-452.[16]Lee JH, Wee WR, Chung ES, et al. Development of a newly designed double-fixed Seoul-type keratoprosthesis. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000;118(12):1673-1678.[17]Wang L, Jeong KJ, Chiang HH, et al. Hydroxyapatite for keratoprosthesis biointegration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(10):7392-7399.[18]Mehta JS, Futter CE, Sandeman SR, et al. Hydroxyapatite promotes superior keratocyte adhesion and proliferation in comparison with current keratoprosthesis skirt materials. Br J Ophthalmol. 2005;89(10):1356-1362.[19]Mittal A, Garg S, Kohli D, et al. Effect of cross linking of PVA/starch and reinforcement of modified barley husk on the properties of composite films. Carbohydr Polym. 2016;151: 926-938.[20]Luo L, Cai W, Zhou J, et al. Facile synthesis of boehmite/PVA composite membrane with enhanced adsorption performance towards Cr(VI). J Hazard Mater. 2016;318:452-459.[21]Ehrenberg M, Zolotariov E, Loeb E, et al. Combining Sodium Hyaluronate and Polyvinylpyrrolidone Therapies for the Rabbit Cornea: A New Approach to Relief of the Human Dry Eye Syndrome. Curr Eye Res. 2015;40(9):913-922.[22]Li L, Zhou D, Wang XM, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases and inhibitor on the cornea tissue in rabbit after implantation of modified titanium skirt for keratoprosthesis. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2012;48(1): 20-26.[23]Kornilovskiy IM, Sultanova AI, Burtsev AA. Riboflavin photoprotection with cross-linking effect in photorefractive ablation of the cornea. Vestn Oftalmol. 2016;132(3):37-41.[24]Su P, Yang Y, Zhang L, et al. Biomechanical simulation of needle insertion into cornea based on distortion energy failure criterion. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2016;18(1):65-75.[25]Su C, Su Y, Li Z, et al. In situ synthesis of bilayered gradient poly(vinyl alcohol)/hydroxyapatite composite hydrogel by directional freezing-thawing and electrophoresis method. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;77:76-83.[26]Iwatsubo T, Kishi R, Miura T, et al. Formation of Hydroxyapatite Skeletal Materials from Hydrogel Matrices via Artificial Biomineralization. J Phys Chem B. 2015;119(28): 8793-8799.[27]Jiang H, Zuo Y, Zhang L, et al. Property-based design: optimization and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) hydrogel and PVA-matrix composite for artificial cornea. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(3):941-952. [28]Xiao Q, Zhou K, Chen C, et al. Hollow and porous hydroxyapatite microspheres prepared with an O/W emulsion by spray freezing method. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;69:1068-1074.[29]Sturm D, Schmidt-Wilcke T, Greiner T, et al. Confocal Cornea Microscopy Detects Involvement of Corneal Nerve Fibers in a Patient with Light-Chain Amyloid Neuropathy Caused by Multiple Myeloma: A Case Report.Case Rep Neurol. 2016; 8(2):134-139. |
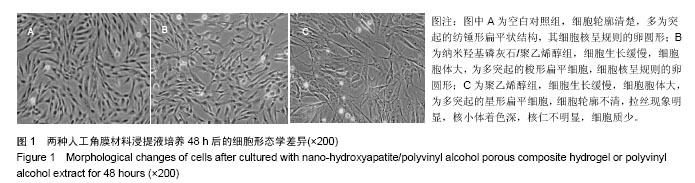
.jpg)
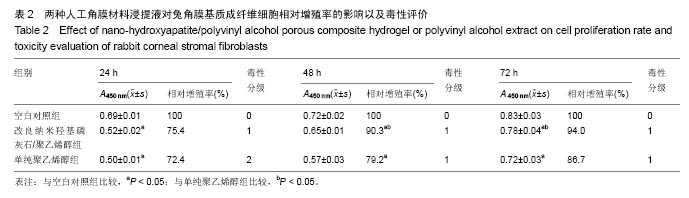
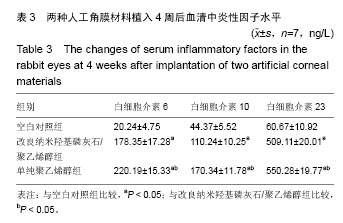
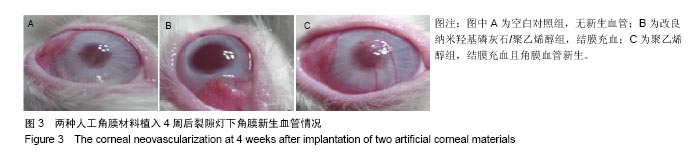
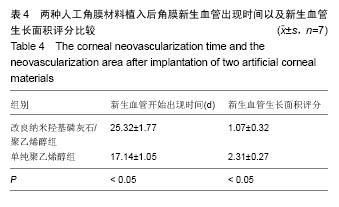
.jpg)
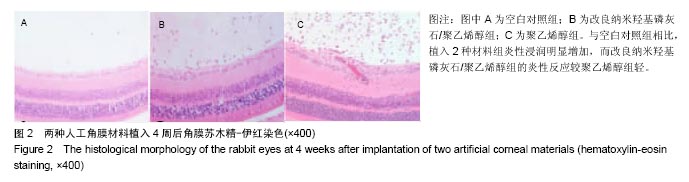
.jpg)